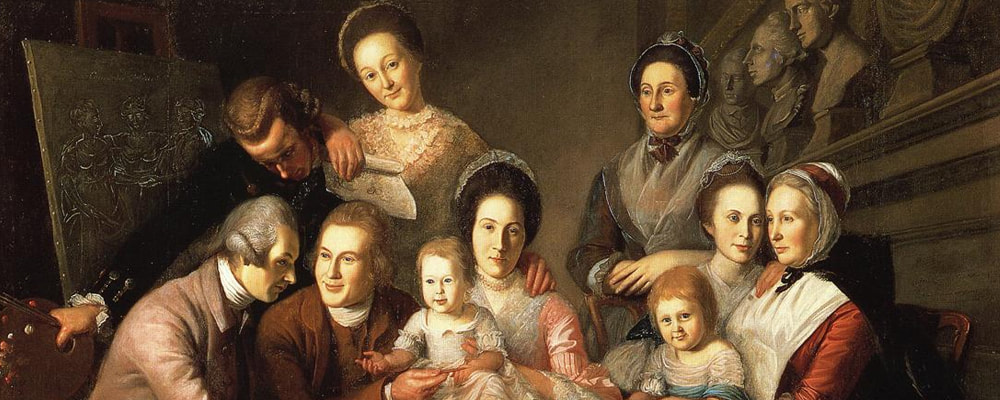Colonization
1490s-1750s
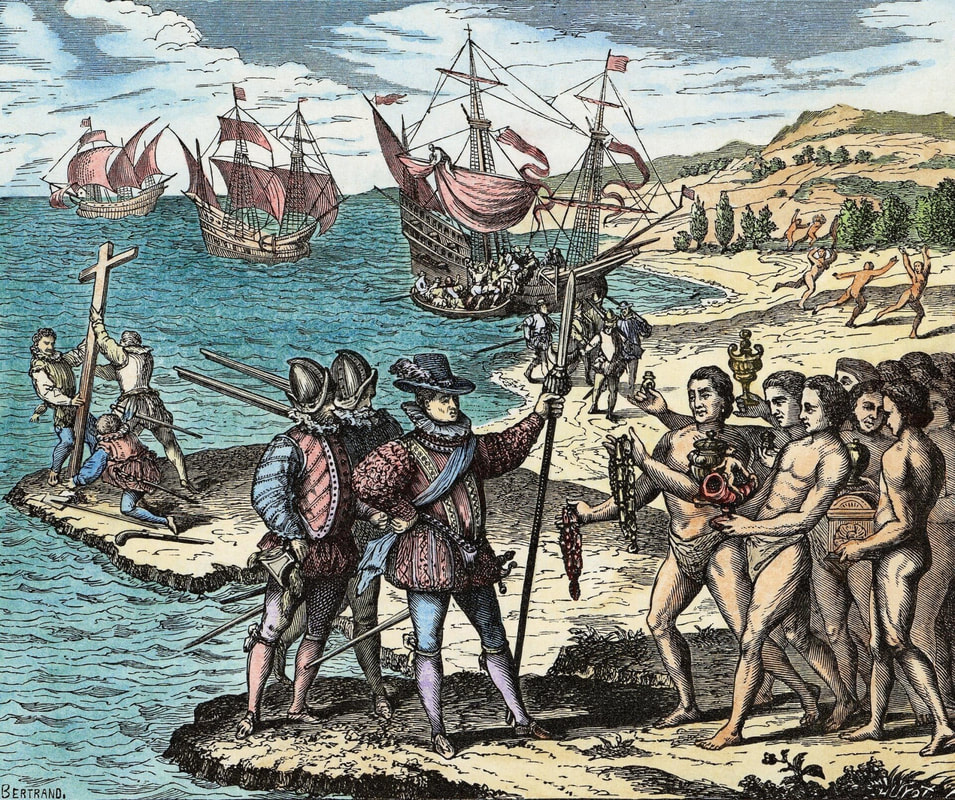
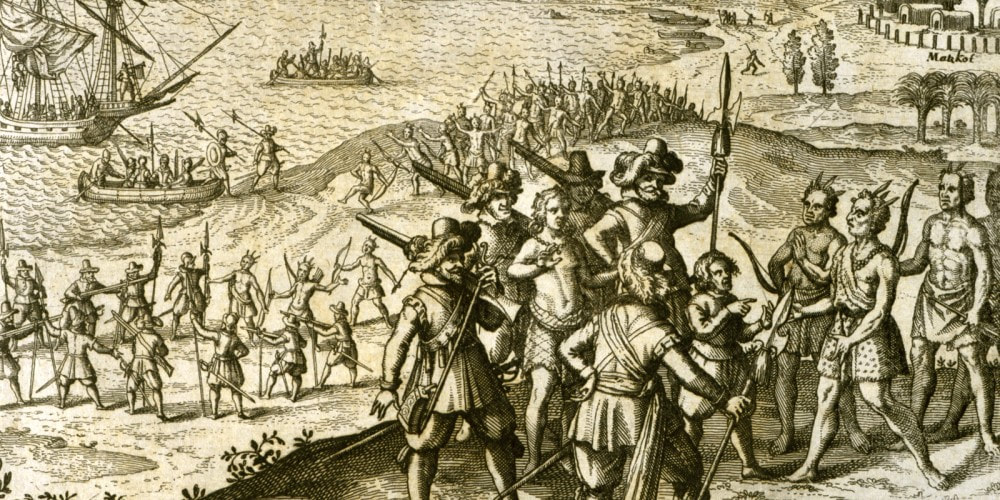
Arrival of Christopher Columbus to the Caribbean. Illustration by Théodore de Bry (1528). Columbus stands confidently, his left foot forward with his pike planted firmly in the ground, signaling his claim over the land. Three Spaniards raise a cross in the landscape, symbolizing a declaration of the land for both the Spanish monarchs and for the Christian God.
Contents
Colonization, 1490s-1750s:
Early Colonization
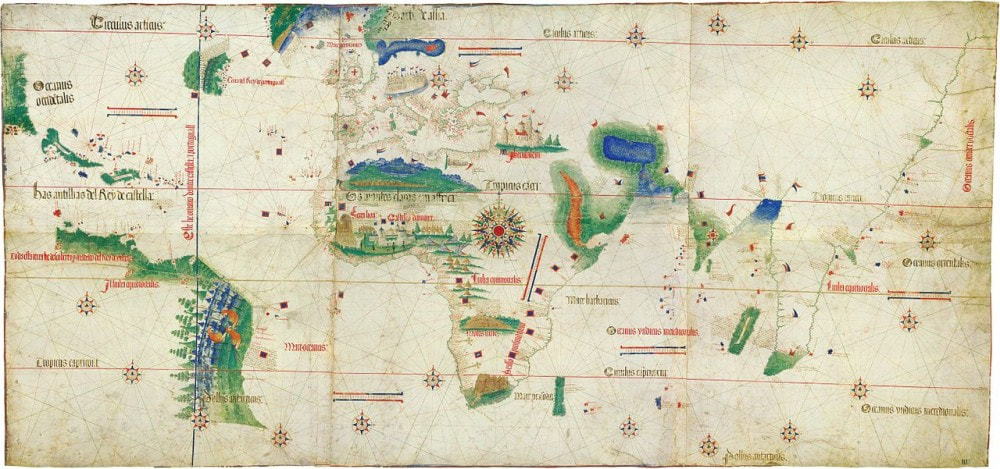
By the fifteenth century, the Portuguese had established forts and colonies on islands and along the rim of the Atlantic Ocean; other major Europeans countries soon followed in step. An anonymous cartographer created this map known as the Cantino Map, the earliest known map of European exploration in the New World, to depict these holdings and argue for the greatness of his native Portugal. Cantino planisphere (1502), Biblioteca Estense, Modena, Italy.
|
The Spanish relied on indigenous allies to defeat the Aztecs. The Tlaxcala were among the most important Spanish allies in their conquest. This nineteenth-century recreation of a sixteenth century drawing depicts Tlaxcalan warriors fighting alongside Spanish soldiers against the Aztec.
|
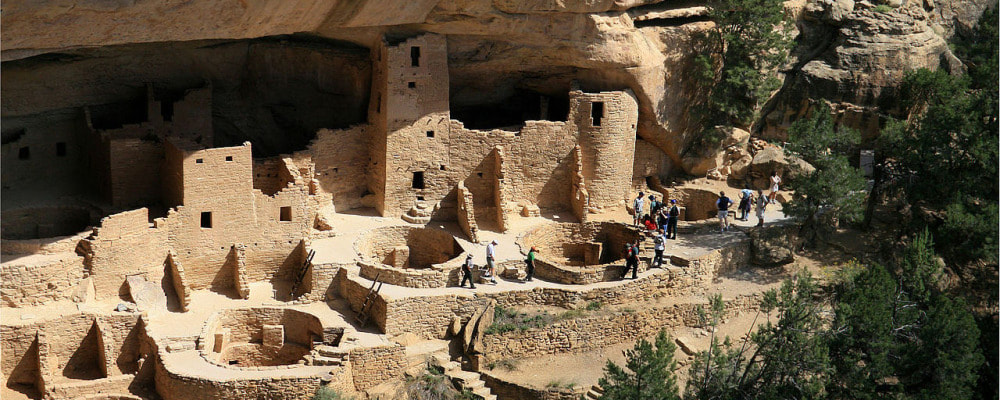
Native peoples in the Southwest began constructing these highly defensible cliff dwellings in 1190 CE and continued expanding and refurbishing them until 1260 CE before abandoning them around 1300 CE. Andreas F. Borchert, Mesa Verde National Park Cliff Palace
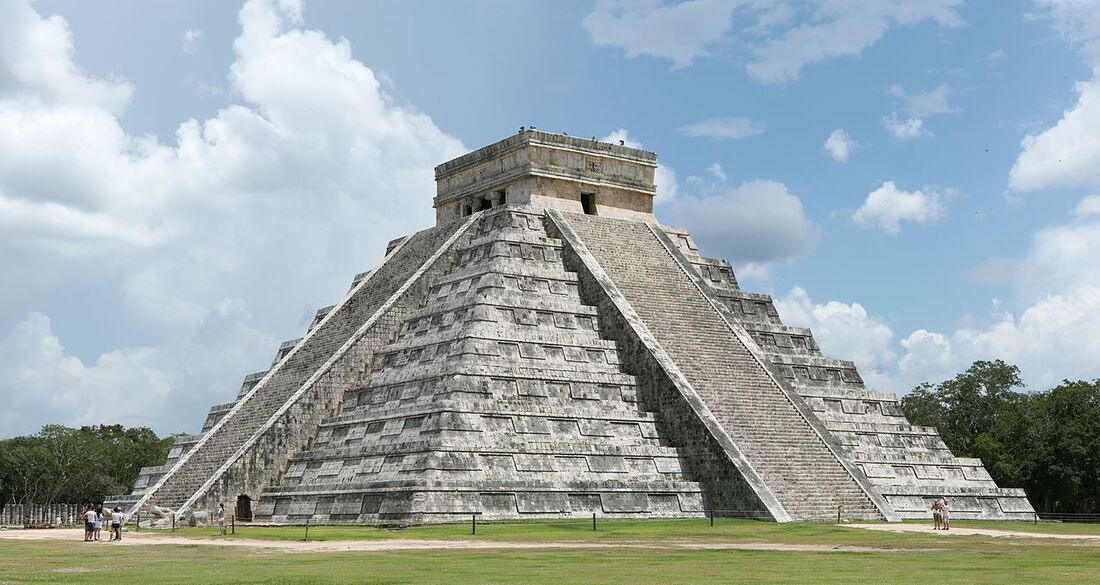
El Castillo (pyramid of Kukulcán) in Chichén Itzá
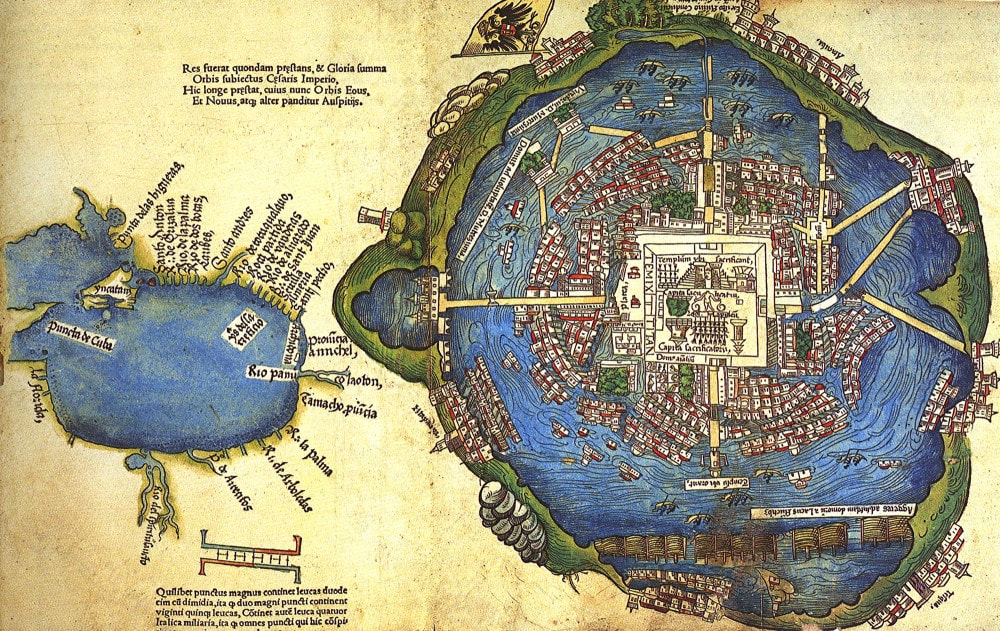
This sixteenth-century map of Tenochtitlan shows the aesthetic beauty and advanced infrastructure of this great Aztec city. Map, c. 1524
|
|
Early Colonization Quizlet
|
Review:
- Why did Native American societies develop different cultural traditions in different regions?
- What cultural traditions did Africans bring with them to America?
- How did the Reformation deepen rivalries between European nations?
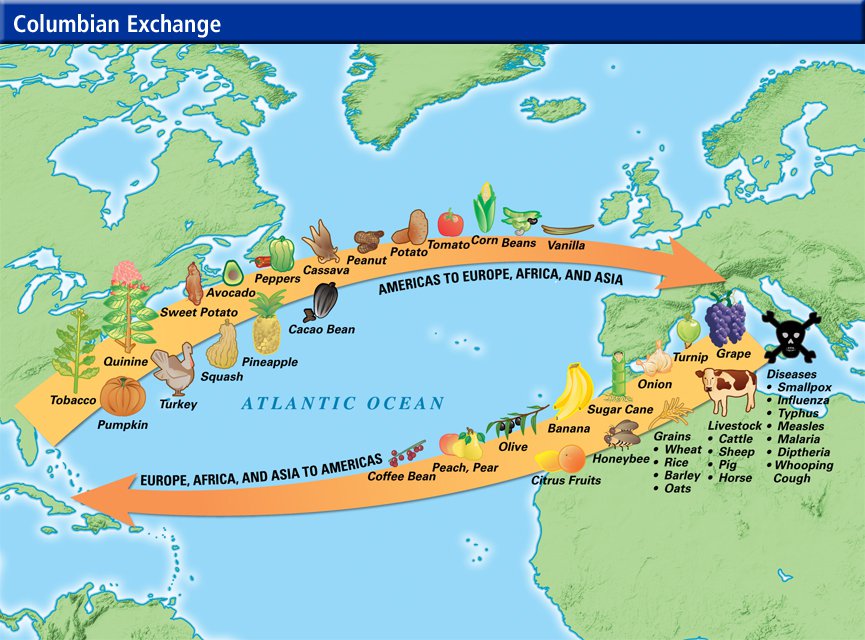
- What impact did the Columbian Exchange have on people’s lives throughout the world?
- How did Mexican culture develop out of both Spanish and Native American elements?
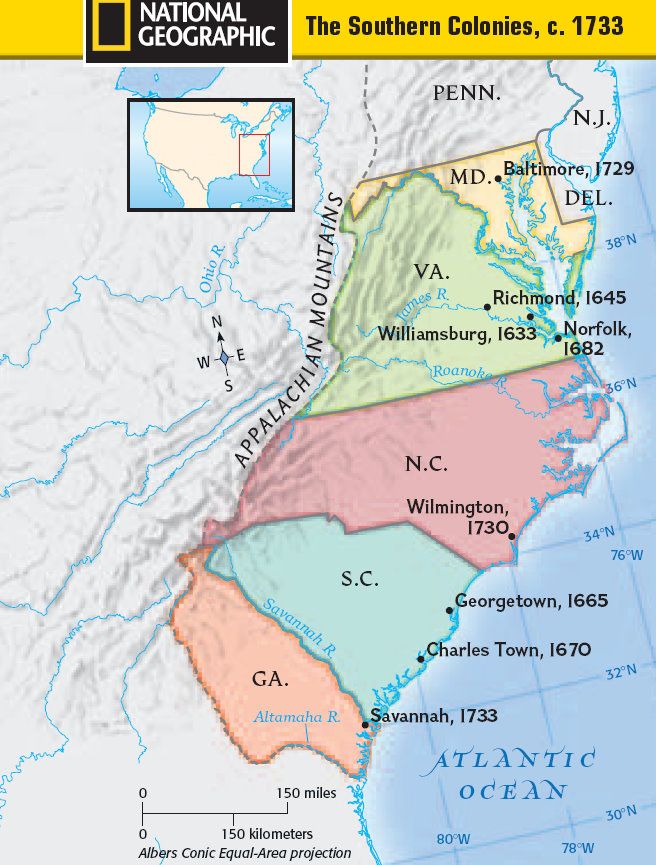
The Southern Colonies
Review:
- How did John Rolfe transform the Virginia colony?
- Which social class came to control the economy as well as the political and social institutions of the South?
- What conditions caused tension and warfare between settlers and Native Americans in Virginia?
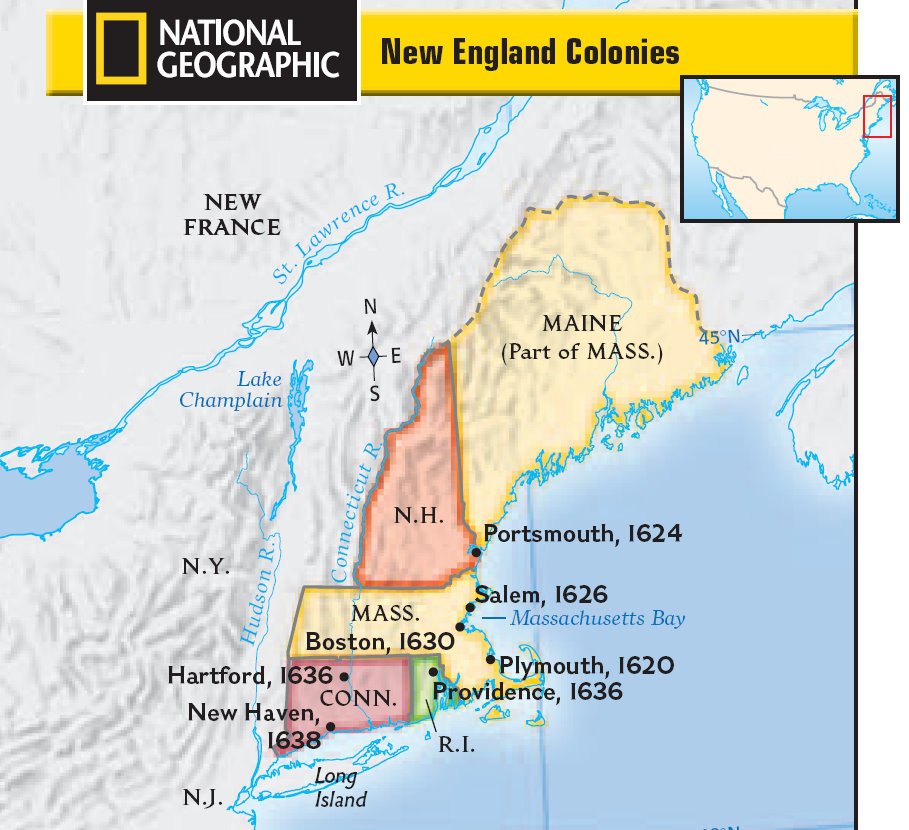
The New England Colonies
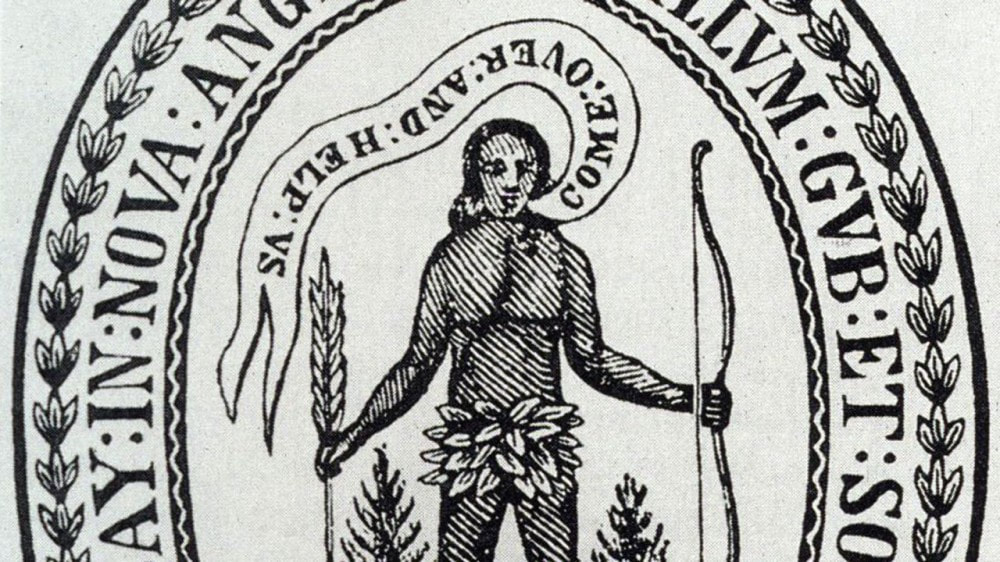
Seal of the Massachusetts Bay Colony
Review:
- What was the role of religion in the lives of Puritans living in the Massachusetts Bay Colony?
- Why did large, single-crop plantations not develop in the North?
- What caused conflicts between New England colonists and Native Americans?
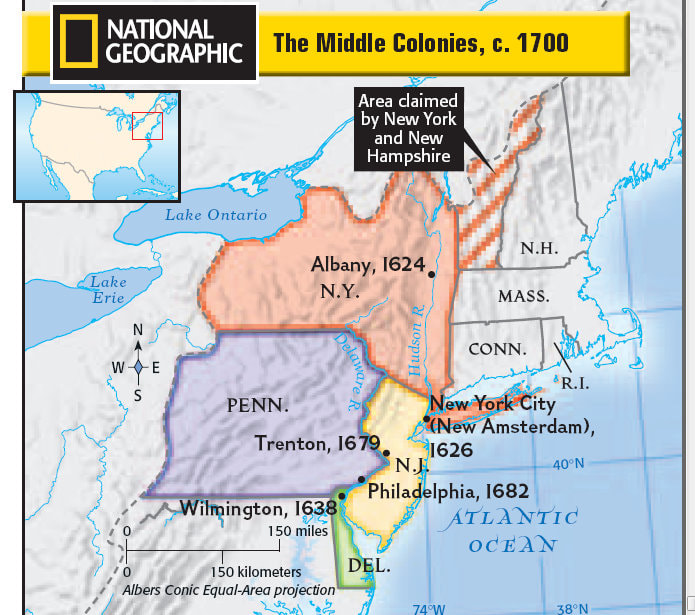
The Middle Colonies
Charles Willson Peale, The Peale Family, c. 1771–1773. Collection of the New-York Historical Society
|
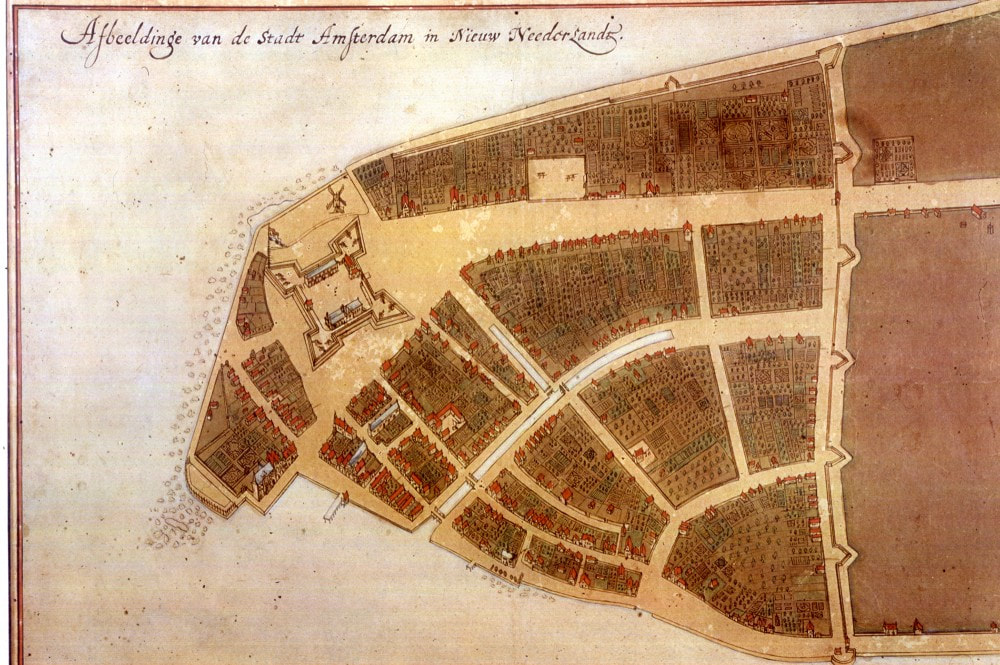
The earliest plan of New Amsterdam (now Manhattan), 1660
|
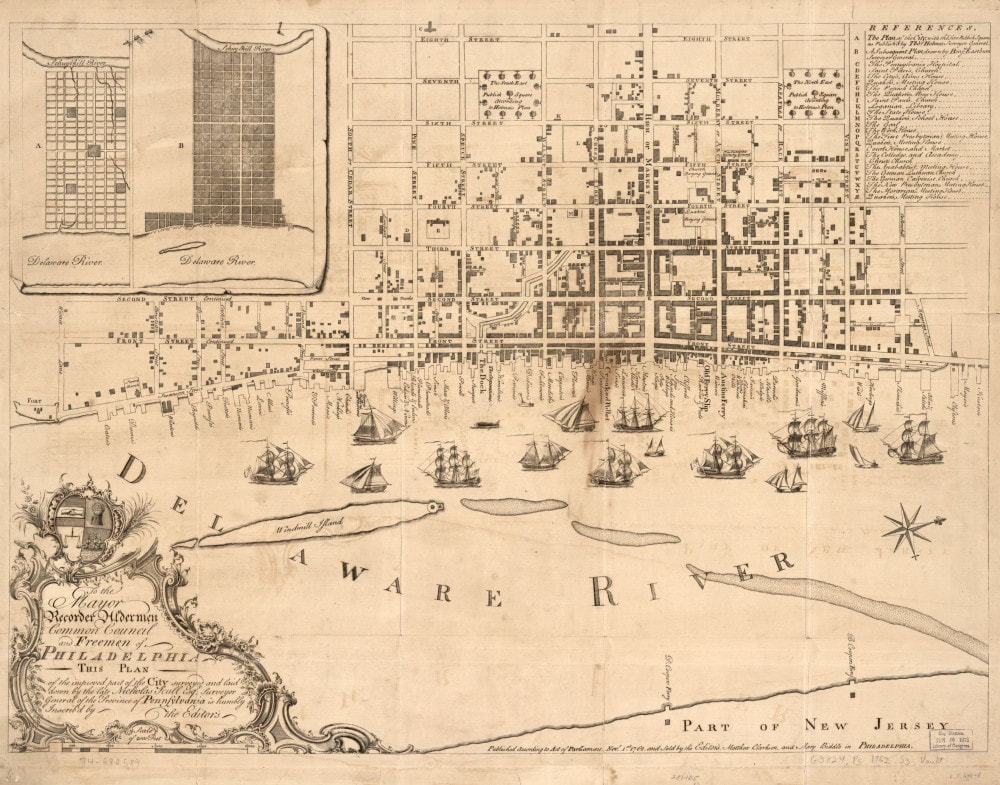
Nicholas Scull, “To the mayor, recorder, aldermen, common council, and freemen of Philadelphia this plan of the improved part of the city surveyed and laid down by the late Nicholas Scull,” Philadelphia, 1762; Note the well planned grid of streets.
|
Review:
- Why did New Netherland develop a reputation for diversity?
- How did Pennsylvania reflect William Penn’s Quaker ideals?
Old-New World Relations
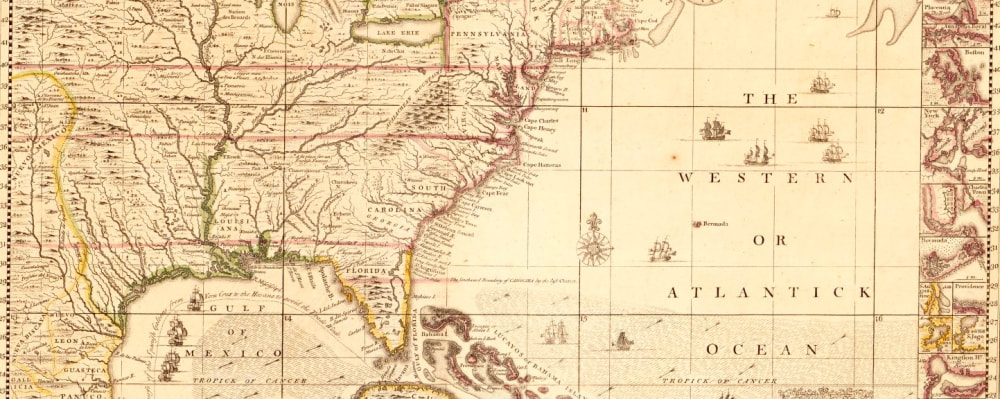
Henry Popple, A map of the British Empire in America with the French and Spanish settlements adjacent thereto, 1733
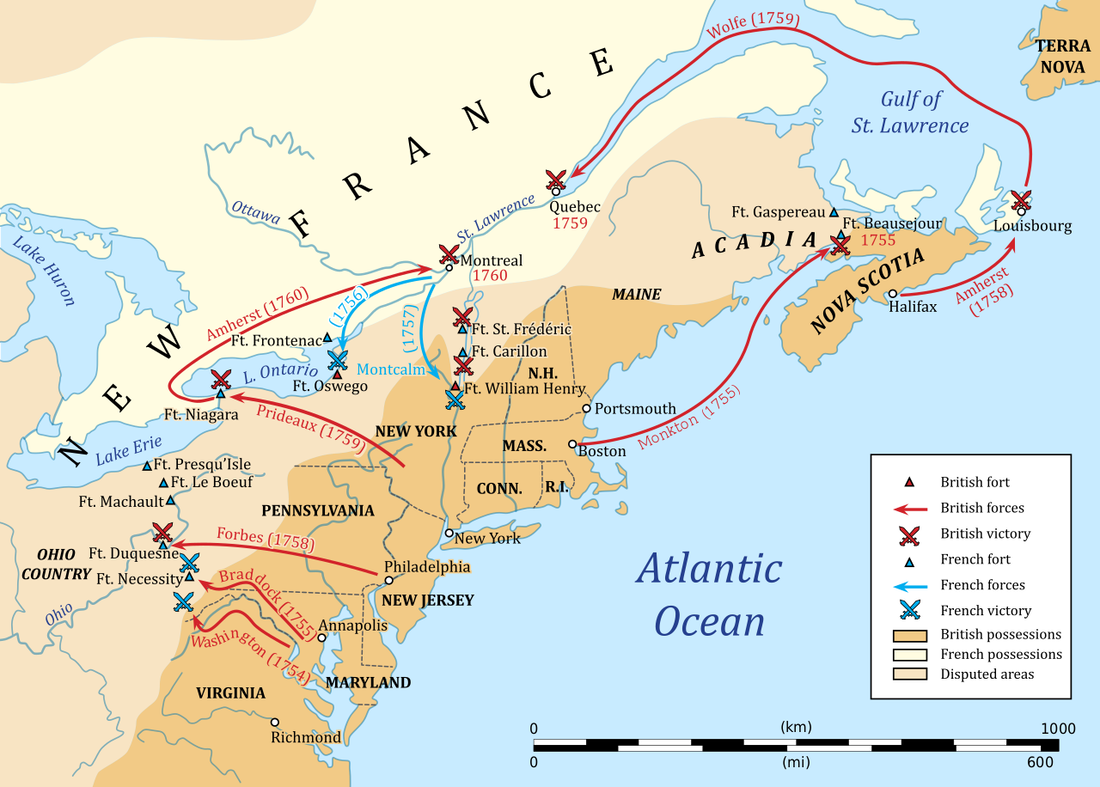
North American theater of the Seven Years' War, 1756-1763
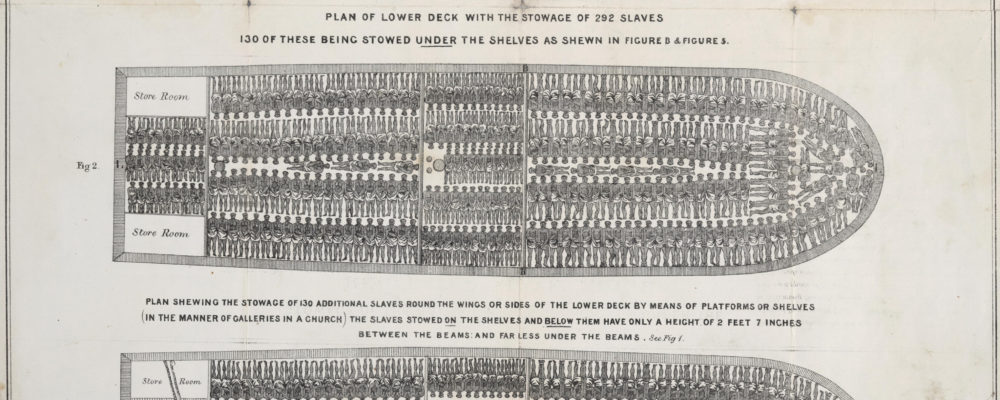
Slave ships transported 11–12 million Africans to destinations in North and South America, but it was not until the end of the 18th century that any regulation was introduced. The Brookes print dates to after the Regulated Slave Trade Act of 1788, but still shows enslaved Africans chained in rows using iron leg shackles. The slave ship Brookes was allowed to carry up to 454 slaves, allotting 6 feet (1.8 m) by 1 foot 4 inches (0.41 m) to each man; 5 feet 10 inches (1.78 m) by 1 foot 4 inches (0.41 m) to each woman, and 5 feet (1.5 m) by 1 foot 2 inches (0.36 m) to each child, but one slave trader alleged that before 1788, the ship carried as many as 609 slaves.
|
Unidentified artist, The Old Plantation, c. 1790–1800
John Hinton, “A representation of the sugar-cane and the art of making sugar,” 1749
|
The first trading post built on the Gulf of Guinea and the oldest European building southern of the Sahara, Elmina Castle was established as a trade settlement by the Portuguese in the fifteenth century. The fort became one of the largest and most important markets for African slaves along the Atlantic slave trade. “View of the castle of Elmina on the north-west side, seen from the river. Located on the gold coast in Guinea,” in Atlas Blaeu van der Hem, c. 1665–1668
|
|
Old-New World Relations
|
Old-New World Relations Quizlet
|
Benjamin Franklin created this image, Join or Die, in 1754 to promote his Albany Plan of Union for the colonies to stand together with Britain against France during the French and Indian War.
Review:
- How did the policy of salutary neglect benefit both England and its colonies?
- How did the goals of the French colonists differ from those of the English colonists?
Assignments and Readings
Map of the United States of America
Right-click on any map in the slideshow to open up in a new tab to view larger.
|
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| |||||||
|
|
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| ||||||
|
|
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| ||||||
|
|
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| ||||||
Map of the 13 British Colonies
|
Right-click on any map in the slideshow to open up in a new tab to view larger.
|
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| ||||||
Primary Sources
| an_advocate_of_english_colonization.pdf | |
| File Size: | 134 kb |
| File Type: | |
Richard Hakluyt makes the case for English colonization, 1584
Richard Hakluyt used this document to persuade Queen Elizabeth I to devote more money and energy into encouraging English colonization. In twenty-one chapters, summarized here, Hakluyt emphasized the many benefits that England would receive by creating colonies in the Americas.
John Winthrop dreams of a city on a hill, 1630
John Winthrop delivered the following sermon before he and his fellow settlers reached New England. The sermon is famous largely for its use of the phrase “a city on a hill,” used to describe the expectation that the Massachusetts Bay colony would shine like an example to the world. But Winthrop’s sermon also reveals how he expected Massachusetts to differ from the rest of the world.
John Lawson encounters North American Indians, 1709
John Lawson took detailed notes on the various peoples he encountered during his exploration of the Carolinas. Lawson recorded many aspects of Native American life and even noticed the progress of disease as it swept through native communities.
A Gaspesian Indian defends his way of life, 1641
Chrestien Le Clercq traveled to New France as a missionary, but found that many Native Americans were not interested in adopting European cultural practices. In this document, LeClercq records the words of a Gaspesian Indian who explained why he believed that his way of life was superior to Le Clercq’s.
The legend of Moshup, 1830
Most Native American peoples shared information solely through the spoken word. These oral cultures present unique challenges to historians, and force us to look beyond traditional written sources. Folk tales offer a valuable window into the ways that Native Americans understood themselves and the wider world. The Wampanoag legend of Moshup describes an ancient giant who lived on Martha’s Vineyard Island and offered stories about the history of the region.
Accusations of witchcraft, 1692 and 1706
These two documents explore the hysteria and death that captured Salem, Massachusetts at the end of the seventeenth century. In the first document, Sarah Carrier testifies that her mother forced her to engage in witchcraft. Her mother, Martha Carrier, was hung one week later. In the second document, Ann Putnam recants her own deadly accusations twenty years after the witchcraft trials.
Manuel Trujillo accuses Asencio Povia and Antonio Yuba of sodomy, 1731
In 1731, Manuel Trujillo accused two Pueblo men, Acensio Povia and Antonio Yuba, of committing sodomy. Both Povia and Yuba denied this accusation, and Yuba invoked his status as a Christian in order to bolster his credibility. Governor Gervasio Cruzat y Góngora chose to exile Povia and Yuba to different pueblos for a period of four months, during which time they were to cease any and all communication with one another. This case explores sexual practices deemed “nefarious sins” as well as illustrates what scholars have called the colonial dilemma—the situation where indigenous peoples remained in a subjected state despite theological equality following their Christian conversion.
Painting of New Orleans, 1726
During the contact period, the frontier was constantly shifting and places that are now considered old were once tenuous settlements. This watercolor painting depicts New Orleans in 1726 when it was an 8-year-old French frontier settlement, nearly forty years prior to the Spanish acquisition of the Louisiana territory. In the foreground, enslaved Africans fell trees on land belonging to the Company of the Indies, and another enslaved man spears a massive alligator. Land has been cleared only just beyond the town limits and a wooden palisade provides meager protection from competing European empires.
Sketch of Algonquin village, 1585
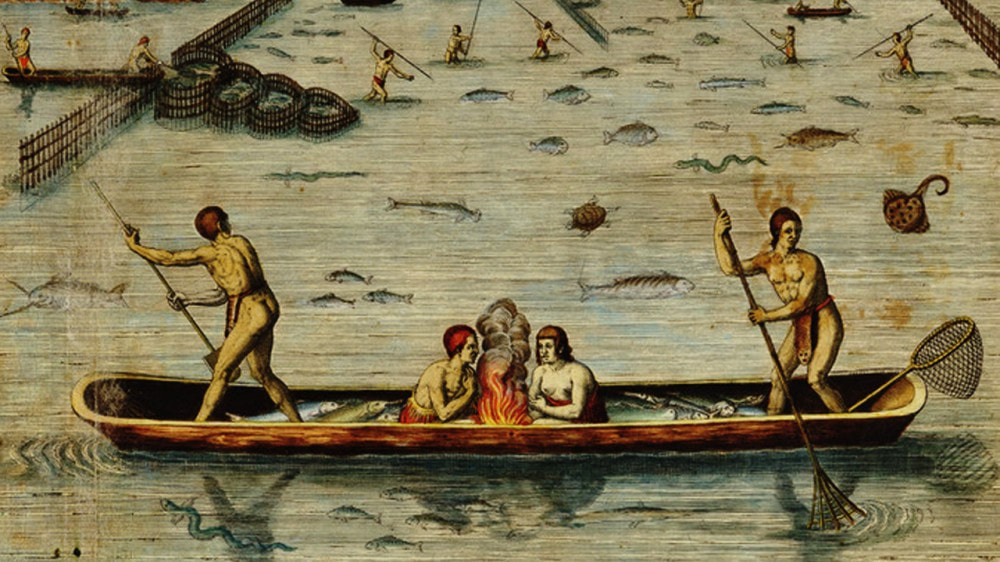
Native settlements were usually organized around political, economic, or religious activity. John White shows this Algonquin community engaged in some kind of celebration across from the fire he identified as “The place of solemne prayer,” indicating that ceremonial activity could be both solemn and raucous. In the center of the image, a communal meal has been laid alongside crops that are in varying stages of growth, suggesting the use of planting techniques like crop rotation. He also shows the interior of several longhouses, made of bent saplings and covered with bark and woven maps. Among the Powhatan, similar structures were called yehakins. In putting the longhouses and the settlement in a series of rows, White’s English perspective comes through: archaeological evidence shows that these houses were usually situated around communal gathering places or moved next to fields under cultivation not ordered in European-style rows.
Olaudah Equiano describes the Middle Passage, 1789
In this harrowing description of the Middle Passage, Olaudah Equiano described the terror of the transatlantic slave trade. Equiano eventually purchased his freedom and lived in London where he advocated for abolition.
Recruiting settlers to Carolina, 1666
Robert Horne’s wanted to entice English settlers to join the new colony of Carolina. According to Horne, natural bounty, economic opportunity, and religious liberty awaited anyone willing to make the journey. Horne wanted to recruit settlers of every social class, from those “of Genteel blood” to those who would have to sign a contract of indentured servitude.
Letter from Carolina, 1682
Thomas Newe’s account of his experience in Carolina offers an interesting counter to Robert Horne’s prediction of what would await settlers. Newe describes deadly disease, war with Indians, and unprepared colonists. Newe longs for news from home but also appears committed to making a new life for himself in Carolina.
Francis Daniel Pastorius describes his ocean voyage, 1684
The journey across the Atlantic was difficult at best and deadly at worst. Francis Pastorius left his home in Germany to create a new life in Pennsylvania. This account shows the discomforts and dangers of oceanic travel in the seventeenth century.
Song about life in Virginia
Some English men and women understood the New World to be a place of opportunity, where they could create new lives. More common, however, was the belief that the New World was a place of great danger and suffering. This song was written from the perspective of a young girl who was sent to Virginia against her will, where she faced a life of hunger and never-ending work.
Haudenosaunee thanksgiving address
This Thanksgiving address was used by the six nations of the Haudenosaunee (Iroquois) to open and close major gatherings or meetings. The prayer was also sometimes used individually at the beginning or end of the day.
Rose Davis is sentenced to a life of slavery, 1715
Rose Davis was born to an indentured servant white woman and a black man. Slave law claimed that children inherited the status of their mother, a law which enabled enslavers to control the reproductive functions of their enslaved women laborers. However, as race increasingly became a marker of slavery, even the children of free white women could be vulnerable to enslavement. Rose had been working as an indentured servant when she petitioned the court for her freedom. Instead, she was sentenced to a lifetime of slavery.
Print of the slave ship Brookes, 1789
Slave ships transported 11-12 million Africans to destinations in North and South America, but it was not until the end of the eighteenth century that any kind of regulation was introduced. The Brookes print dates to after the Regulated Slave Trade Act of 1788, but still shows enslaved Africans chained in rows using bilboes, which were iron leg shackles used to chain pairs of slaves together during the Middle Passage throughout the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. The slave ship Brookes was allowed to carry up to 454 slaves, allotting 6 feet (1.8 m) by 1 foot 4 inches (0.41 m) to each man; 5 feet 10 inches (1.78 m) by 1 foot 4 inches (0.41 m) to each woman, and 5 feet (1.5 m) by 1 foot 2 inches (0.36 m) to each child, but one slave trader alleged that before 1788, the ship carried as many as 609 slaves.
Map of British North America, 1733
British colonists in the seventeenth and early eighteenth centuries occupied a constantly contested frontier. The British Empire competed with French, Spanish, Portuguese, Dutch, and even Scottish explorers to claim land in North America and the Caribbean – much of it already settled by Native Americans. This diverse territory would continue to be contested throughout the eighteenth century. Eventually, the British Empire included twenty-six colonies in North America, producing everything from grain and timber to luxury goods like tobacco and sugar.
Richard Hakluyt used this document to persuade Queen Elizabeth I to devote more money and energy into encouraging English colonization. In twenty-one chapters, summarized here, Hakluyt emphasized the many benefits that England would receive by creating colonies in the Americas.
John Winthrop dreams of a city on a hill, 1630
John Winthrop delivered the following sermon before he and his fellow settlers reached New England. The sermon is famous largely for its use of the phrase “a city on a hill,” used to describe the expectation that the Massachusetts Bay colony would shine like an example to the world. But Winthrop’s sermon also reveals how he expected Massachusetts to differ from the rest of the world.
John Lawson encounters North American Indians, 1709
John Lawson took detailed notes on the various peoples he encountered during his exploration of the Carolinas. Lawson recorded many aspects of Native American life and even noticed the progress of disease as it swept through native communities.
A Gaspesian Indian defends his way of life, 1641
Chrestien Le Clercq traveled to New France as a missionary, but found that many Native Americans were not interested in adopting European cultural practices. In this document, LeClercq records the words of a Gaspesian Indian who explained why he believed that his way of life was superior to Le Clercq’s.
The legend of Moshup, 1830
Most Native American peoples shared information solely through the spoken word. These oral cultures present unique challenges to historians, and force us to look beyond traditional written sources. Folk tales offer a valuable window into the ways that Native Americans understood themselves and the wider world. The Wampanoag legend of Moshup describes an ancient giant who lived on Martha’s Vineyard Island and offered stories about the history of the region.
Accusations of witchcraft, 1692 and 1706
These two documents explore the hysteria and death that captured Salem, Massachusetts at the end of the seventeenth century. In the first document, Sarah Carrier testifies that her mother forced her to engage in witchcraft. Her mother, Martha Carrier, was hung one week later. In the second document, Ann Putnam recants her own deadly accusations twenty years after the witchcraft trials.
Manuel Trujillo accuses Asencio Povia and Antonio Yuba of sodomy, 1731
In 1731, Manuel Trujillo accused two Pueblo men, Acensio Povia and Antonio Yuba, of committing sodomy. Both Povia and Yuba denied this accusation, and Yuba invoked his status as a Christian in order to bolster his credibility. Governor Gervasio Cruzat y Góngora chose to exile Povia and Yuba to different pueblos for a period of four months, during which time they were to cease any and all communication with one another. This case explores sexual practices deemed “nefarious sins” as well as illustrates what scholars have called the colonial dilemma—the situation where indigenous peoples remained in a subjected state despite theological equality following their Christian conversion.
Painting of New Orleans, 1726
During the contact period, the frontier was constantly shifting and places that are now considered old were once tenuous settlements. This watercolor painting depicts New Orleans in 1726 when it was an 8-year-old French frontier settlement, nearly forty years prior to the Spanish acquisition of the Louisiana territory. In the foreground, enslaved Africans fell trees on land belonging to the Company of the Indies, and another enslaved man spears a massive alligator. Land has been cleared only just beyond the town limits and a wooden palisade provides meager protection from competing European empires.
Sketch of Algonquin village, 1585
Native settlements were usually organized around political, economic, or religious activity. John White shows this Algonquin community engaged in some kind of celebration across from the fire he identified as “The place of solemne prayer,” indicating that ceremonial activity could be both solemn and raucous. In the center of the image, a communal meal has been laid alongside crops that are in varying stages of growth, suggesting the use of planting techniques like crop rotation. He also shows the interior of several longhouses, made of bent saplings and covered with bark and woven maps. Among the Powhatan, similar structures were called yehakins. In putting the longhouses and the settlement in a series of rows, White’s English perspective comes through: archaeological evidence shows that these houses were usually situated around communal gathering places or moved next to fields under cultivation not ordered in European-style rows.
Olaudah Equiano describes the Middle Passage, 1789
In this harrowing description of the Middle Passage, Olaudah Equiano described the terror of the transatlantic slave trade. Equiano eventually purchased his freedom and lived in London where he advocated for abolition.
Recruiting settlers to Carolina, 1666
Robert Horne’s wanted to entice English settlers to join the new colony of Carolina. According to Horne, natural bounty, economic opportunity, and religious liberty awaited anyone willing to make the journey. Horne wanted to recruit settlers of every social class, from those “of Genteel blood” to those who would have to sign a contract of indentured servitude.
Letter from Carolina, 1682
Thomas Newe’s account of his experience in Carolina offers an interesting counter to Robert Horne’s prediction of what would await settlers. Newe describes deadly disease, war with Indians, and unprepared colonists. Newe longs for news from home but also appears committed to making a new life for himself in Carolina.
Francis Daniel Pastorius describes his ocean voyage, 1684
The journey across the Atlantic was difficult at best and deadly at worst. Francis Pastorius left his home in Germany to create a new life in Pennsylvania. This account shows the discomforts and dangers of oceanic travel in the seventeenth century.
Song about life in Virginia
Some English men and women understood the New World to be a place of opportunity, where they could create new lives. More common, however, was the belief that the New World was a place of great danger and suffering. This song was written from the perspective of a young girl who was sent to Virginia against her will, where she faced a life of hunger and never-ending work.
Haudenosaunee thanksgiving address
This Thanksgiving address was used by the six nations of the Haudenosaunee (Iroquois) to open and close major gatherings or meetings. The prayer was also sometimes used individually at the beginning or end of the day.
Rose Davis is sentenced to a life of slavery, 1715
Rose Davis was born to an indentured servant white woman and a black man. Slave law claimed that children inherited the status of their mother, a law which enabled enslavers to control the reproductive functions of their enslaved women laborers. However, as race increasingly became a marker of slavery, even the children of free white women could be vulnerable to enslavement. Rose had been working as an indentured servant when she petitioned the court for her freedom. Instead, she was sentenced to a lifetime of slavery.
Print of the slave ship Brookes, 1789
Slave ships transported 11-12 million Africans to destinations in North and South America, but it was not until the end of the eighteenth century that any kind of regulation was introduced. The Brookes print dates to after the Regulated Slave Trade Act of 1788, but still shows enslaved Africans chained in rows using bilboes, which were iron leg shackles used to chain pairs of slaves together during the Middle Passage throughout the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. The slave ship Brookes was allowed to carry up to 454 slaves, allotting 6 feet (1.8 m) by 1 foot 4 inches (0.41 m) to each man; 5 feet 10 inches (1.78 m) by 1 foot 4 inches (0.41 m) to each woman, and 5 feet (1.5 m) by 1 foot 2 inches (0.36 m) to each child, but one slave trader alleged that before 1788, the ship carried as many as 609 slaves.
Map of British North America, 1733
British colonists in the seventeenth and early eighteenth centuries occupied a constantly contested frontier. The British Empire competed with French, Spanish, Portuguese, Dutch, and even Scottish explorers to claim land in North America and the Caribbean – much of it already settled by Native Americans. This diverse territory would continue to be contested throughout the eighteenth century. Eventually, the British Empire included twenty-six colonies in North America, producing everything from grain and timber to luxury goods like tobacco and sugar.
Slideshows
Videos
|
|
| ||||||
|
|
| ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Digital History Textbook
Exploration and Discovery
The encounter that began in 1492 among the peoples of the Eastern and Western Hemispheres was one of the truly epochal events in world history. This cultural collision not only produced an extraordinary transformation of the natural environment and human cultures in the New World, it also initiated far-reaching changes in the Old World as well.
17th Century
The economic, religious, and social developments that led Europeans to colonize new lands; the differences between Spanish, French, and English colonization; and the difficulties they encountered as a result of the varied climates and topographies.
18th Century
England's efforts to create an empire based on mercantilist principles and the conflicts that these efforts to assert control produce. You will also learn about the forces that transformed colonial life, including an expanding population, economic stratification, the Enlightenment, and the Great Awakening.
The encounter that began in 1492 among the peoples of the Eastern and Western Hemispheres was one of the truly epochal events in world history. This cultural collision not only produced an extraordinary transformation of the natural environment and human cultures in the New World, it also initiated far-reaching changes in the Old World as well.
- The Significance of 1492
- European Commercial and Financial Expansion
- Slavery and Spanish Colonization
- The Meaning of America
- The Black Legend
17th Century
The economic, religious, and social developments that led Europeans to colonize new lands; the differences between Spanish, French, and English colonization; and the difficulties they encountered as a result of the varied climates and topographies.
- European Colonization North of Mexico
- Spanish Colonization
- English Colonization Begins
- Life in Early Virginia
- Slavery Takes Root in Colonial Virginia
- Founding New England
- The Puritans
- The Puritan Idea of the Covenant
- Regional Contrasts
- Dimensions of Change in Colonial New England
- The Salem Witch Scare
- Slavery in the Colonial North
- Struggles for Power in Colonial America
- Diversity in Colonial America
- The Middle Colonies: New York
- Slave Revolts
- The Middle Colonies: William Penn’s Holy Commonwealth
- The Southernmost Colonies: The Carolinas and Georgia
18th Century
England's efforts to create an empire based on mercantilist principles and the conflicts that these efforts to assert control produce. You will also learn about the forces that transformed colonial life, including an expanding population, economic stratification, the Enlightenment, and the Great Awakening.