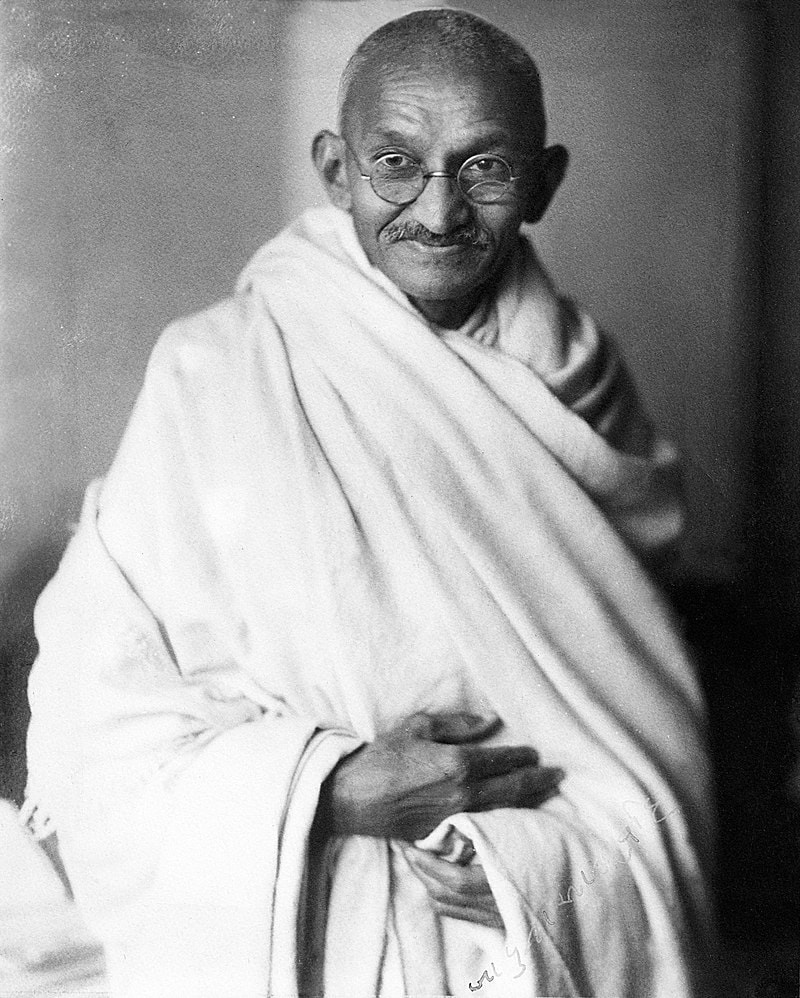
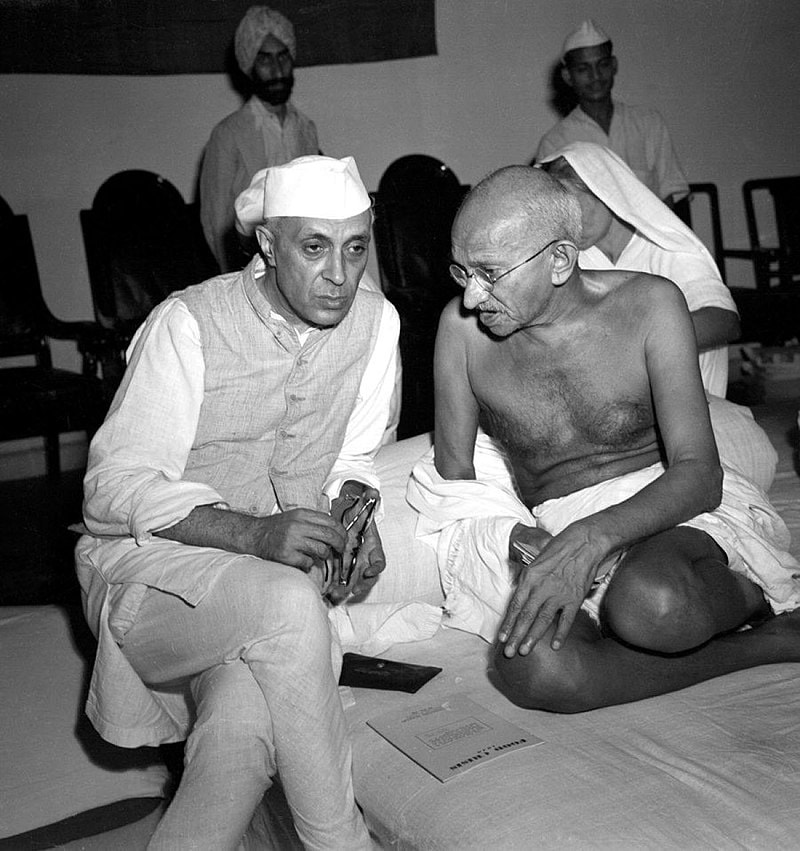
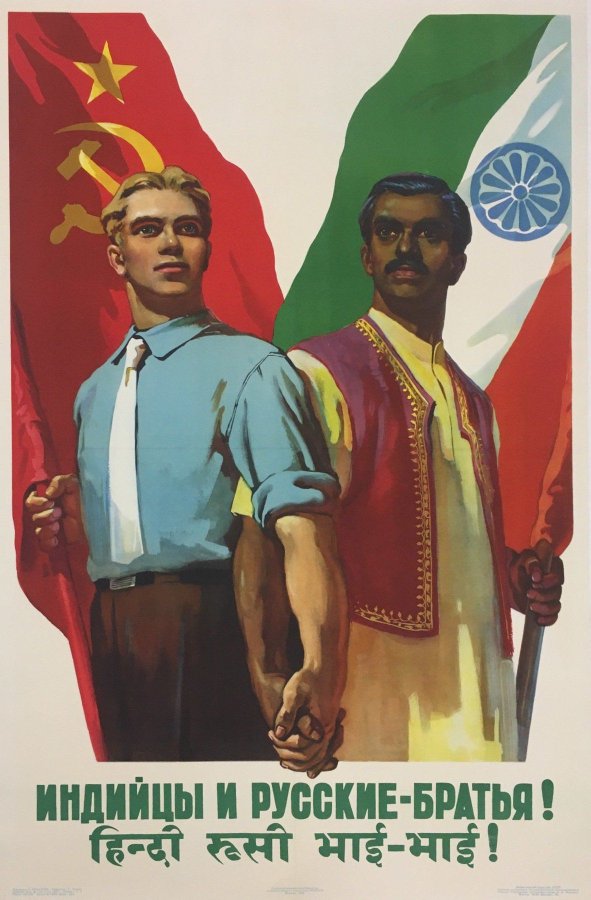
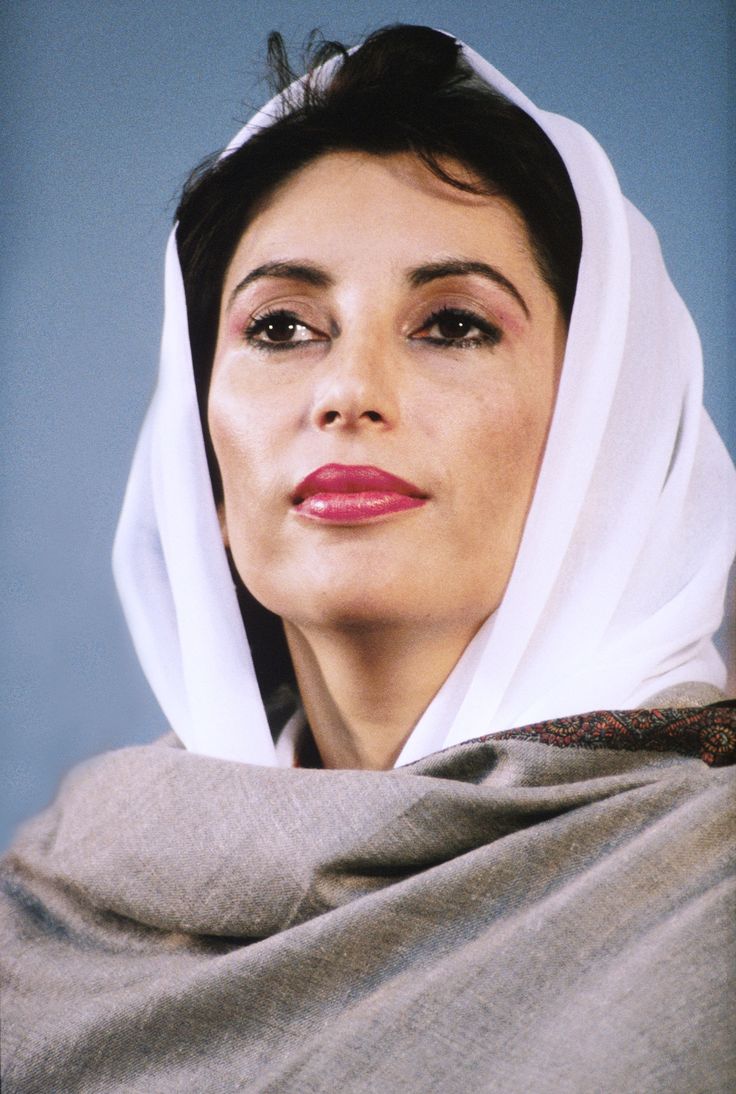
The Postwar World
c. 1900-Today
Contents
The Postwar World, c. 1900-Today:
Objectives
- Explain the historical context of the Cold War after 1945.
- Explain the causes and effects of the ideological struggle of the Cold War.
- Compare the ways in which the United States and the Soviet Union sought to maintain influence over the course of the Cold War.
- Explain the causes and consequences of China’s adoption of communism.
- Explain the causes and effects of movements to redistribute economic resources.
- Explain the causes of the end of the Cold War.
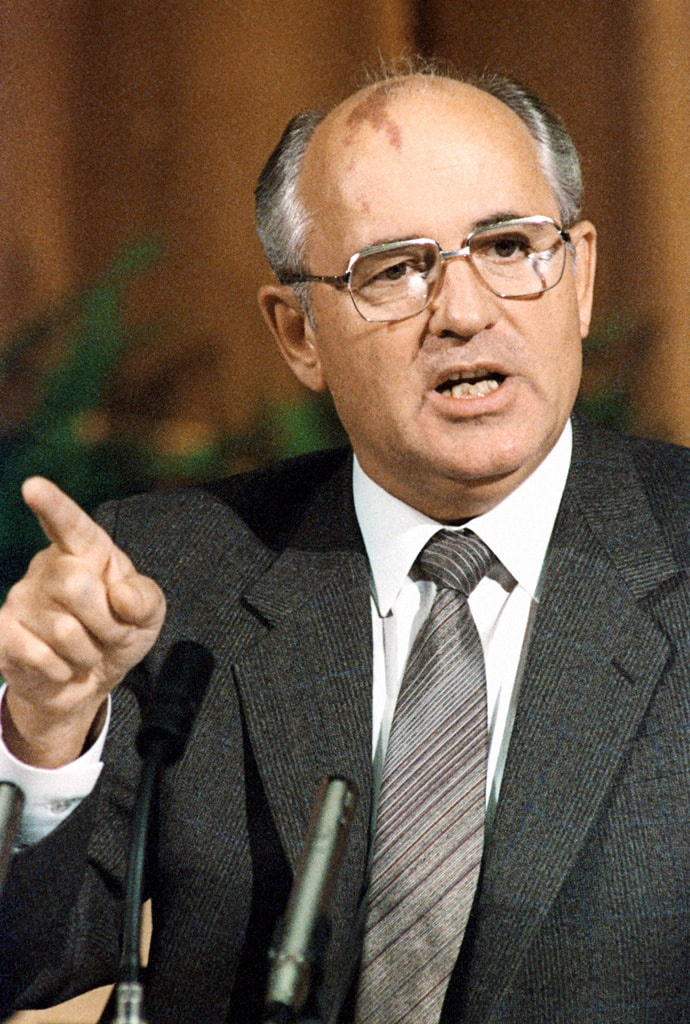
- Advances in U.S. military and technological development, the Soviet Union’s costly and ultimately failed invasion of Afghanistan, and public discontent and economic weakness in communist countries led to the end of the Cold War and the collapse of the Soviet Union.
- Compare the processes by which various peoples pursued independence after 1900.
- Explain how political changes in the period from c. 1900 to the present led to territorial, demographic, and nationalist developments.
- Explain the economic changes and continuities resulting from the process of decolonization.
- Explain various reactions to existing power structures in the period after 1900.
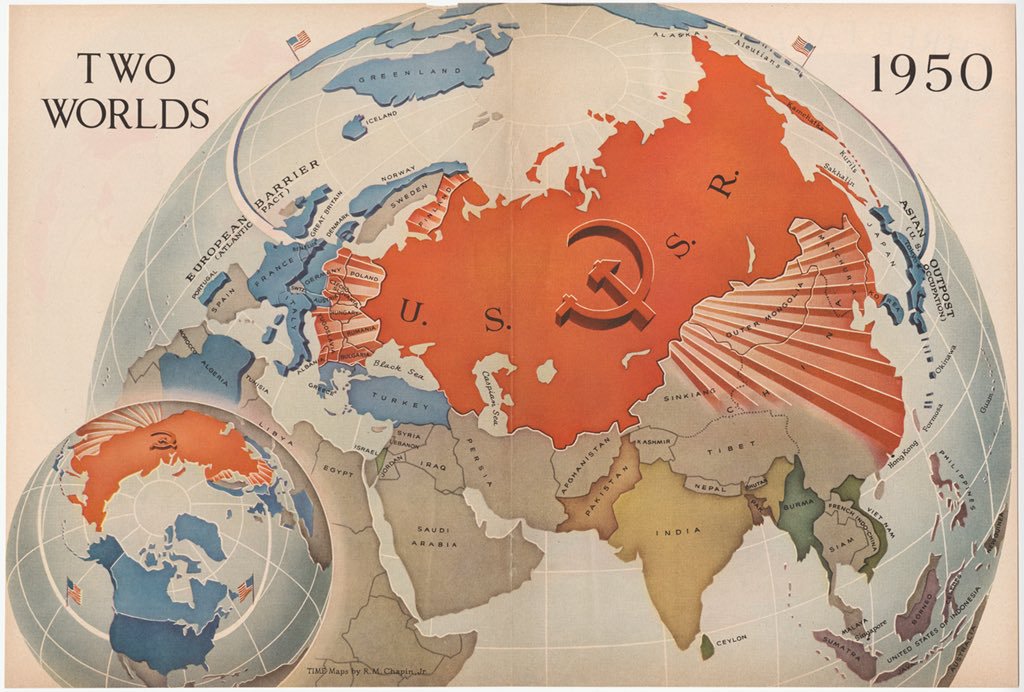
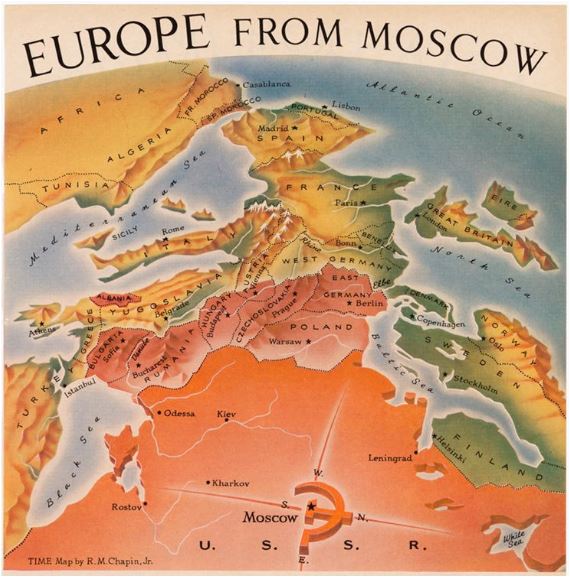
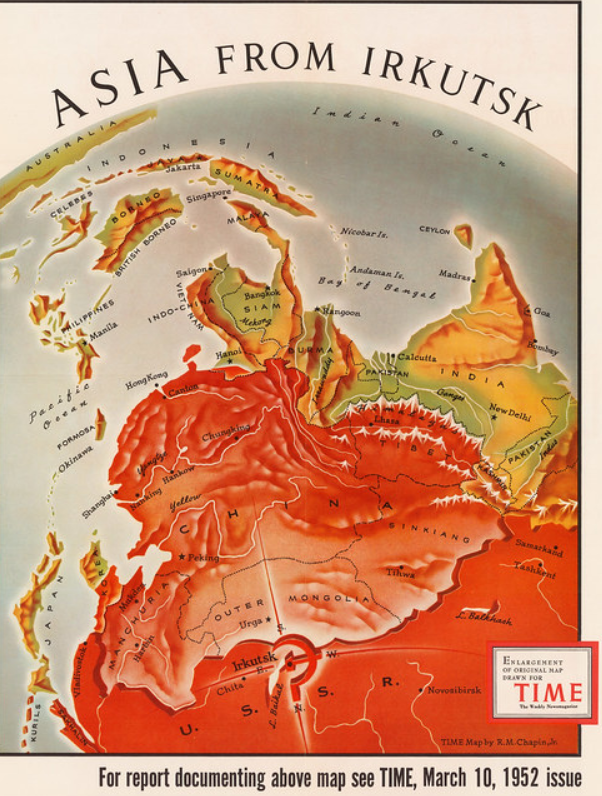
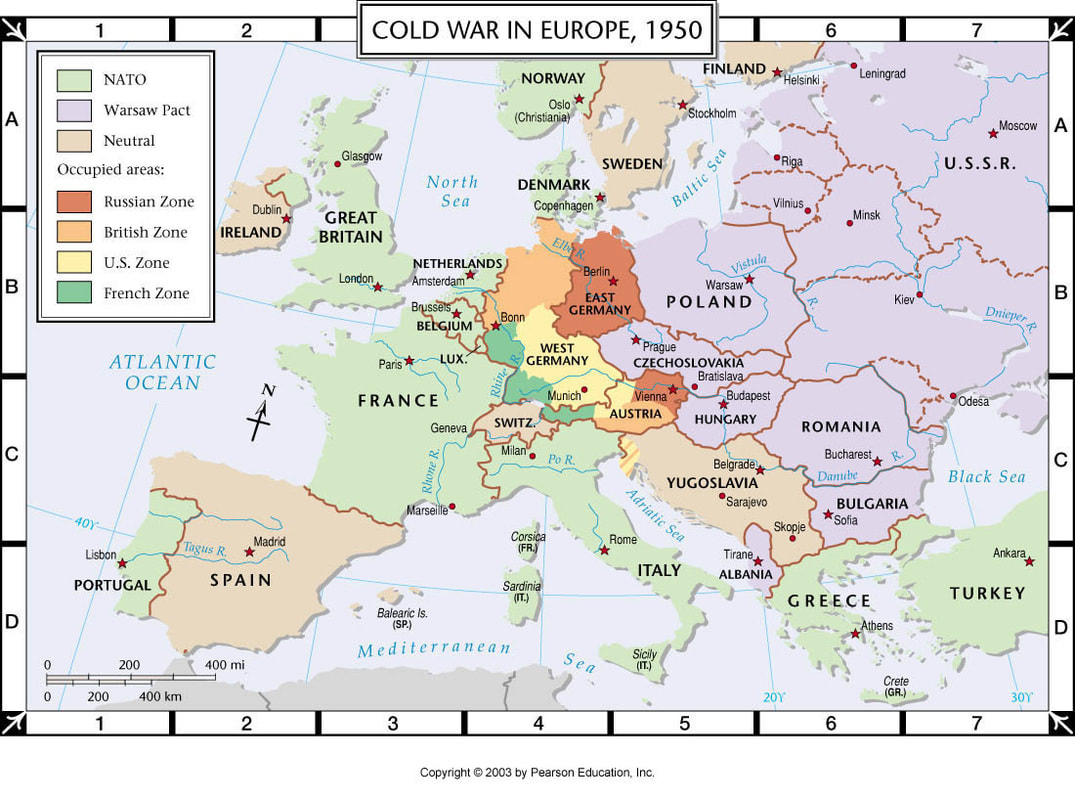
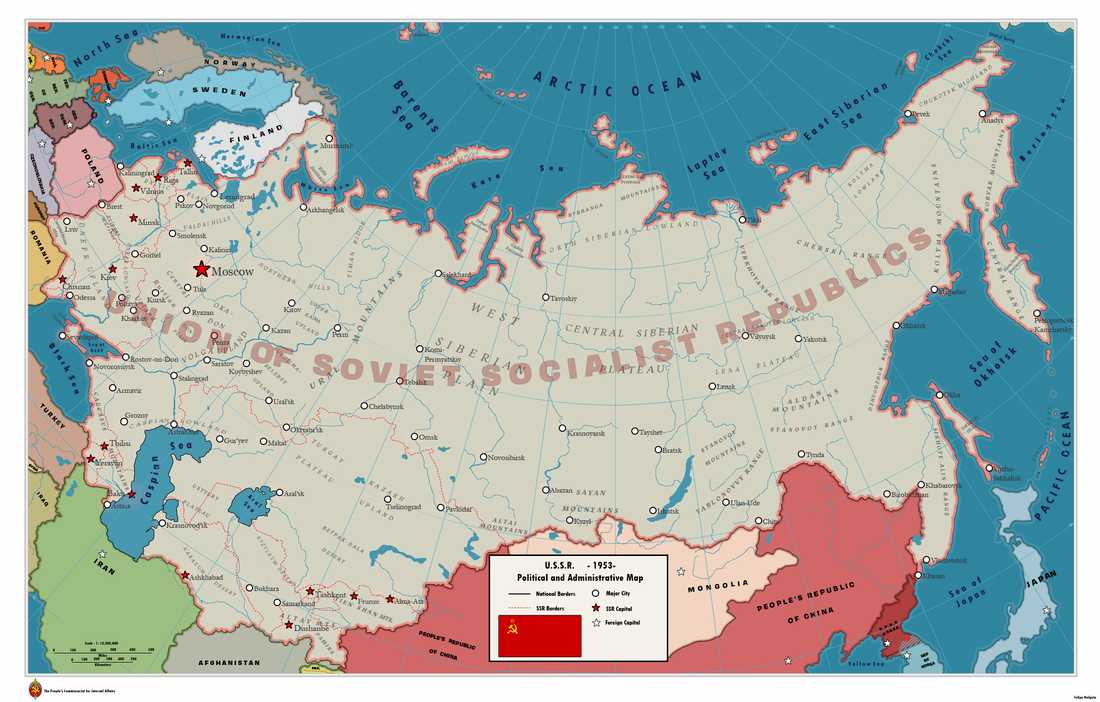
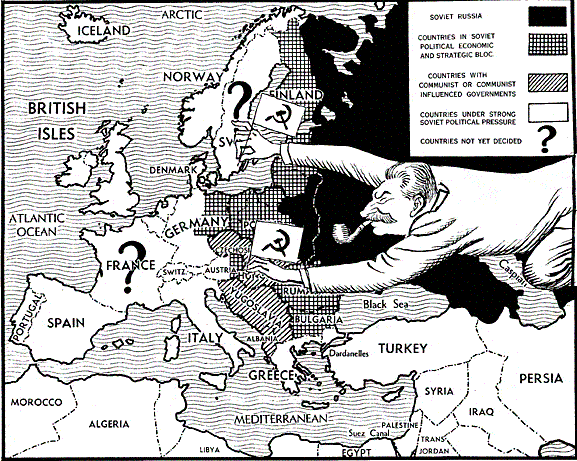
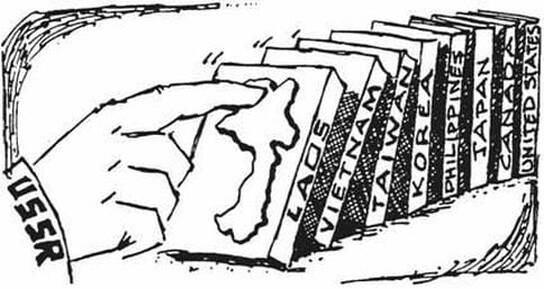
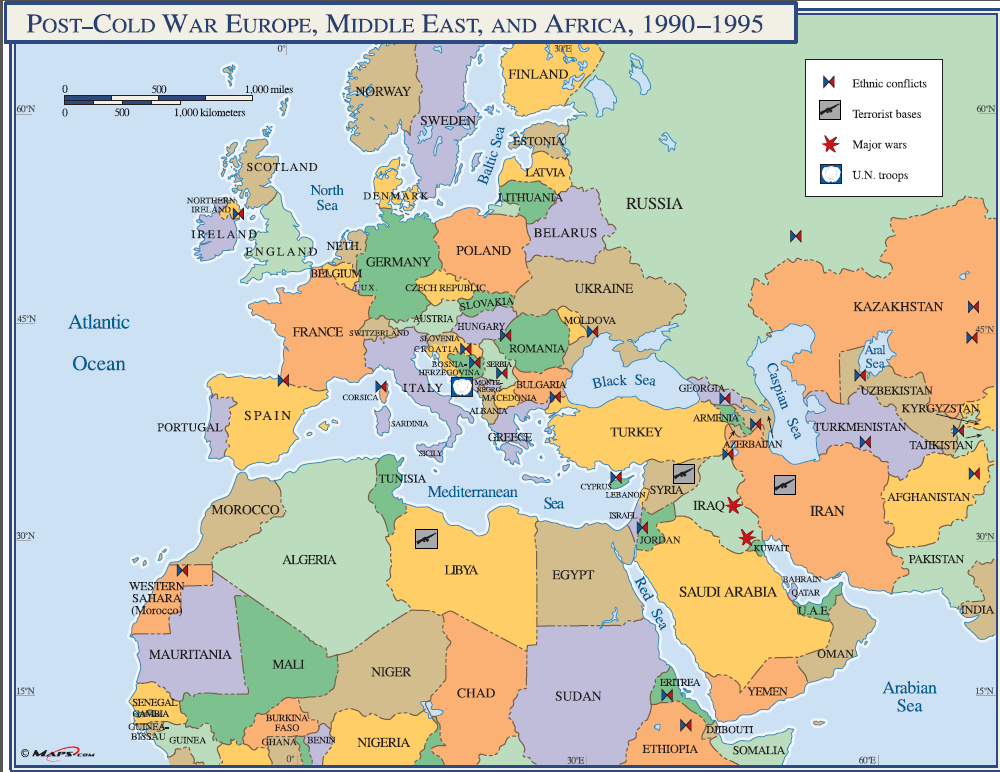
The Iron Curtain
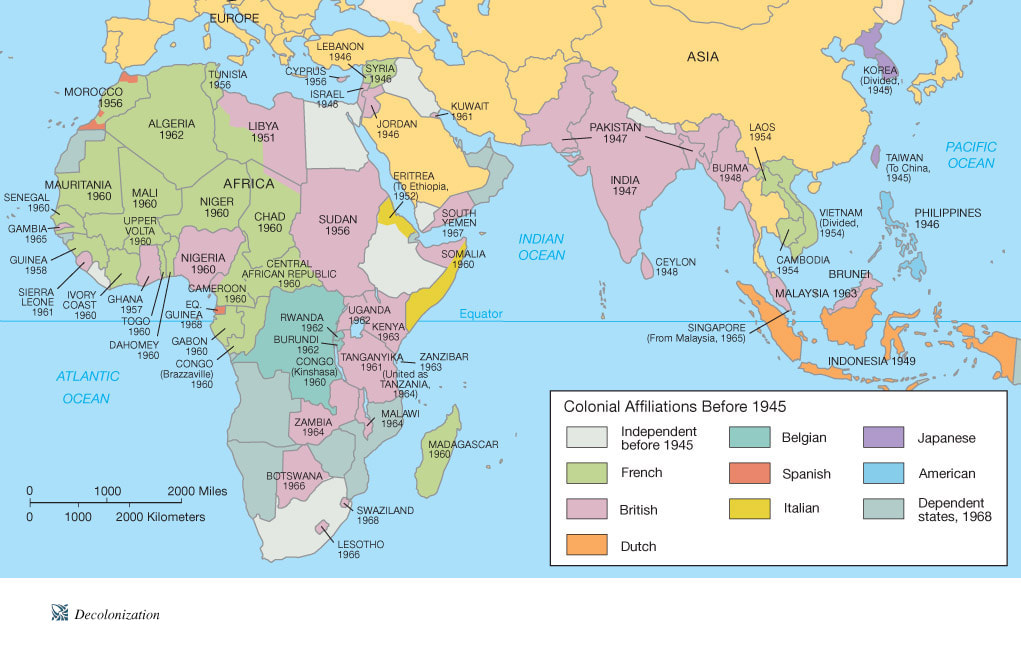
- Hopes for greater self-government were largely unfulfilled following World War I; however, in the years following World War II, increasing anti-imperialist sentiment contributed to the dissolution of empires and the restructuring of states.
- Technological and economic gains experienced during World War II by the victorious nations shifted the global balance of power.
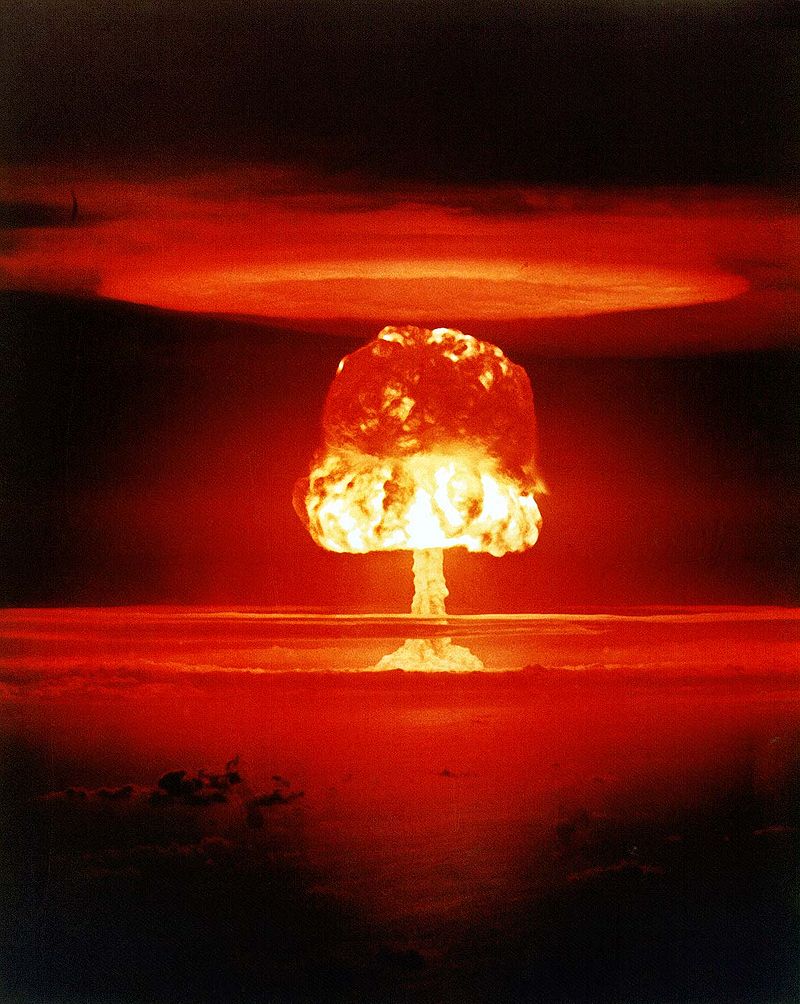
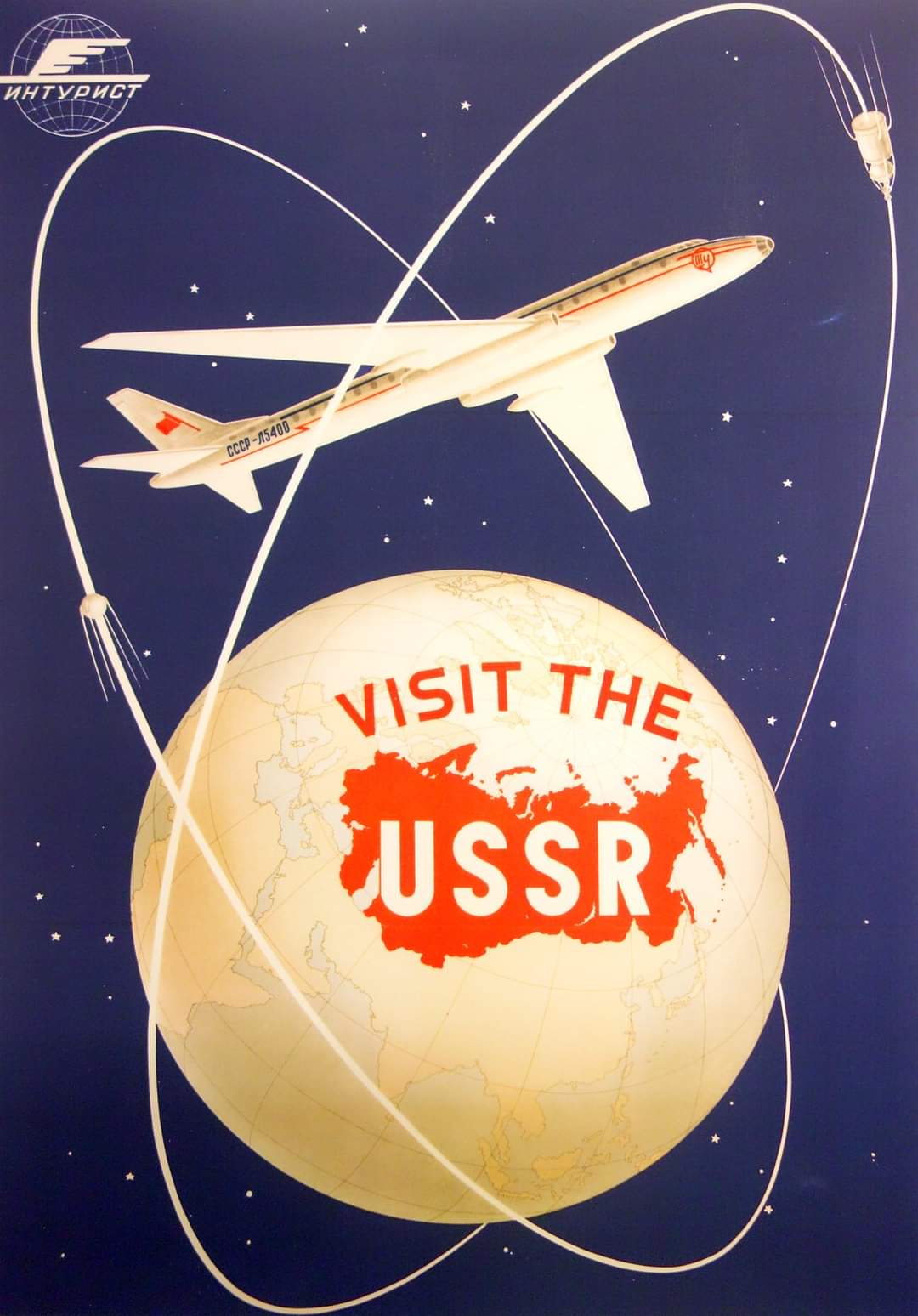
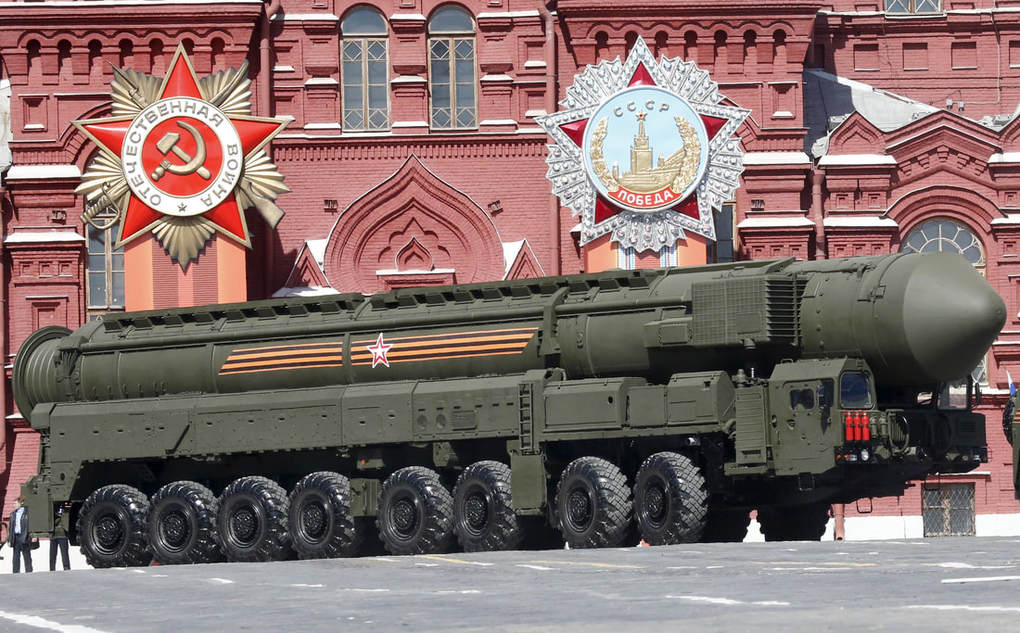
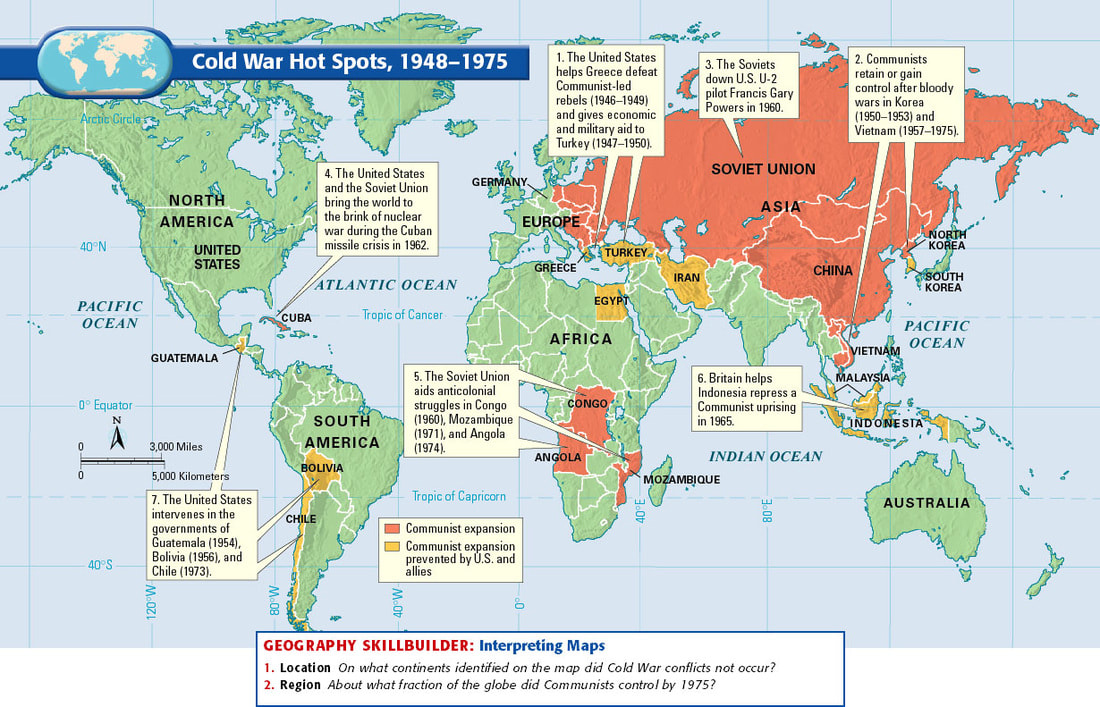
- The global balance of economic and political power shifted during and after World War II and rapidly evolved into the Cold War. The democracy of the United States and the authoritarian communist Soviet Union emerged as superpowers, which led to ideological conflict and a power struggle between capitalism and communism across the globe.
|
The Iron Curtain (comprehensive)
The Iron Curtain (abridged)
|
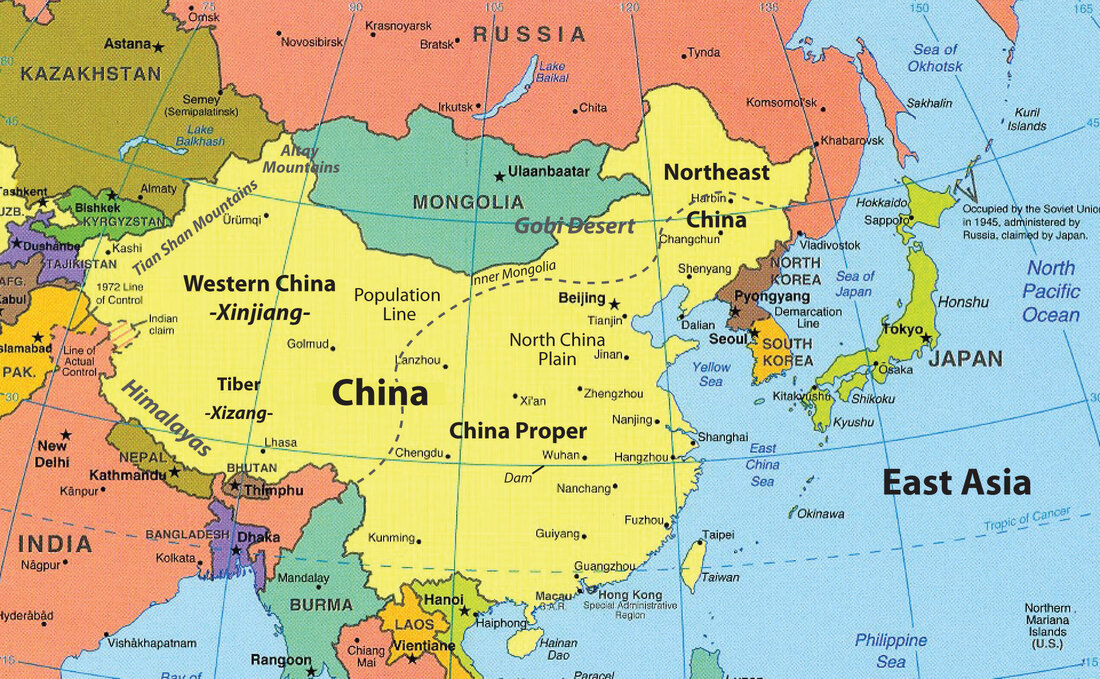
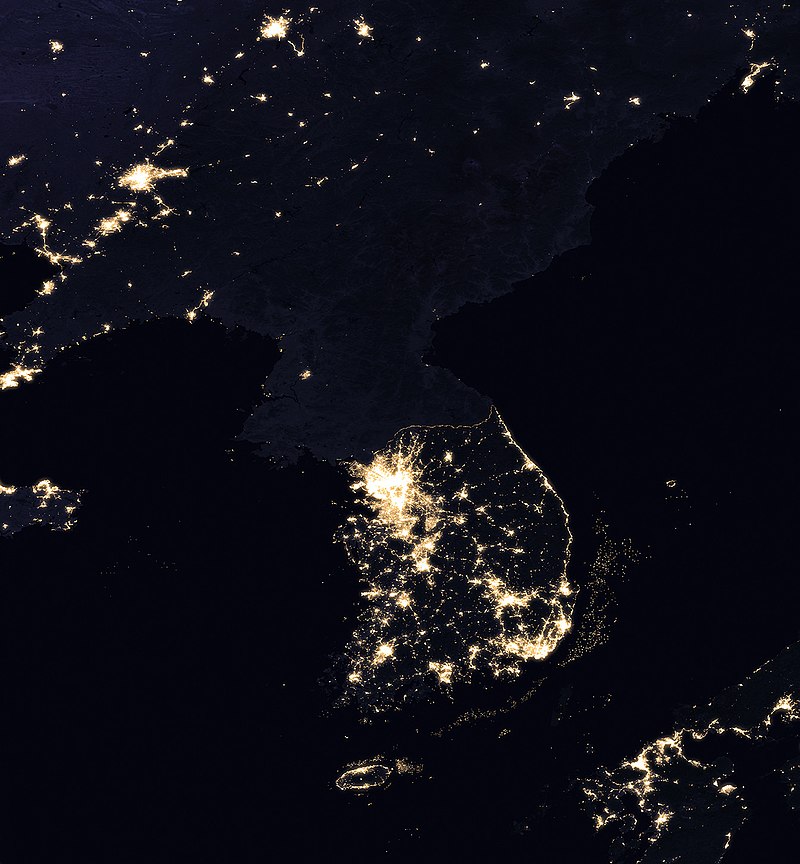
East Asia, 1945-present
|
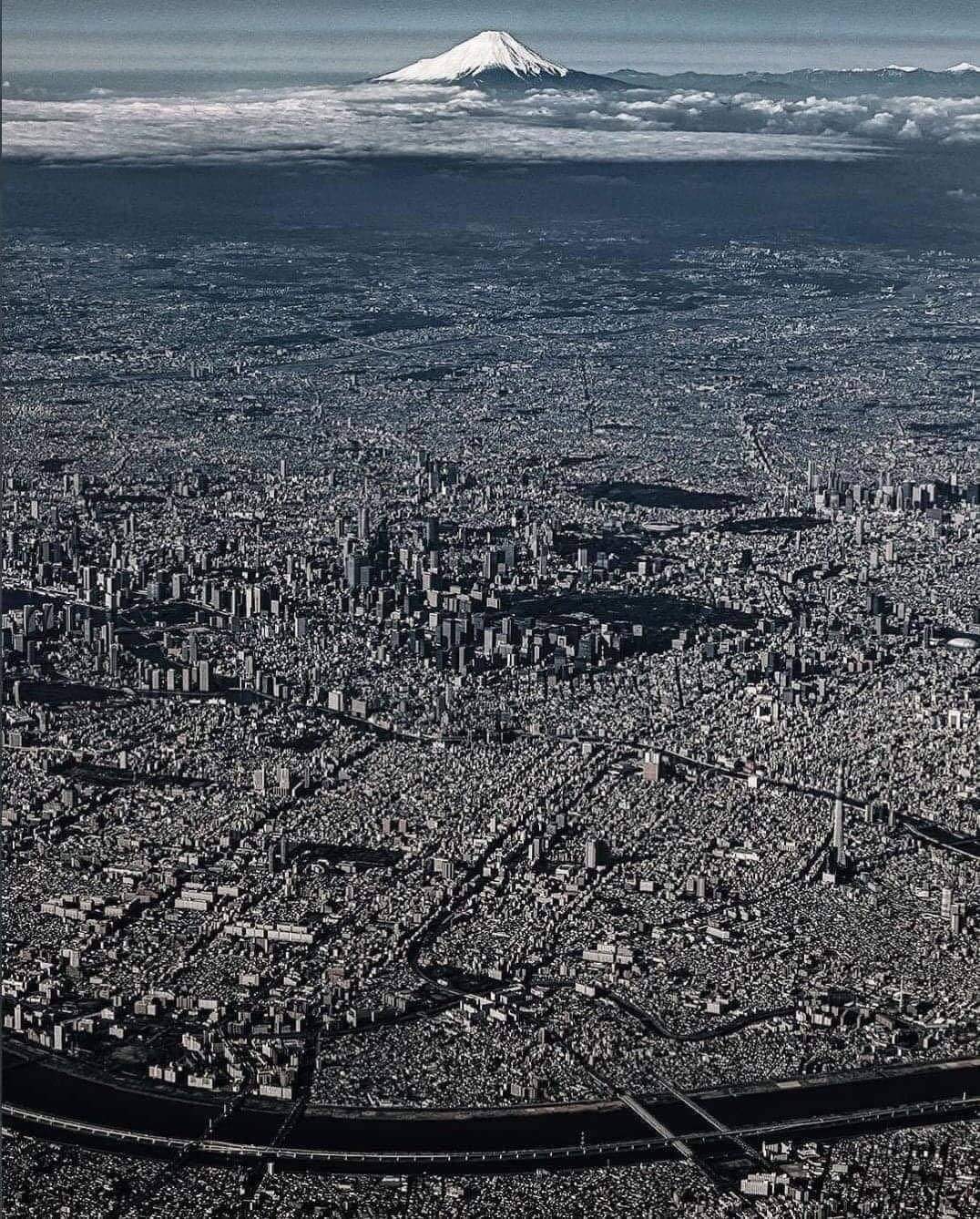
After World War II, Tokyo was completely rebuilt. Today, with a population of around 37 million people, it is the most populated urban area on Earth. Japan experienced tremendous growth during the Japanese economic miracle from 1945 to 1991.
|
|
East Asia, 1945-present (comprehensive)
East Asia, 1945-present (abridged)
|
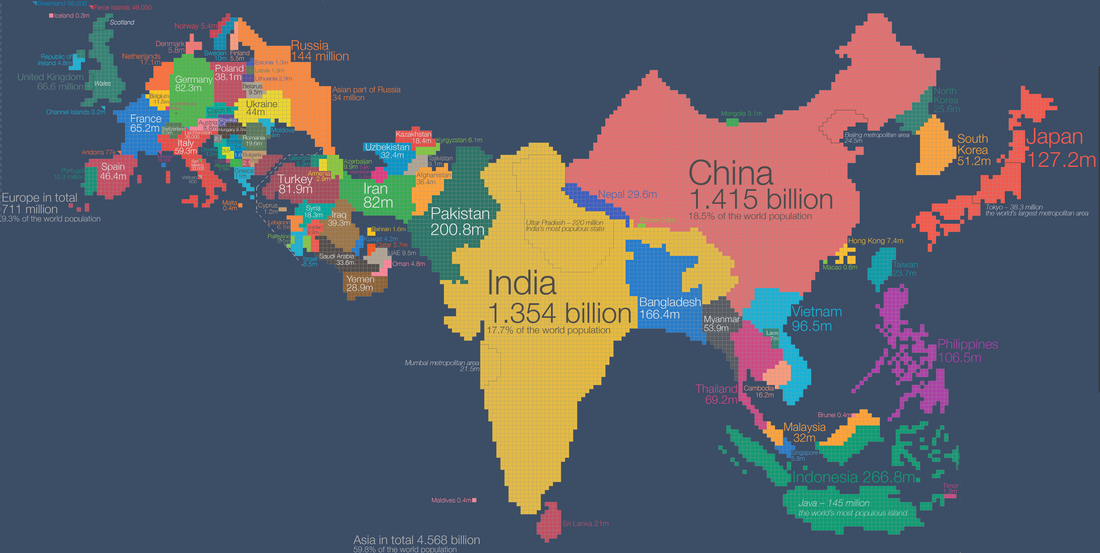
Together China and India are home to more than 1/3 of the human population.
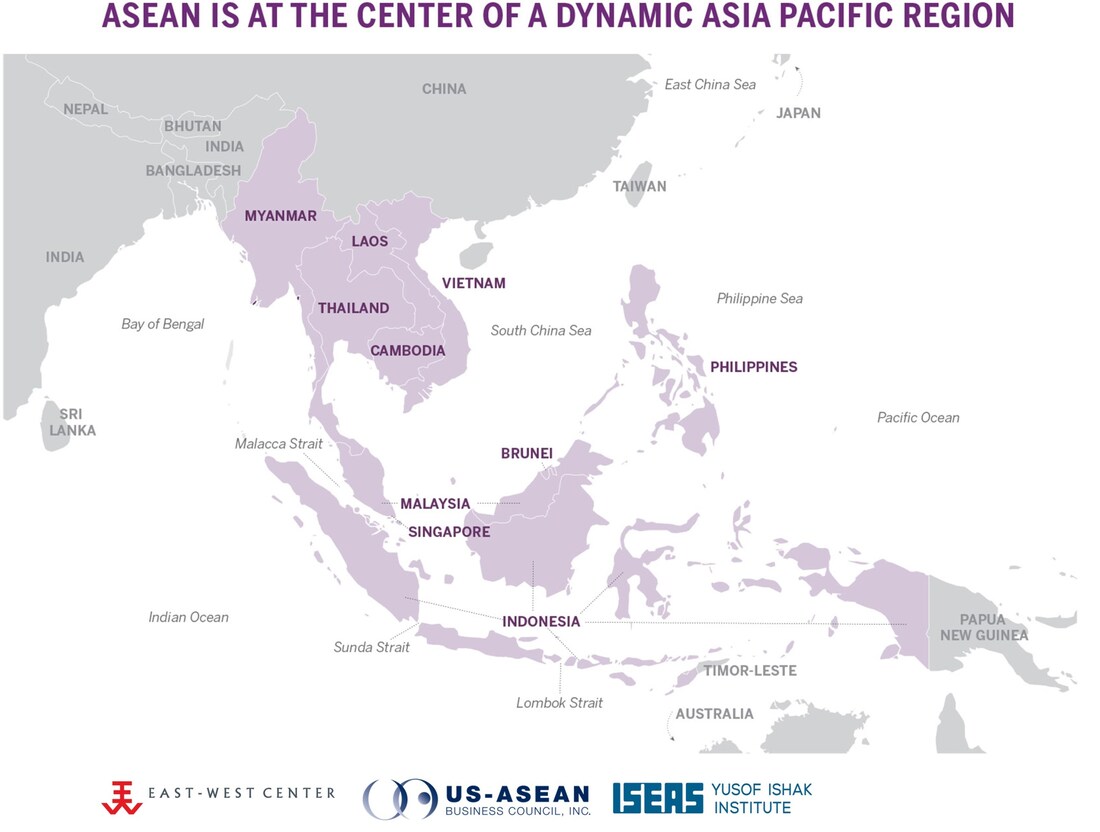
South Asia, 1945-present
|
South Asia, 1945-present (comprehensive)
South Asia, 1945-present (abridged)
|
The Middle East, 1945-present
|
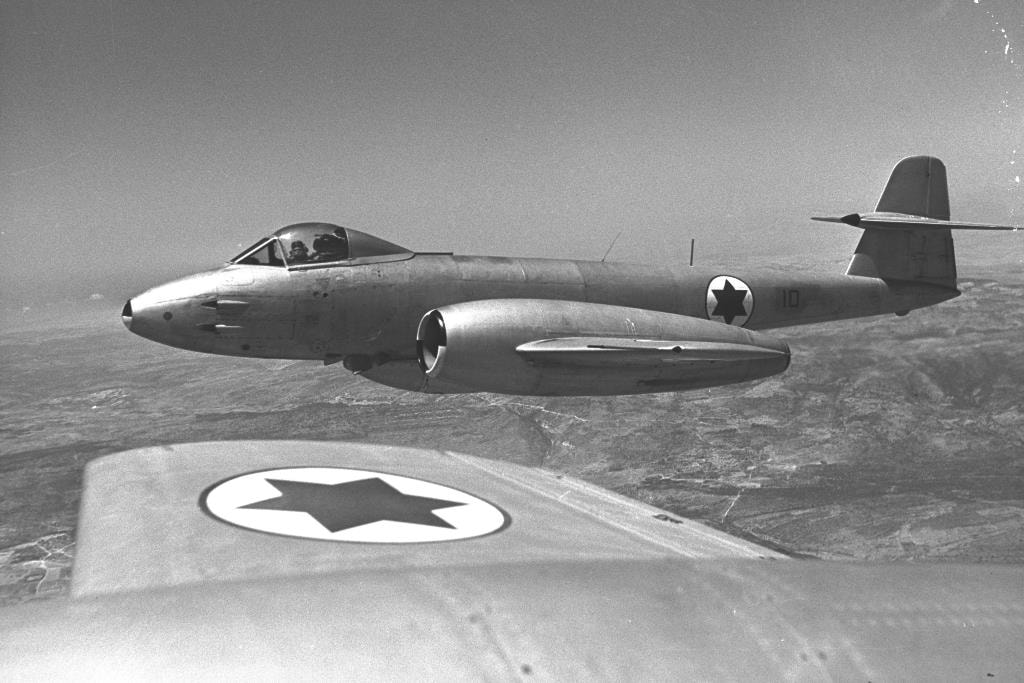
Israeli jets during the 1956 Suez Crisis. Israel fought neighboring Arab states in 1948, 1956, 1967, and 1973. Arab terrorist campaigns have continued against Israel since the 1979 Camp David Accords with Egypt.
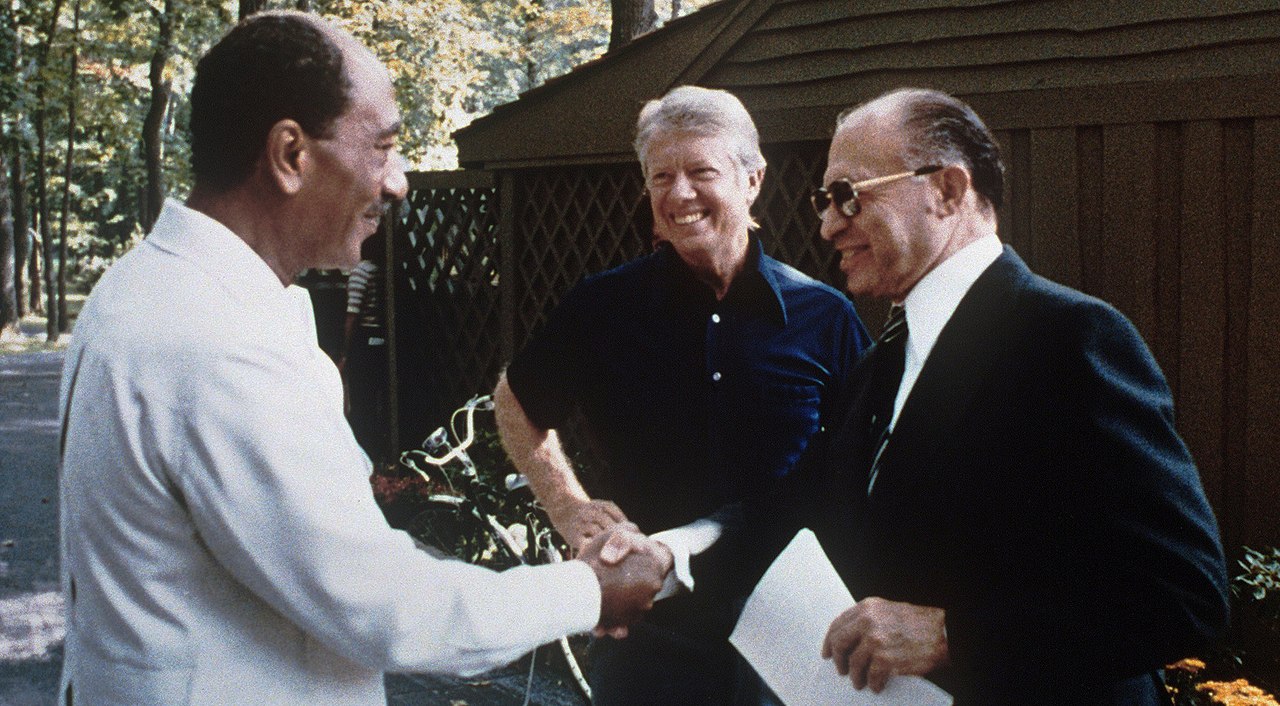
American president Jimmy Carter mediated the Camp David Accords signed by Egyptian president Anwar Sadat and Israeli prime minister Menachem Begin.
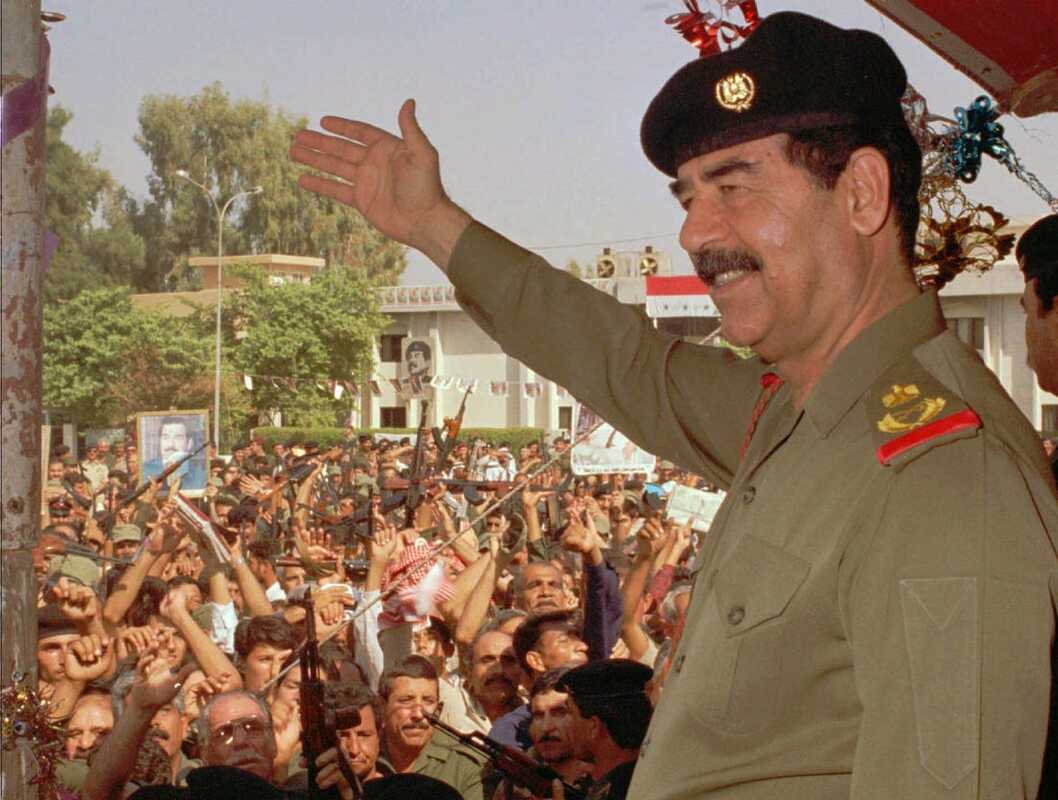
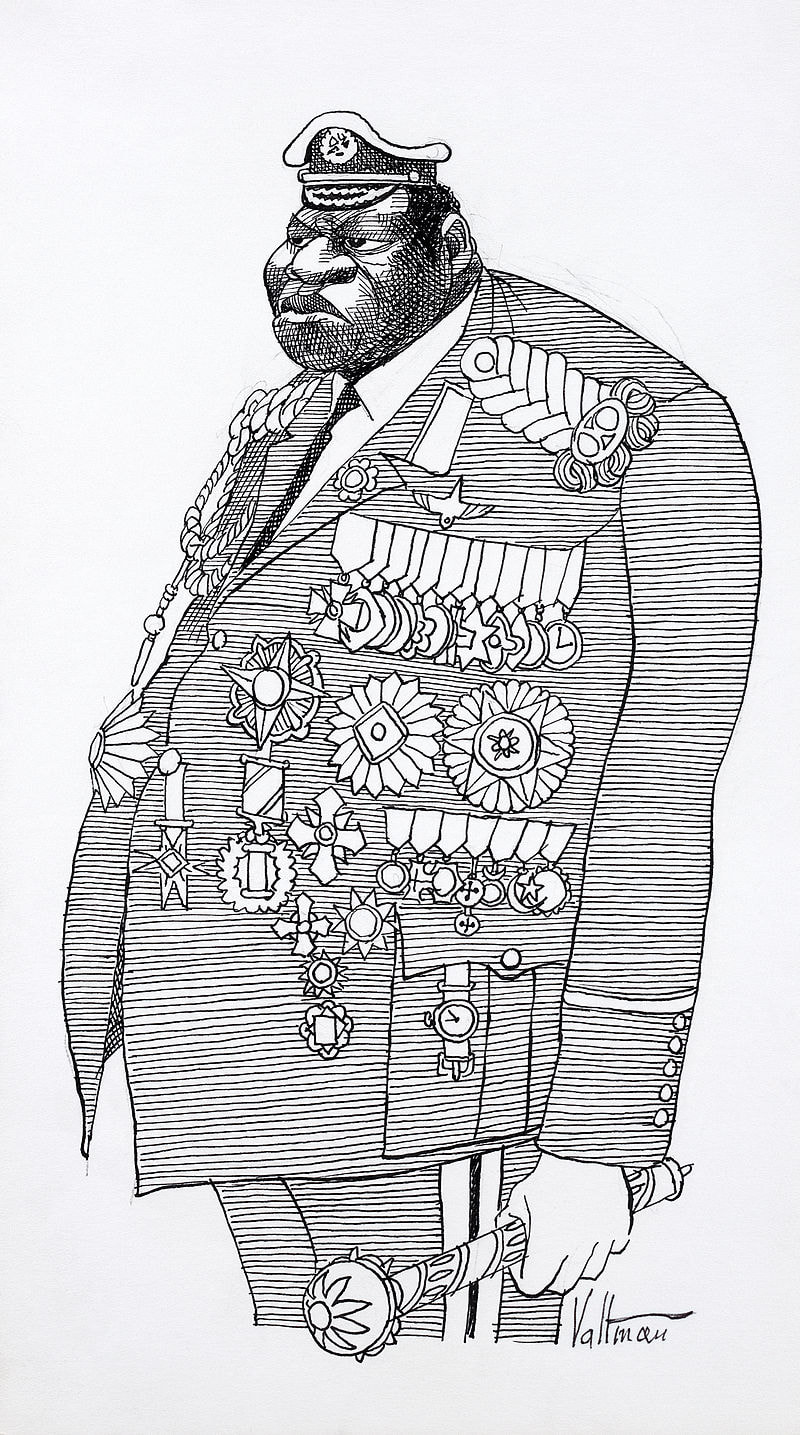
Iraqi dictator Saddam Hussein in 1995
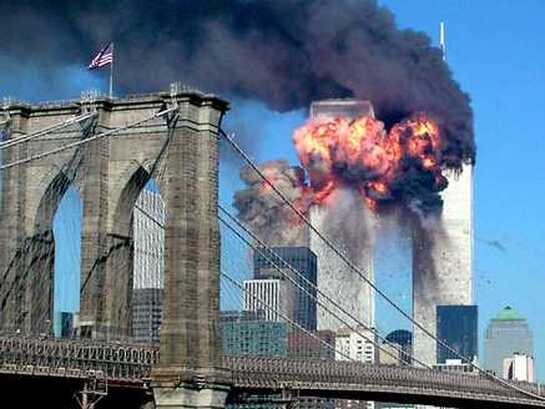
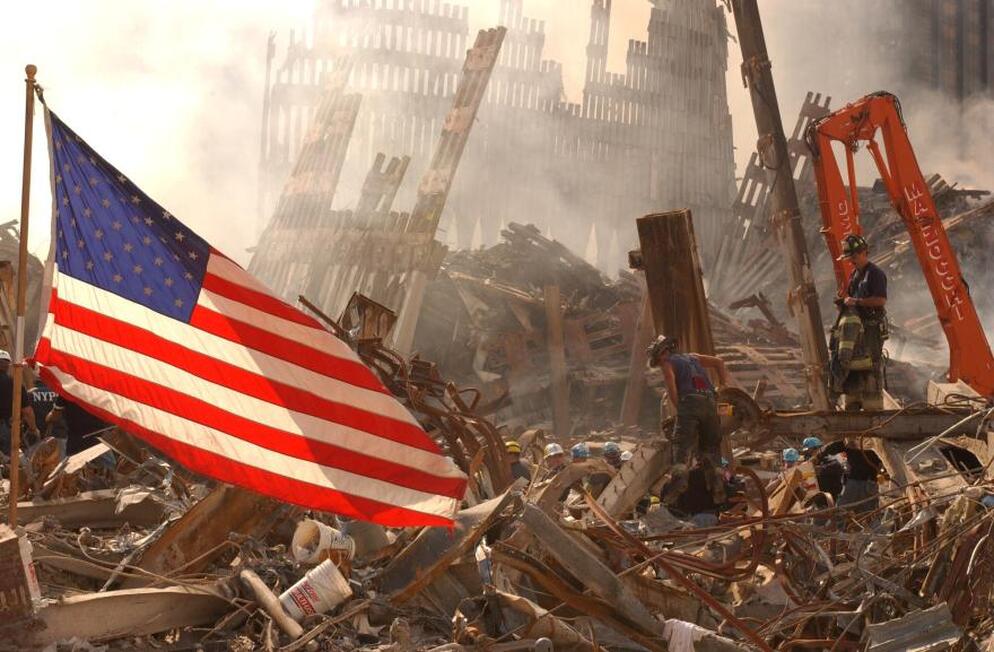
The 9/11 terrorist attacks carried out by al-Qaeda led to the United States' Global War on Terror.
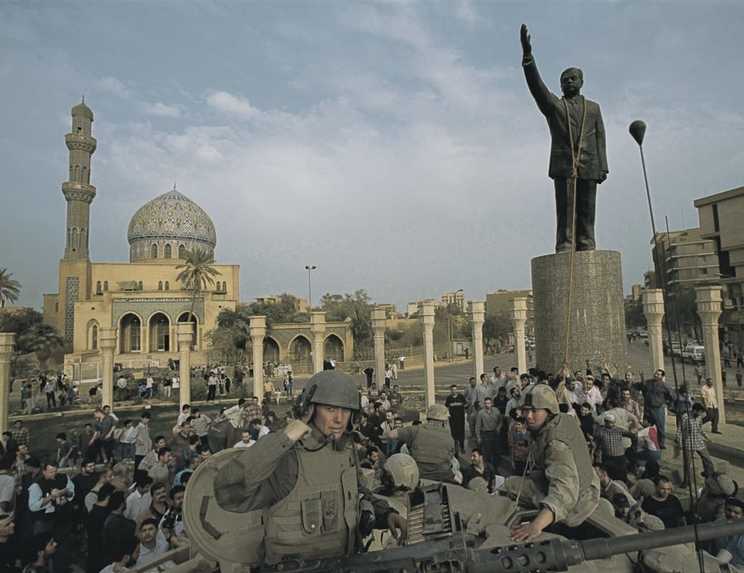
US marines toppling the statue of Saddam Hussein in Baghdad, Iraq (2003) shortly after the start of the Iraq War. Instability in Iraq led to the rise of ISIS.
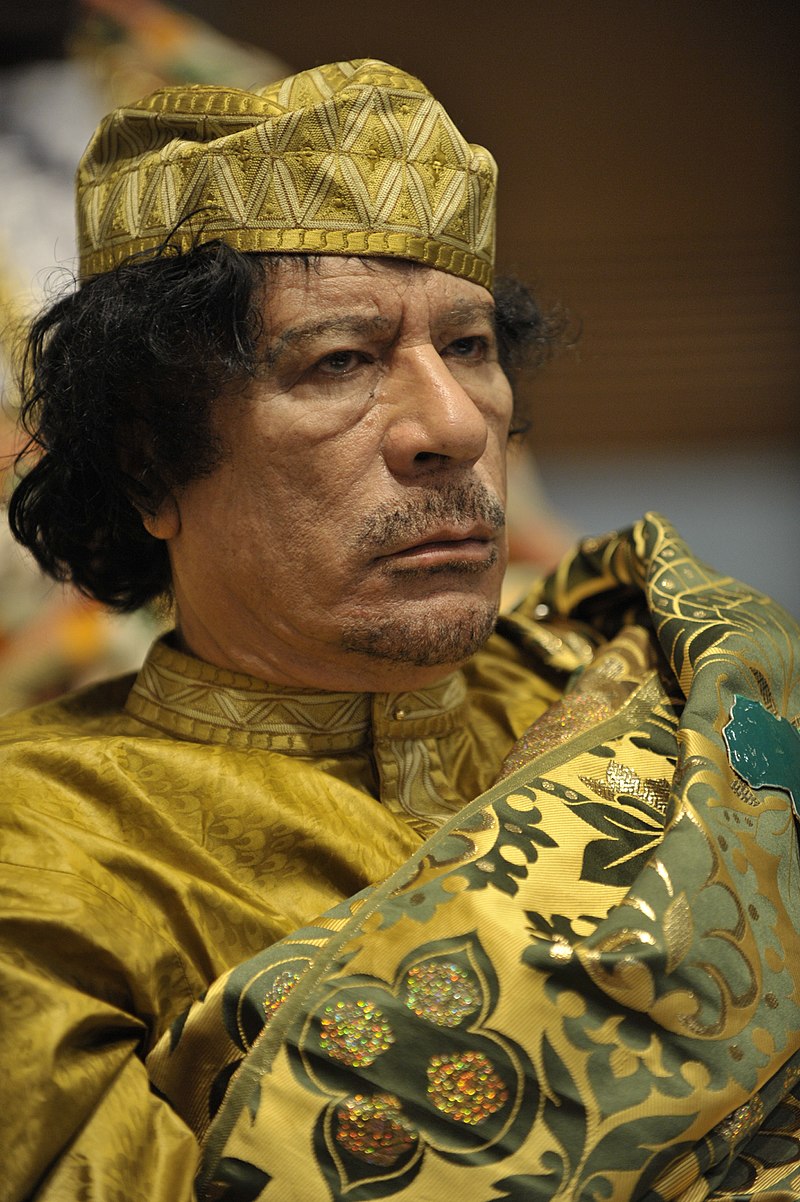
Long-term Libyan dictator Muammar Gaddafi (1969-2011) was overthrown during the pro-democracy Arab Spring revolts.
|
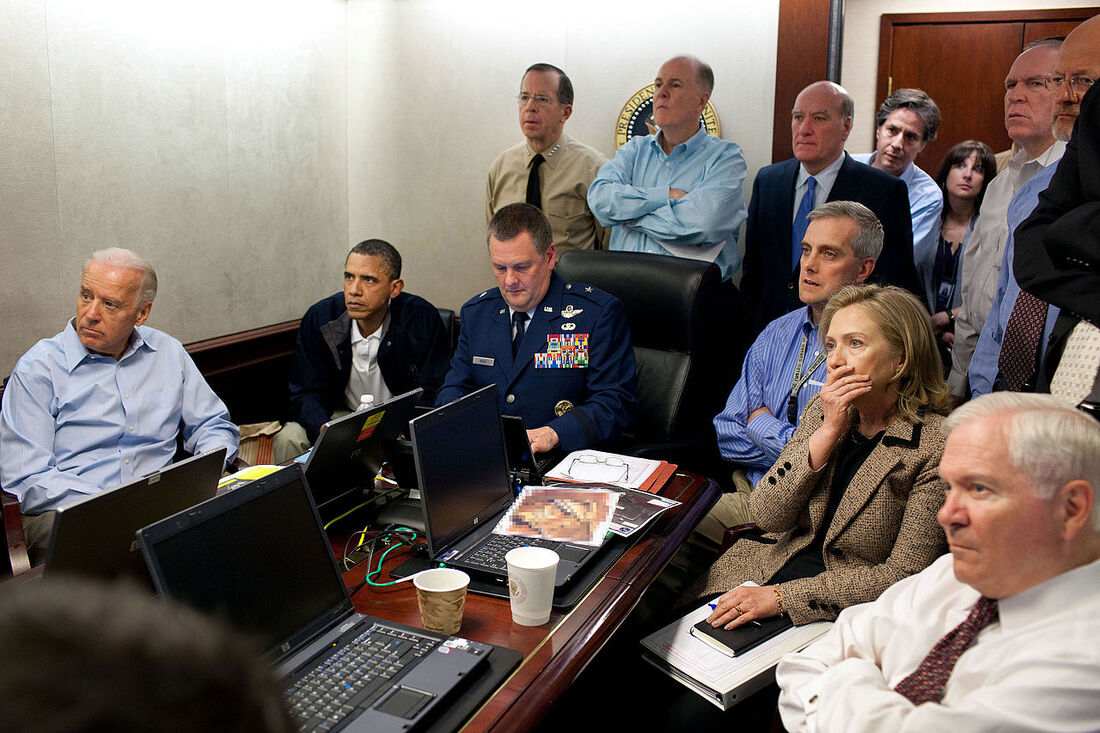
U.S. President Barack Obama, Vice President Joe Biden, and other members of the national security team watch updates in the White House Situation Room during the 2011 special forces mission that killed Osama bin Laden, the founder and leader of the al-Qaeda terror network.
|
|
|
|
|
The Middle East, 1945-present (comprehensive)
The Middle East, 1945-present (abridged)
|
Africa, 1945-present
|
Gold Coast became the first British African colony to win independence in 1957. Under the leadership of Kwame Nkrumah, the new state called itself Ghana after the medieval empire of that name.
Tshibumba Kanda-Matulu painted key moments from Congo’s brutal colonial past, the fight for independence and later struggles for power.
Nelson Mandela, leader of the African National Congress (ANC) party worked with F.W. de Klerk to dismantle the apartheid system. He became the first black prime minister of South Africa in 1994 after the ANC won the first genuinely democratic elections in the country's history.
|
|
|
Africa, 1945-present (comprehensive)
Africa, 1945-present (abridged)
|
Latin America, 1945-present
|
The beautiful Evita Peron, wife of Argentine president Juan Peron, campaigned for women and the poor during her time as First Lady of Argentina (1946-1952). Beloved by the masses, three million attended her funeral when she died of cancer at age 33.
Left-wing movement such as the Zapatistas, Sandinistas, FARC, and Shining Path have been suppressed by U.S.-backed counterrevolutionaries such as the Contras and right-wing dictators including Augusto Pinochet.
Images of Argentine communist revolutionary Ernesto "Che" Guevara, a key actor in the Cuban Revolution, are prolific symbols of socialist revolution throughout Latin America.
PEMEX, PDVSA, and Petrobras, the state-owned oil companies of Mexico, Venezuela, and Brazil, are the three largest corporations in Latin America.
Brasilia was built between 1956 and 1960 to be the new federal capital of Brazil. It was designed by modernist architect Lúcio Costa.
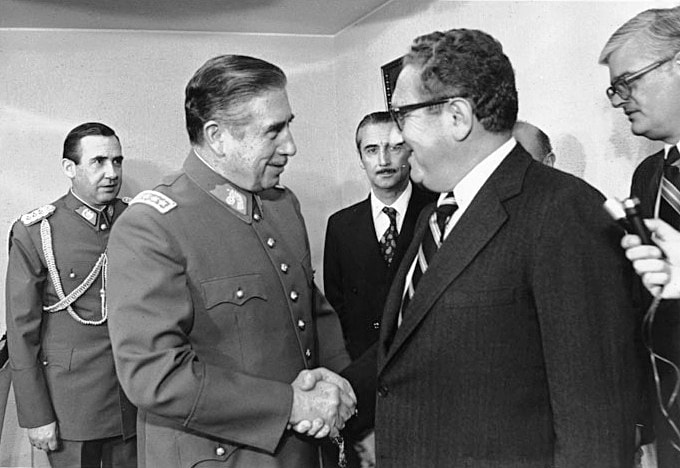
Chilean right-wing military dictator meeting Augusto Pinochet with American Secretary of State Henry Kissinger. Pinochet waged a Dirty War against socialists and communists with heavy U.S. assistance through Operation Condor.
|
|
|
Latin America, 1945-present (comprehensive)
Latin America, 1945-present (abridged)
|
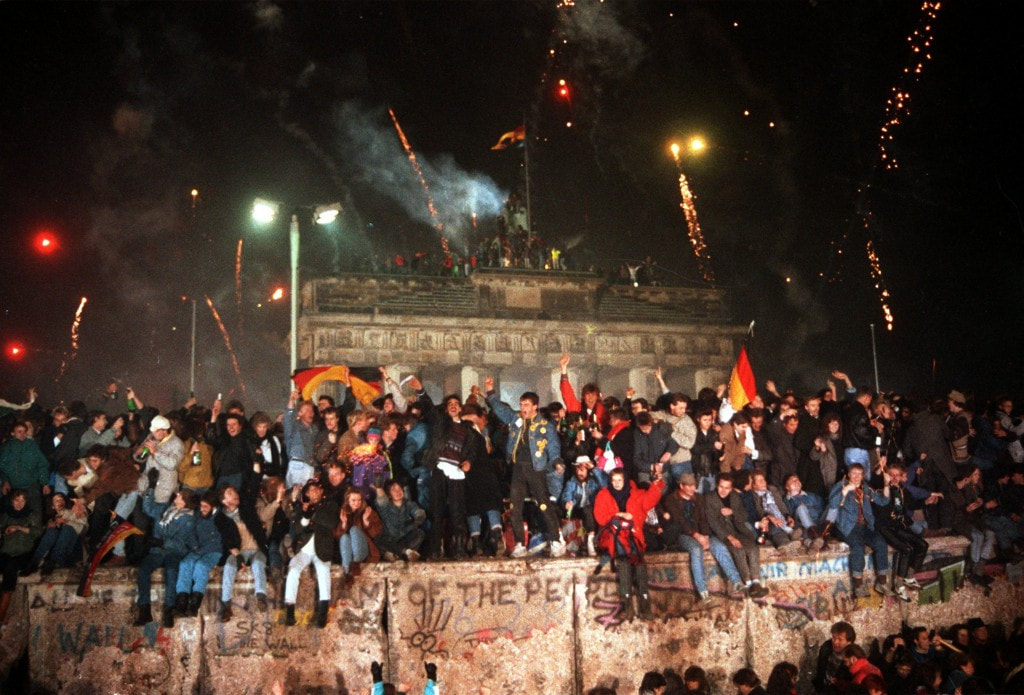
Fall of Communism
|
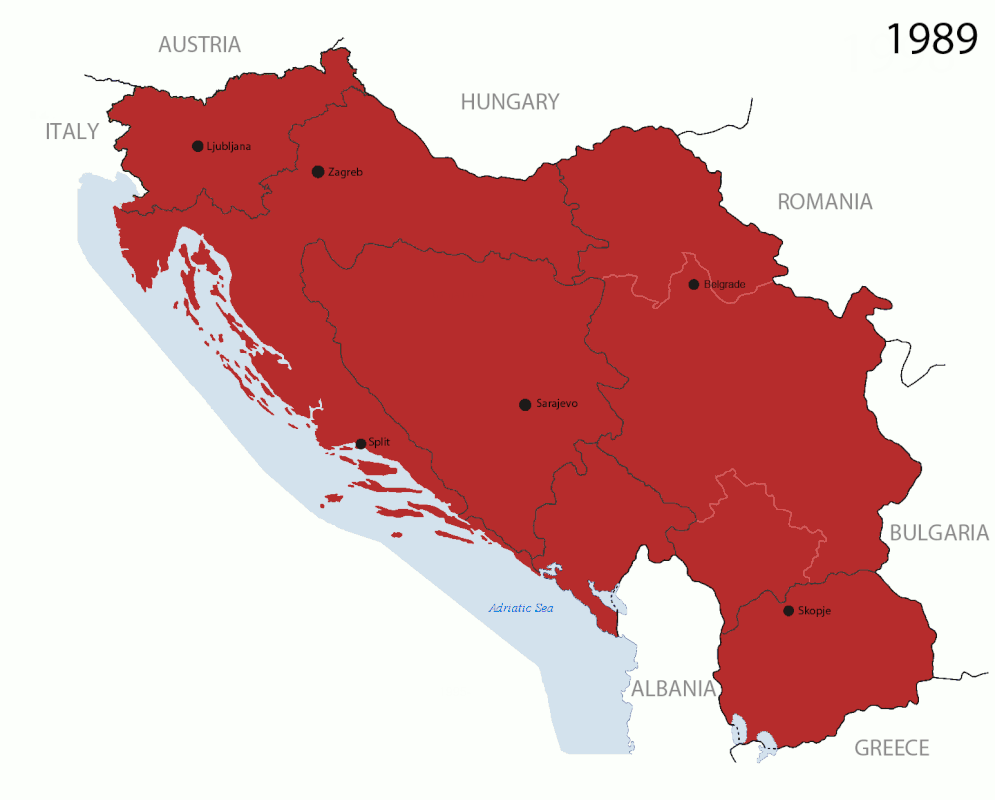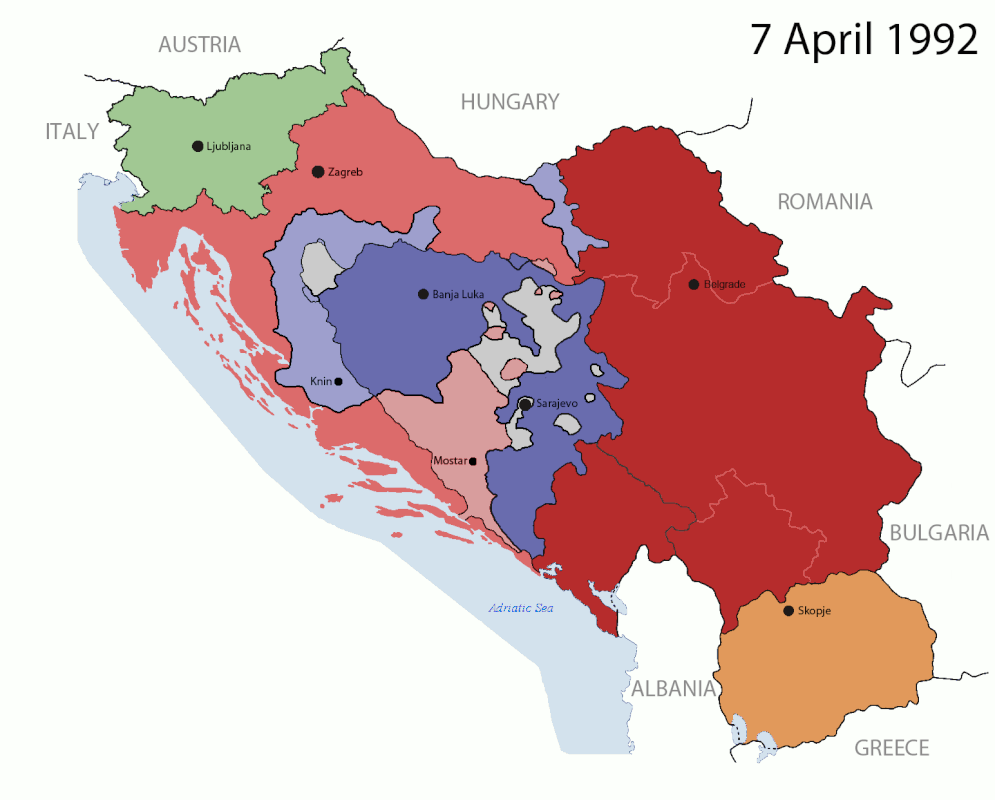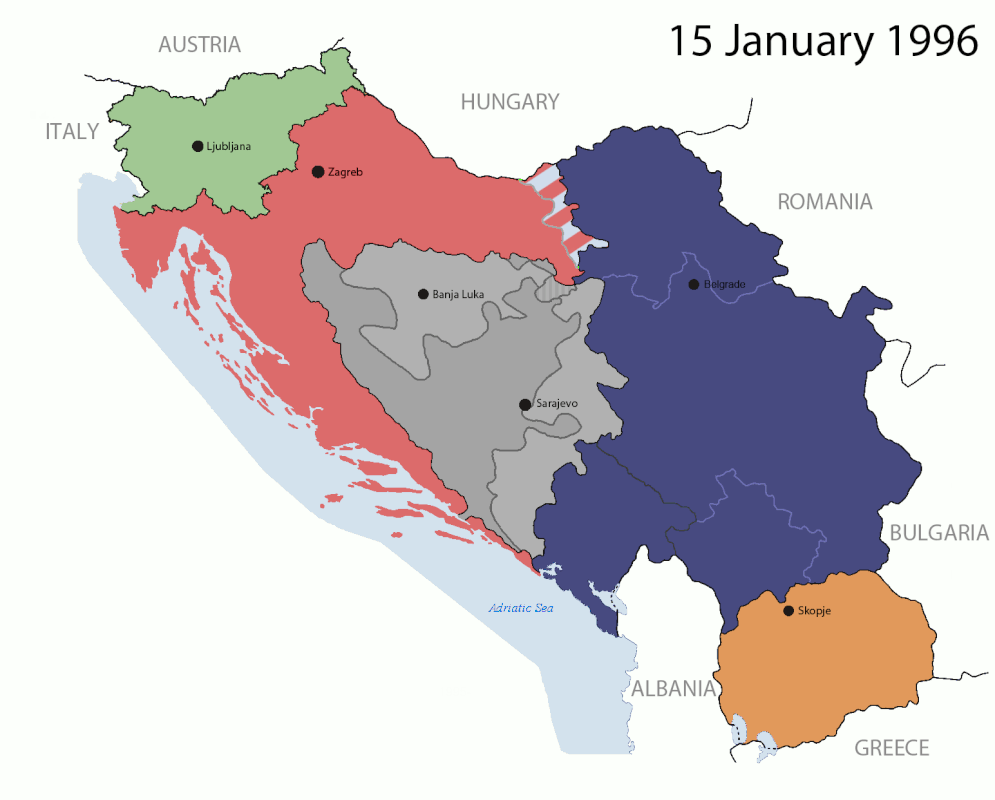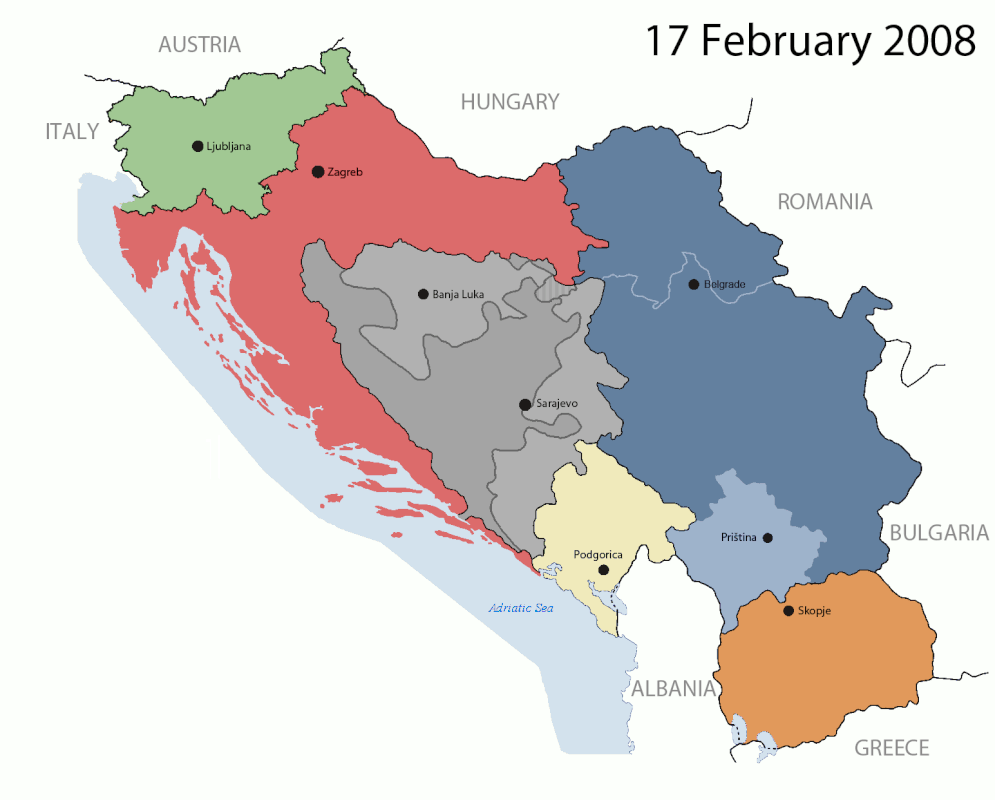
The 1991-2008 breakup of Yugoslavia led to the genocidal Yugoslav Wars.
|
|
Fall of Communism (comprehensive)
Fall of Communism (abridged)
|
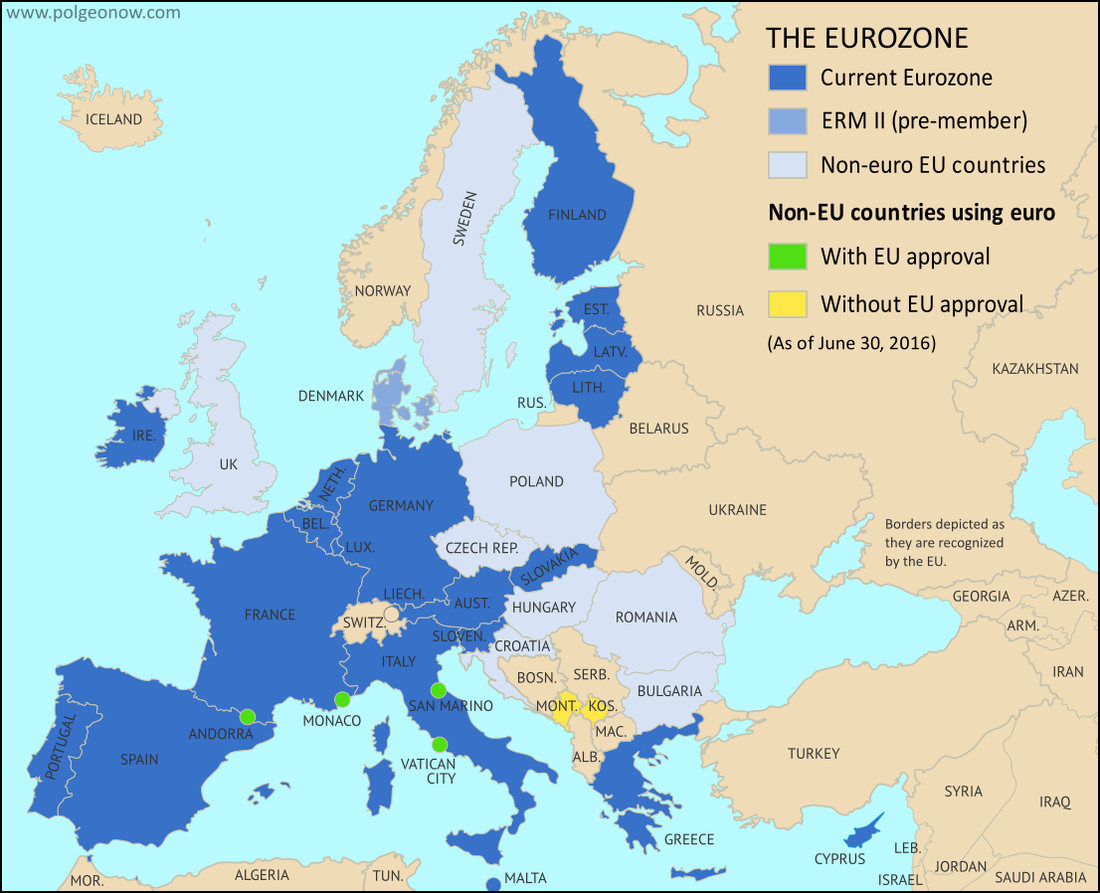
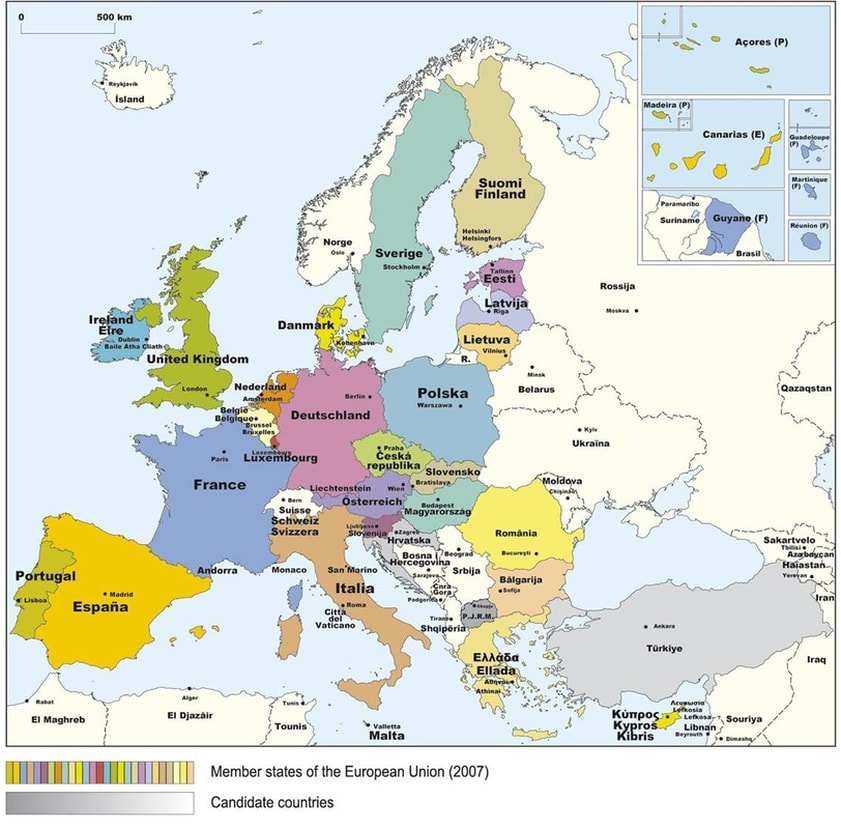
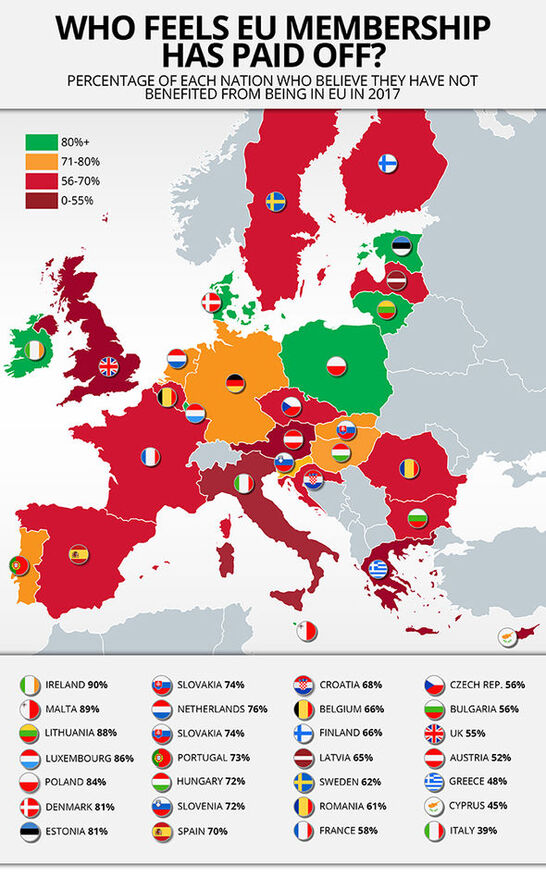
The European Union and Russia
|
Formed in the Cold War's wake in the 1992 Maastricht Treaty, falling British support for the European Union led to the 2016 Brexit referendum to leave the EU.
France's large Muslim population, largely descended from France's former North African colonies, has clashed with French police and with French nationalists who argue that Islamic values are contradictory to traditional French liberal and Christian values.
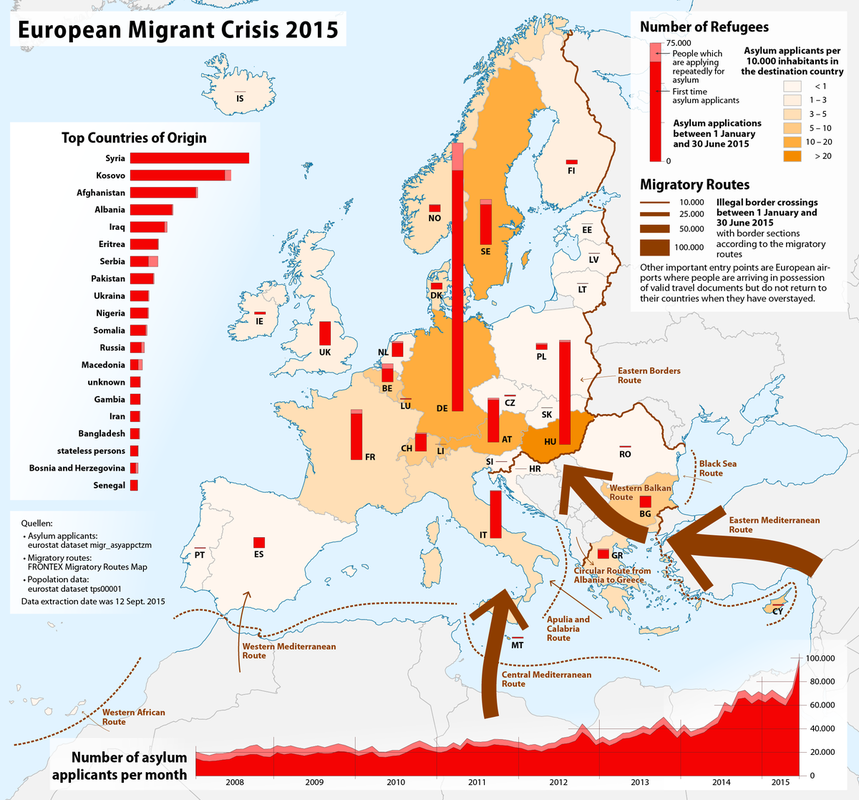
Conflicts in African and the Middle East led to a humanitarian disaster as a flood of immigrants crossed the Mediterranean into Europe during the 2015 Refugee Crisis.
|
In newly independent states after World War II, governments often took on a strong role in guiding economic life to promote development.
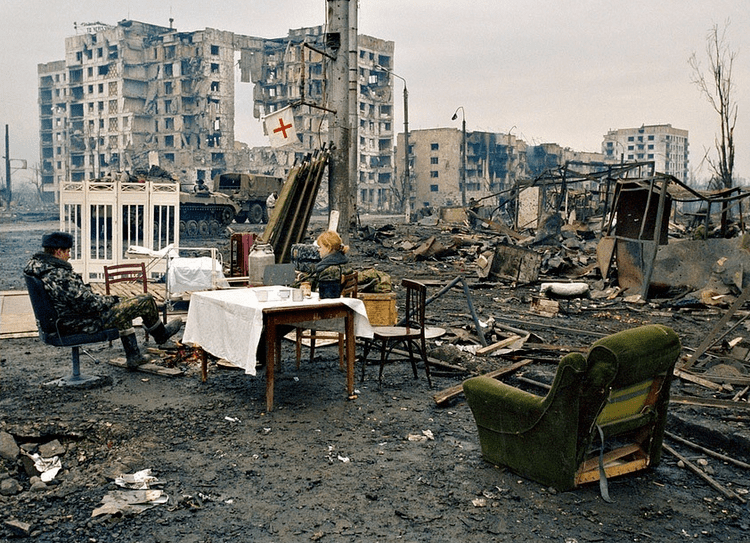
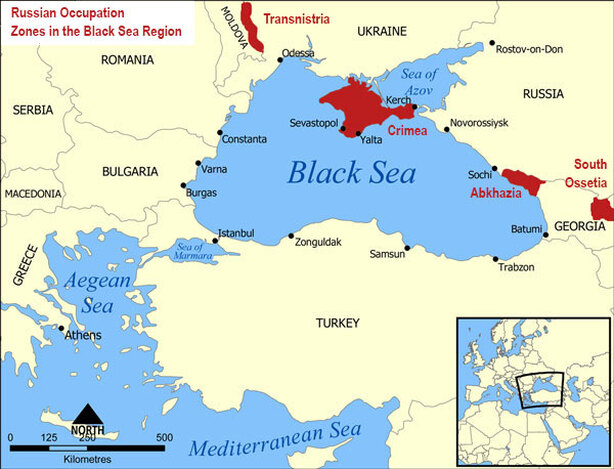
Russia destroyed most of Grozny, the capital of Chechnya, suppressing a Chechen independence movement in the 1990s-2000s.
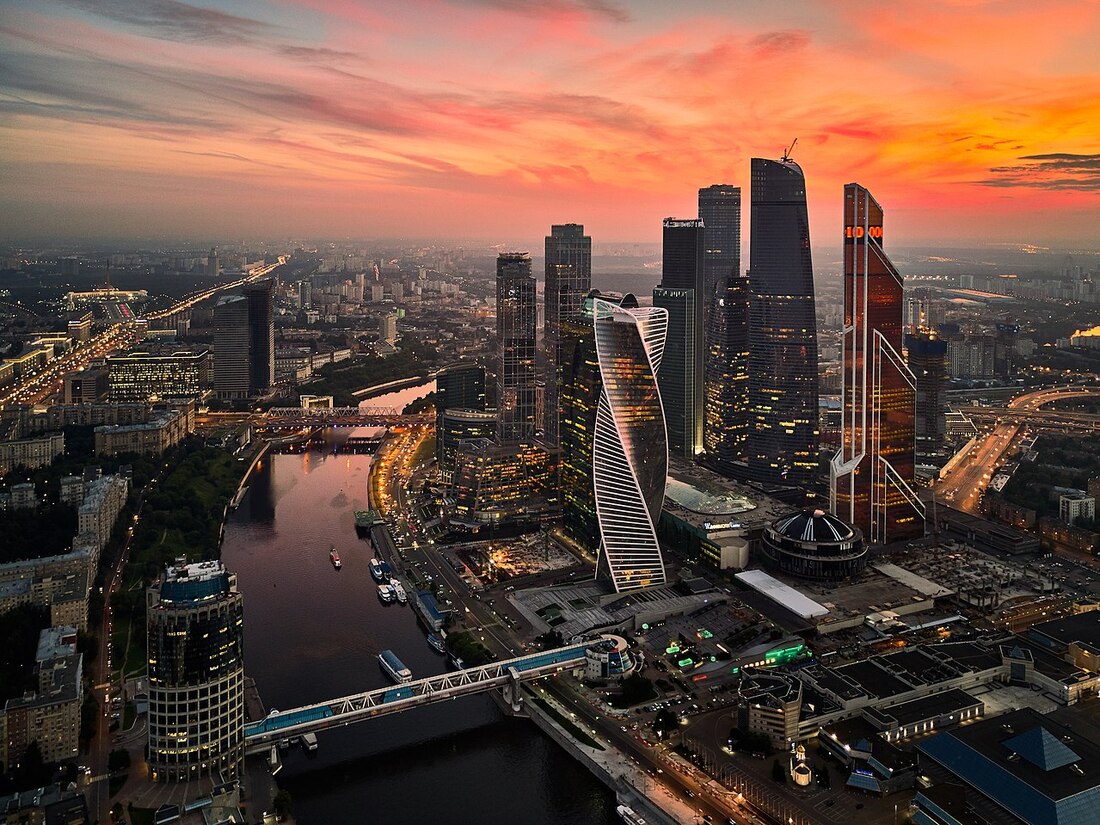
The still under construction Moscow International Business Center is home to $12 billion of newly constructed skyscrapers. However, much of the office space sits empty.
|
|
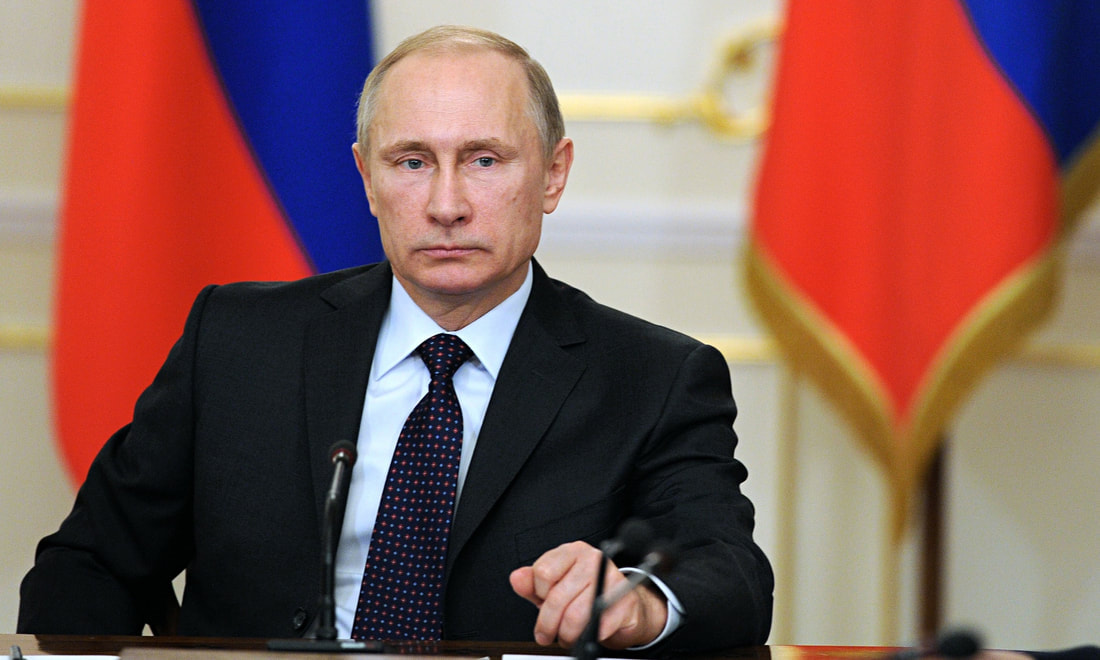
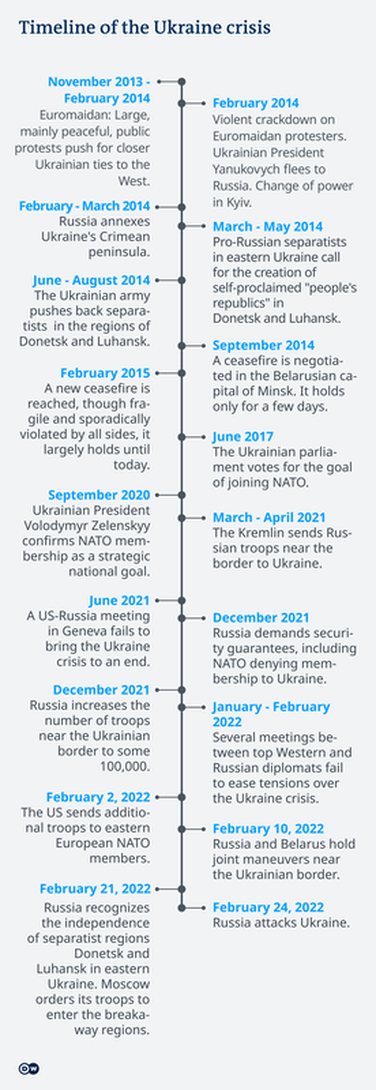
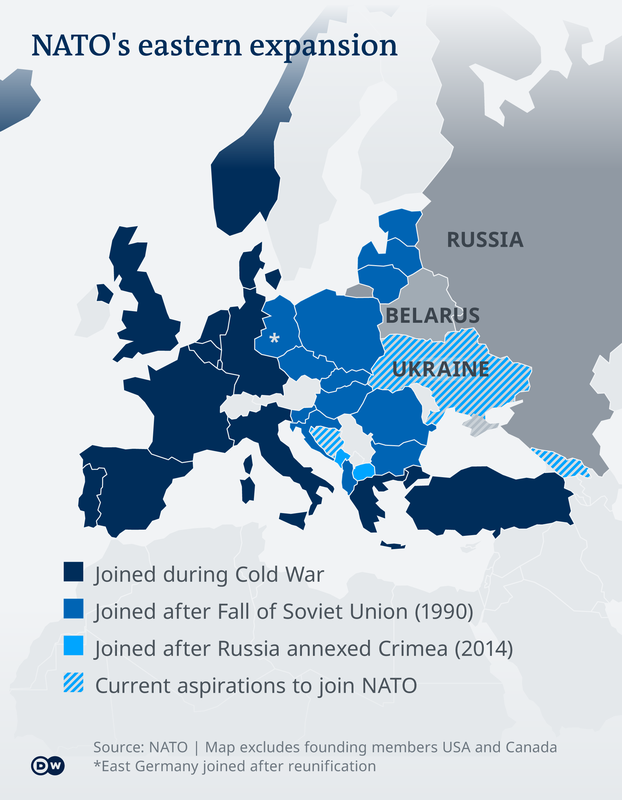
Vladimir Putin has overseen a Russian resurgence with military expansion in the brief Georgian War, annexation of Crimea, and involvement in the Syrian Civil War.
|
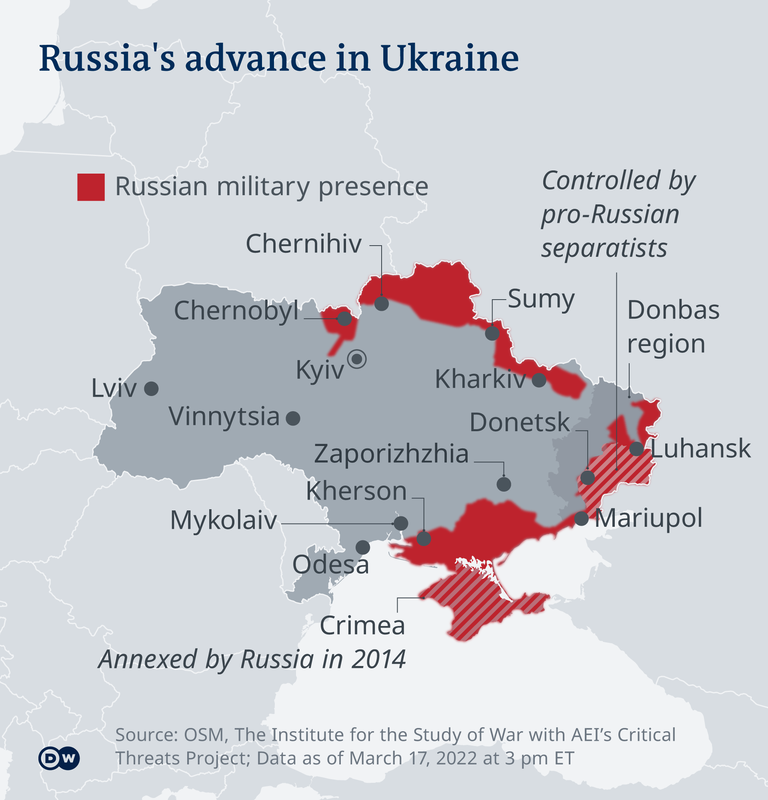
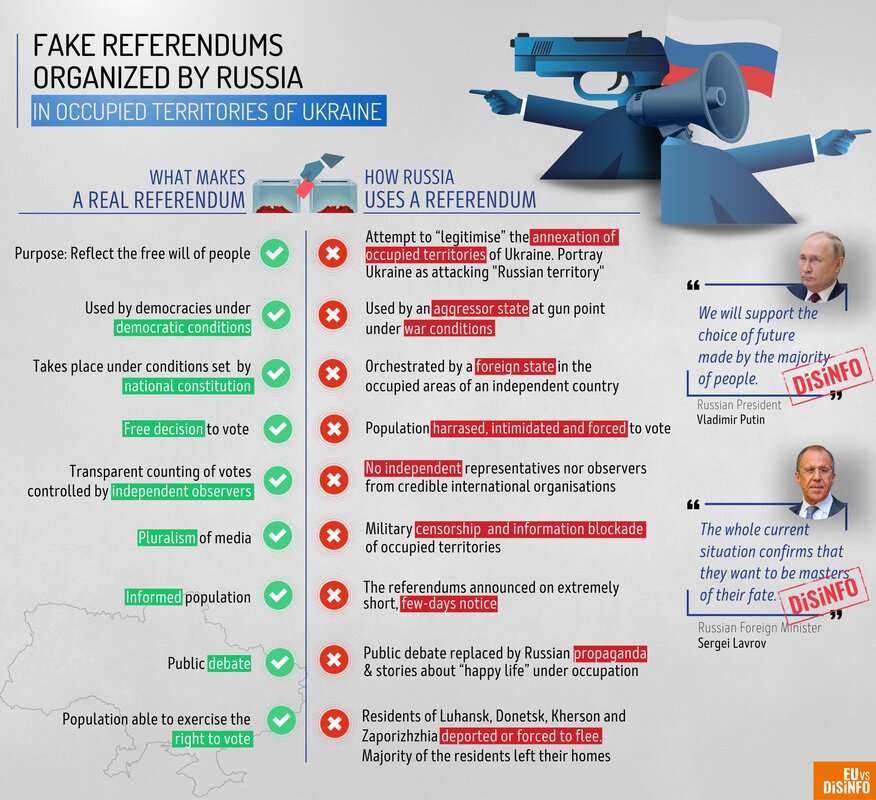
In February 2022, Vladimir Putin ordered a Russian invasion of Ukraine that was opposed by Ukrainian president Volodymyr Zelenskyy.
|
The European Union and Russia (comprehensive)
The European Union and Russia (abridged)
|
The Post-Cold War United States
|
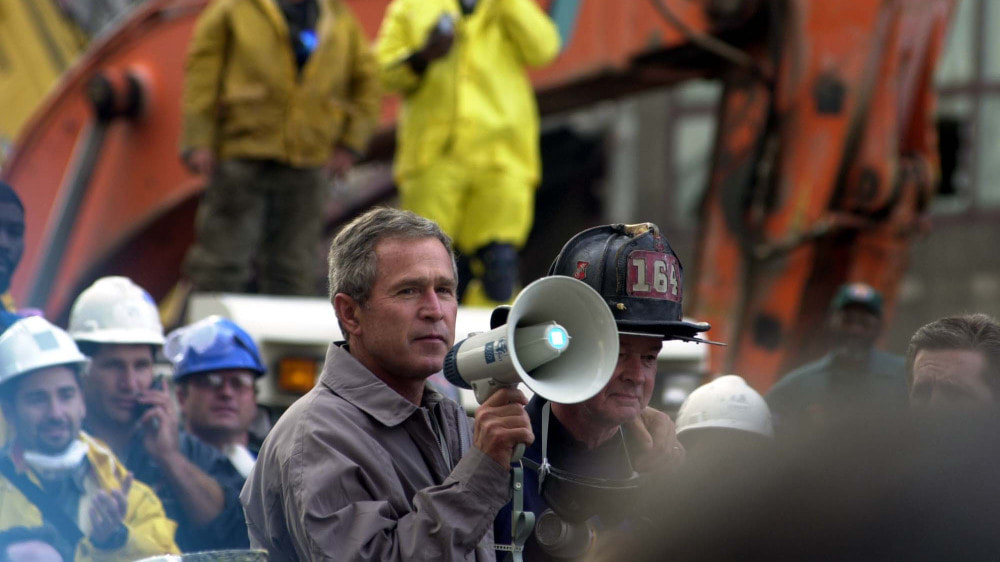
President George W. Bush addresses rescue workers in New York City after the 9/11 terrorist attacks.
|
|
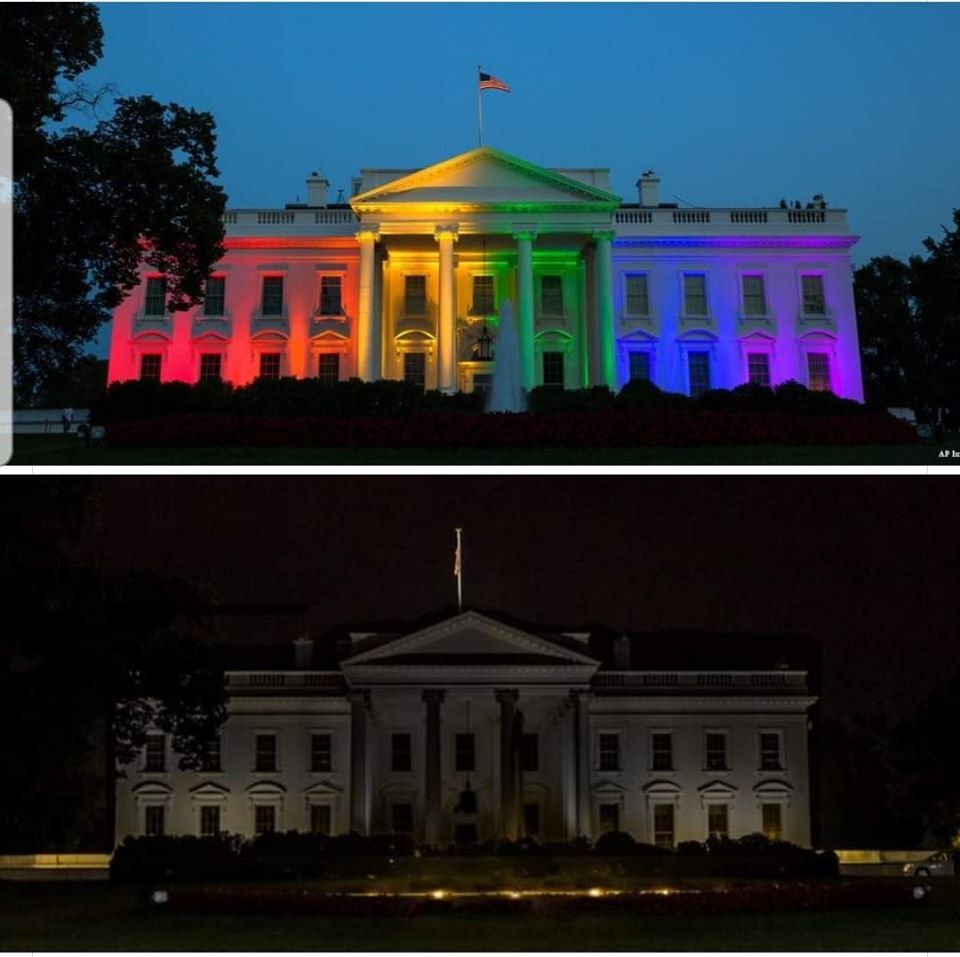
Above: The White House was lit with rainbow colors after the Obergefell v. Hodges Supreme Court decision recognizing constitutionality of same-sex marriages.
Below: The White House went dark on May 31, 2020 as President Trump sheltered in a bunker during Black Lives Matter protests against police murder of George Floyd. |
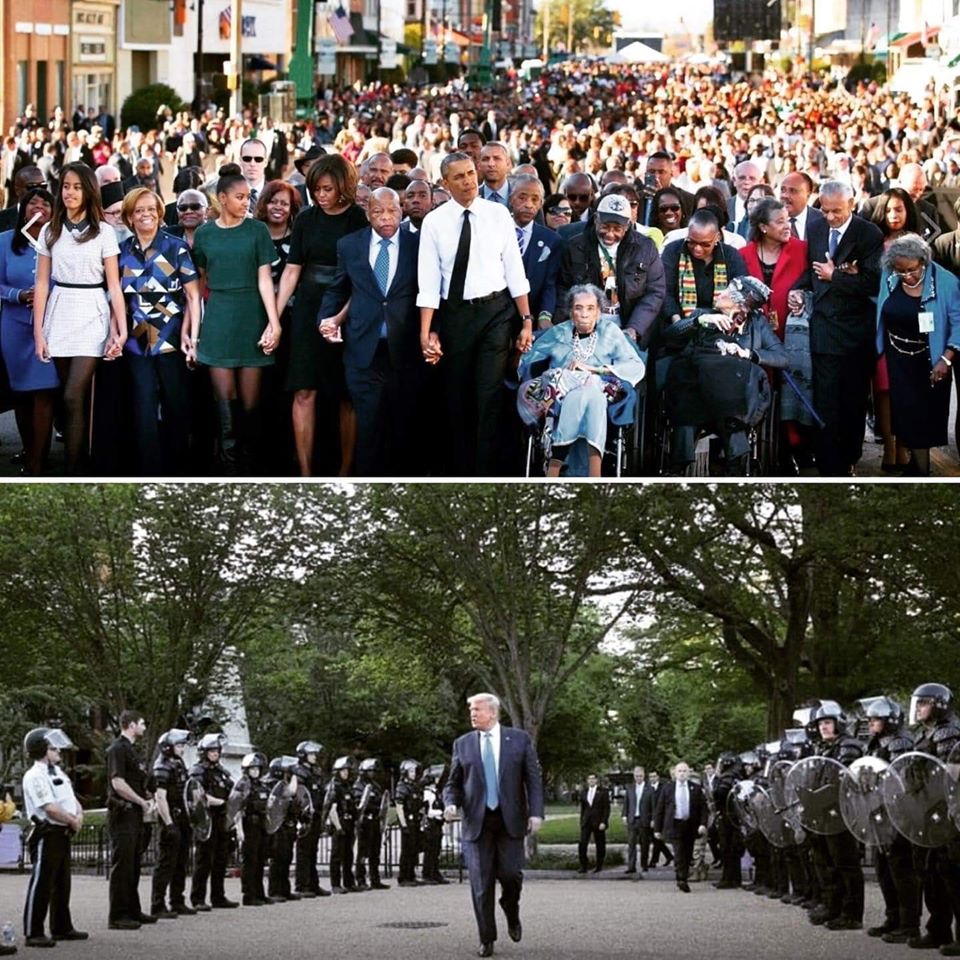
Above: Barack Obama, the first African American president, ringed by citizens during the 50th anniversary of the Selma-to-Montgomery marches which led to passage of the 1965 Voting Rights Act.
Below: President Donald J. Trump flanked by militarized riot police during a heavily-criticized photo op on June 1, 2020. |
|
Acts of terror committed by right-wing extremists have been a grave threat to American society.
|
The development of ideas, beliefs, and religions illustrates how groups in society view themselves, and the interactions of societies and their beliefs often have political, social, and cultural implications.
|
|
The Post-Cold War United States (comprehensive)
The Post-Cold War United States (abridged)
|
Global Separatist Movements
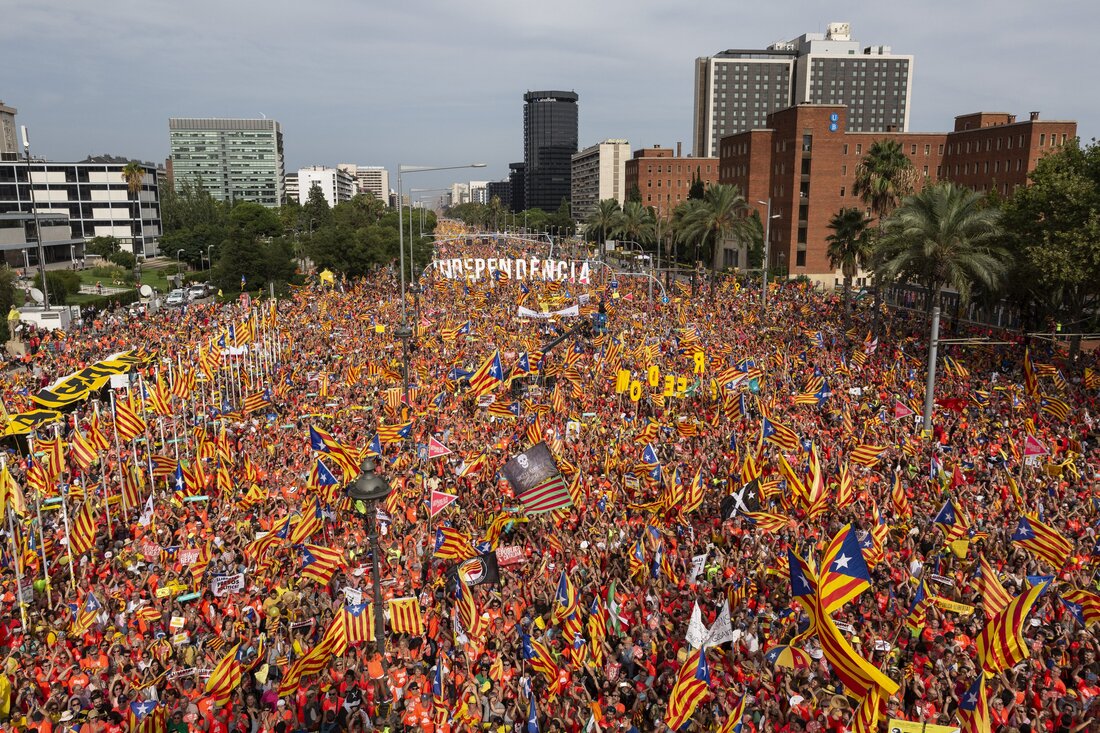
rally for Catalan independence from Spain held in Barcelona in 2012
|
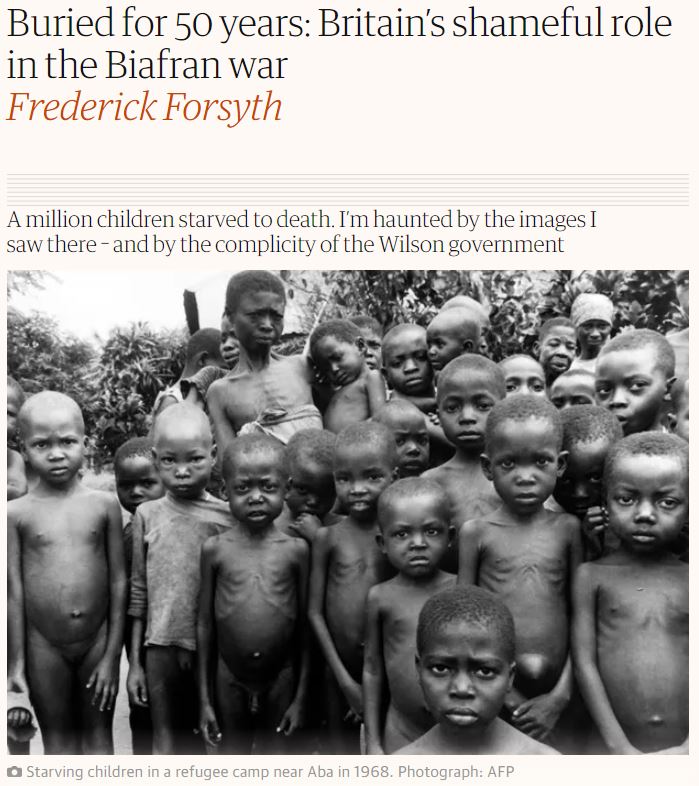
The Nigerian Civil War was fought to prevent Biafran independence.
|
Regional, religious, and ethnic movements challenged colonial rule and inherited imperial boundaries. Some of these movements advocated for autonomy.
|
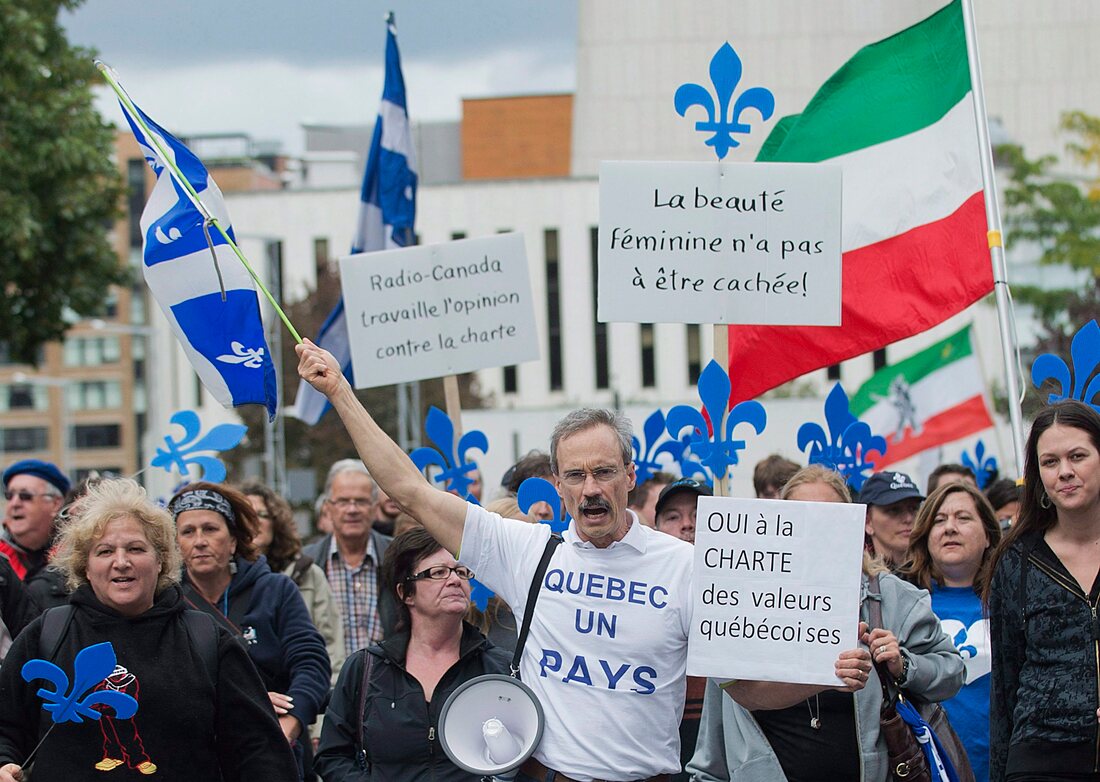
Many French-speaking Canadians seek independence for Quebec. A 1995 independence referendum was narrowly defeated with 49.42% in favor of independence and 50.58% against.
|
Global Separatist Movements (comprehensive)
Global Separatist Movements (abridged)
|