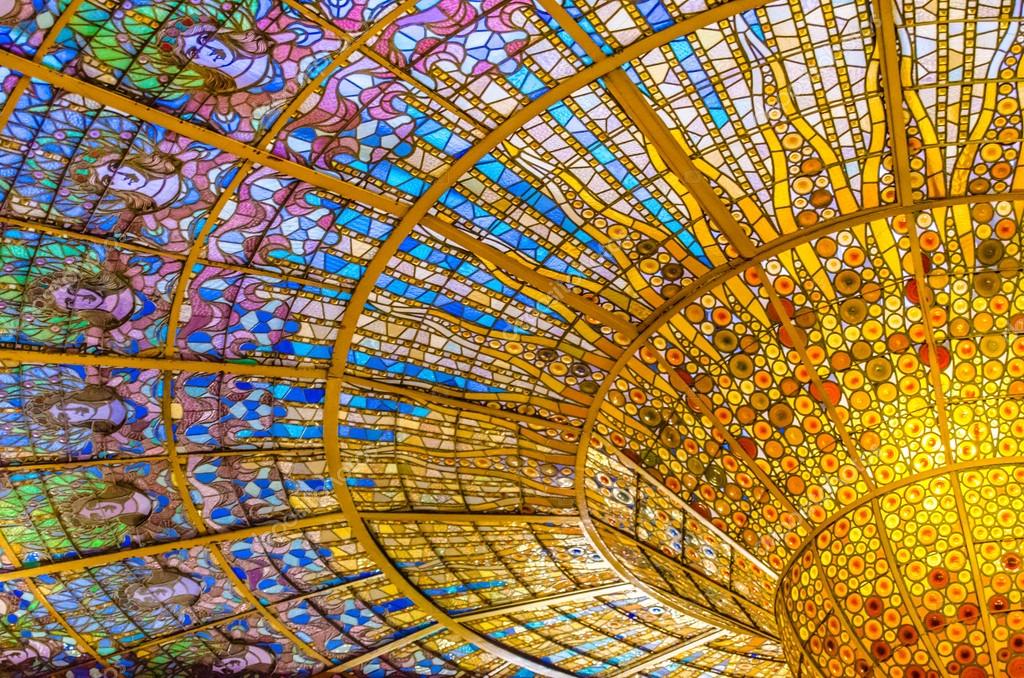
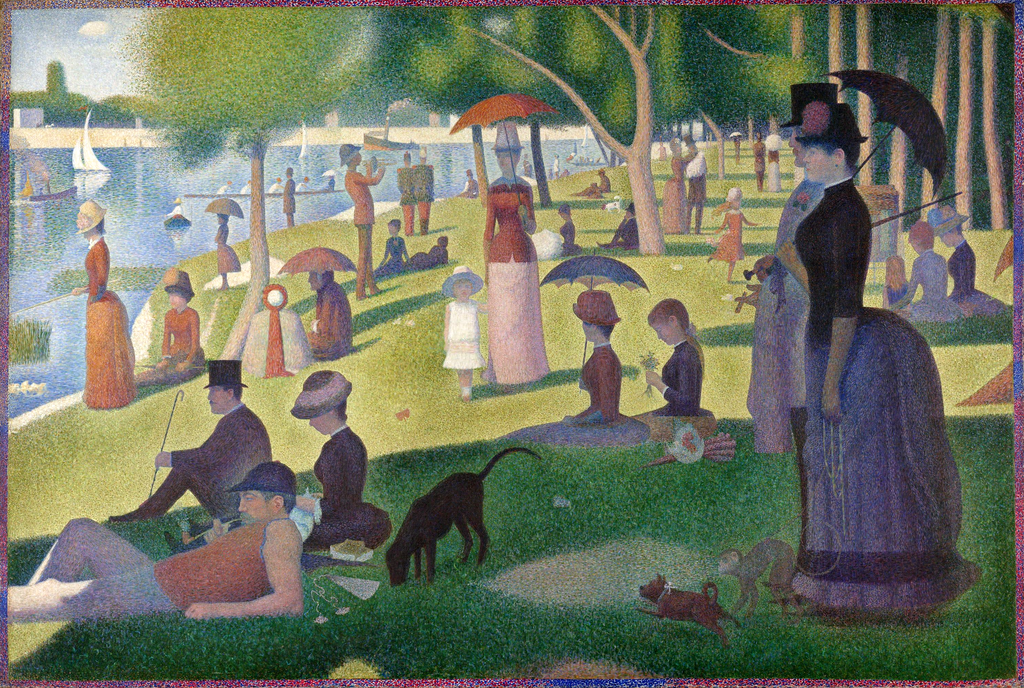stained glass skylight at the Palau de la Música Catalana, Barcelona, Spain
Many writers saw humans as governed by spontaneous, irrational forces and believed that intuition and will were as important as reason and science in the search for truth.
Modernity,
c. 1815-1914 CE
Contents
A. Modern Art
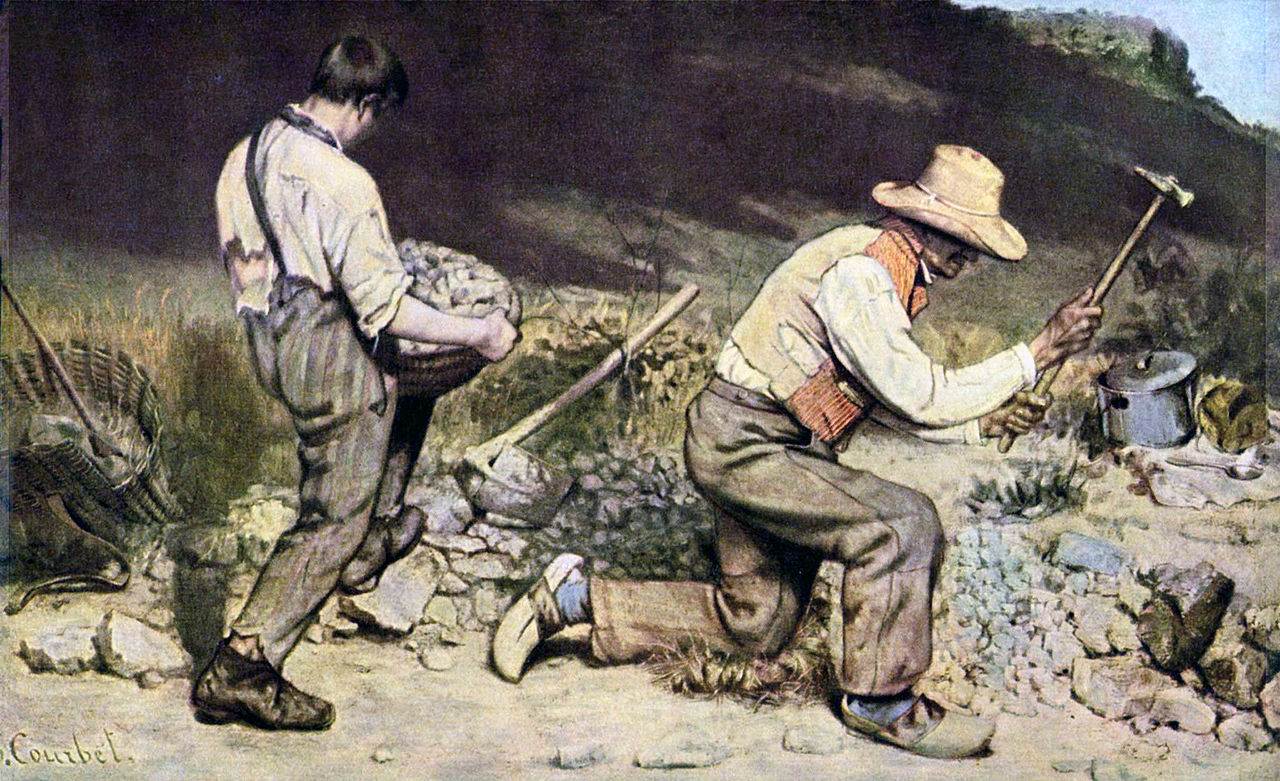
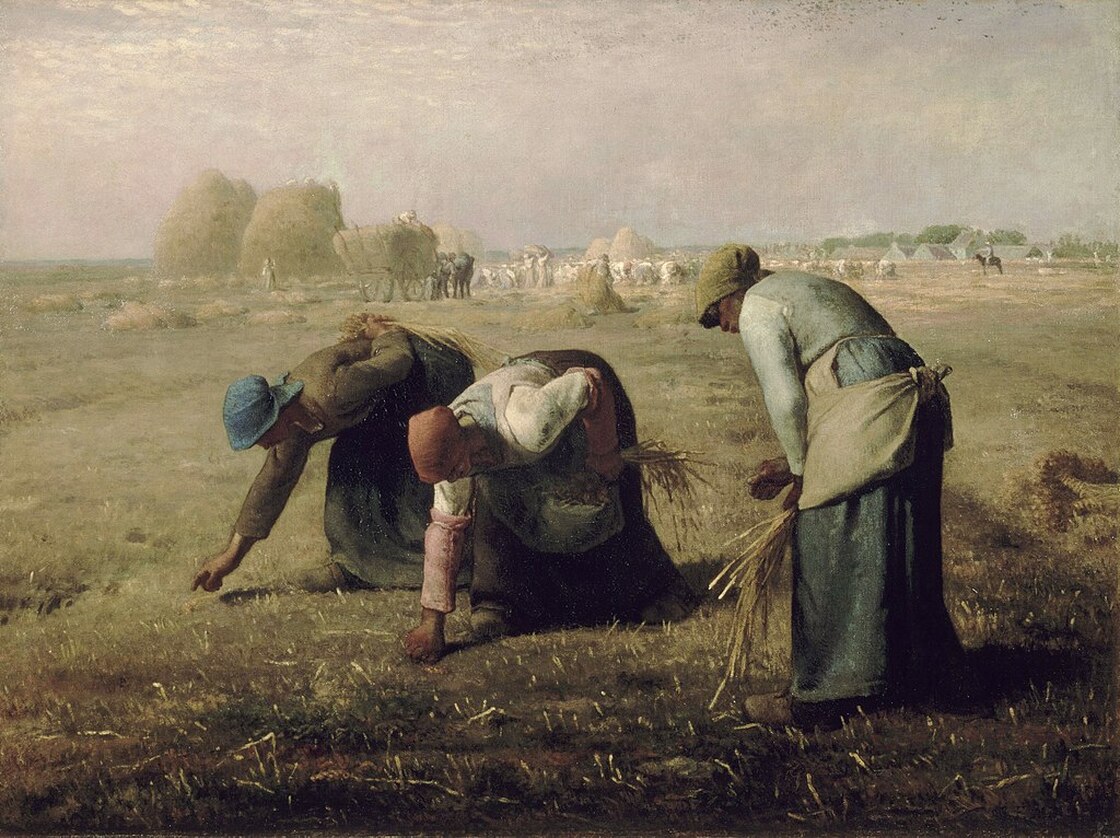
- Realism
- Impressionism
- Post-impressionism
- Pointillism
- Cubism
- Fauvism
- Expressionism
- Art Nouveau
- Italian Futurism
- Architecture
- Photography and Film
- Music
B. 19th Century Science
C. 19th Century Philosophy
D. 19th Century Religion
Artistic movements such as Impressionism, Expressionism, and Cubism, which rested on subjective interpretations of reality by the individual artist or writer, arose from the attitudes fostered by romanticism. The sensitivity of artists to non-European traditions that imperialism brought to their attention also can be traced to the romantics’ emphasis on the primacy of culture in defining the character of individuals and groups.
In science, Darwin’s evolutionary theory raised questions about human nature, and physicists began to challenge the uniformity and regularity of the Newtonian universe. In 1905, Einstein’s theory of relativity underscored the position of the observer in defining reality, while the quantum principles of randomness and probability called the objectivity of Newtonian mechanics into question. The emergence of psychology as an independent discipline, separate from philosophy on the one hand and neurology on the other, led to investigations of human behavior that gradually revealed the need for more subtle methods of analysis than those provided by the physical and biological sciences. Freud’s investigations into the human psyche suggested the power of irrational motivations and unconscious drives. Many writers saw humans as governed by spontaneous, irrational forces and believed that intuition and will were as important as reason and science in the search for truth.
In art, literature, and science, traditional notions of objective, universal truths and values increasingly shared the stage with a commitment to and recognition of subjectivity, skepticism, and cultural relativism.
Source: https://apcentral.collegeboard.org/pdf/ap-european-history-course-and-exam-description.pdf
In science, Darwin’s evolutionary theory raised questions about human nature, and physicists began to challenge the uniformity and regularity of the Newtonian universe. In 1905, Einstein’s theory of relativity underscored the position of the observer in defining reality, while the quantum principles of randomness and probability called the objectivity of Newtonian mechanics into question. The emergence of psychology as an independent discipline, separate from philosophy on the one hand and neurology on the other, led to investigations of human behavior that gradually revealed the need for more subtle methods of analysis than those provided by the physical and biological sciences. Freud’s investigations into the human psyche suggested the power of irrational motivations and unconscious drives. Many writers saw humans as governed by spontaneous, irrational forces and believed that intuition and will were as important as reason and science in the search for truth.
In art, literature, and science, traditional notions of objective, universal truths and values increasingly shared the stage with a commitment to and recognition of subjectivity, skepticism, and cultural relativism.
Source: https://apcentral.collegeboard.org/pdf/ap-european-history-course-and-exam-description.pdf
Modern Art
Objective: Explain the continuities and changes in European artistic expression from 1815 to 1914.
- Realist and materialist themes and attitudes influenced art and literature as painters and writers depicted the lives of ordinary people and drew attention to social problems.
- Modern art, including Impressionism, Post-Impressionism, and Cubism, moved beyond the representational to the subjective, abstract, and expressive and often provoked audiences that believed that art should reflect shared and idealized values, including beauty and patriotism.
- In the later 19th century, a new relativism in values and the loss of confidence in the objectivity of knowledge led to modernism in intellectual and cultural life.
Modern Thought and Culture in 1900: Crash Course European History #31
Europe was in transition politically and culturally at the beginning of the 20th century. Today, we're looking at the dawn of modern science, and the rise of Modernism in the arts, especially in music, dance, and visual arts. We'll look at changes in music and dance with Stravinsky's Rite of Spring and explore the groundbreaking visual art of the Impressionists.
Realism
|
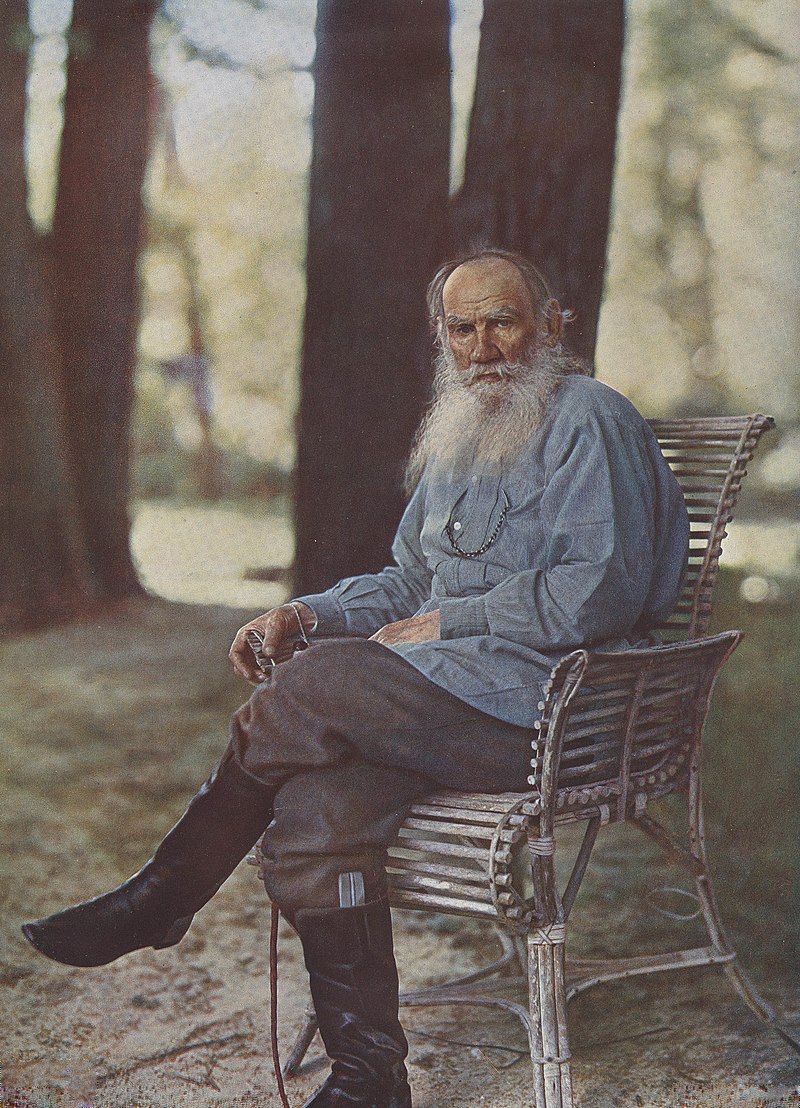
British author Charles Dickens and Russian author Leo Tolstoy are considered among the greatest writers of all time.
|
Realism
|
Impressionism
Post-impressionism
Pointillism
Cubism
Fauvism
Expressionism
Art Nouveau
|
|
Art Nouveau style was prevalent in advertising, architecture, and design.
|
Italian Futurism
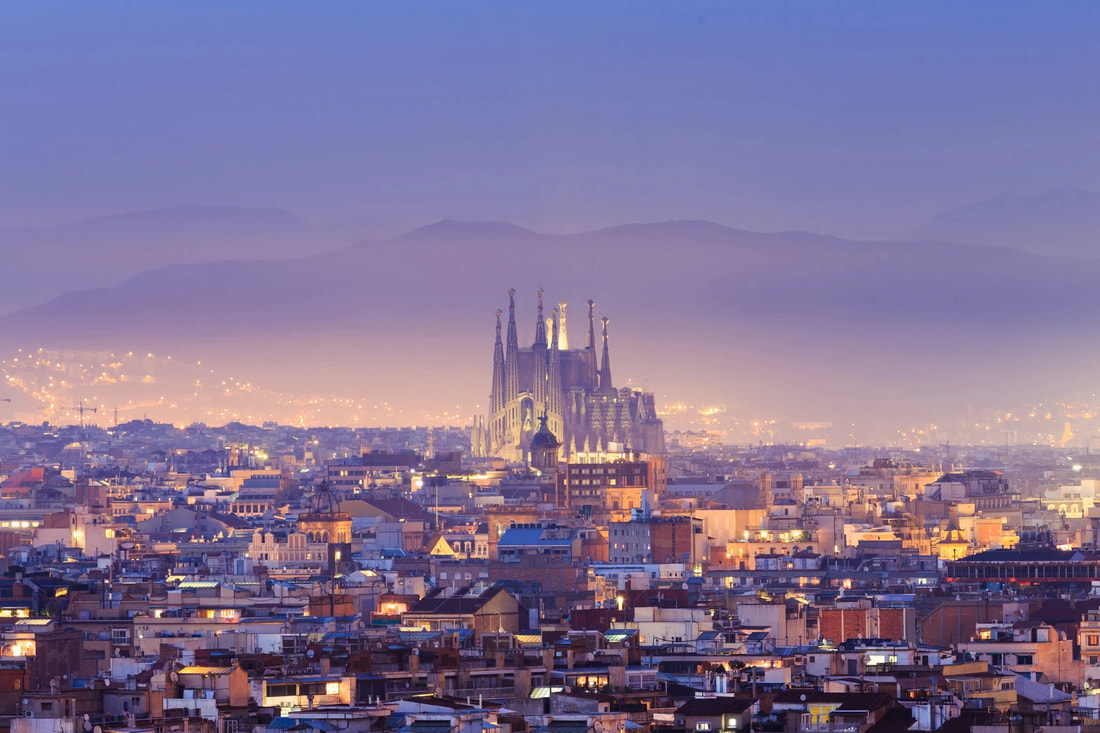
Architecture
The Sagrada Familia Cathedral, Barcelona, Spain was designed by Antoni Gaudi.
Photography and Film
Music
|
Modern Art Quizlet (comprehensive)
Modern Art Quizlet (abridged)
|
19th Century Science
Objectives:
- Explain how science and other intellectual disciplines developed and changed throughout the period from 1815 to 1914.
- Explain how Darwin’s theories influenced scientific and social developments from 1815 to 1914.
- Positivism, or the philosophy that science alone provides knowledge, emphasized the rational and scientific analysis of nature and human affairs.
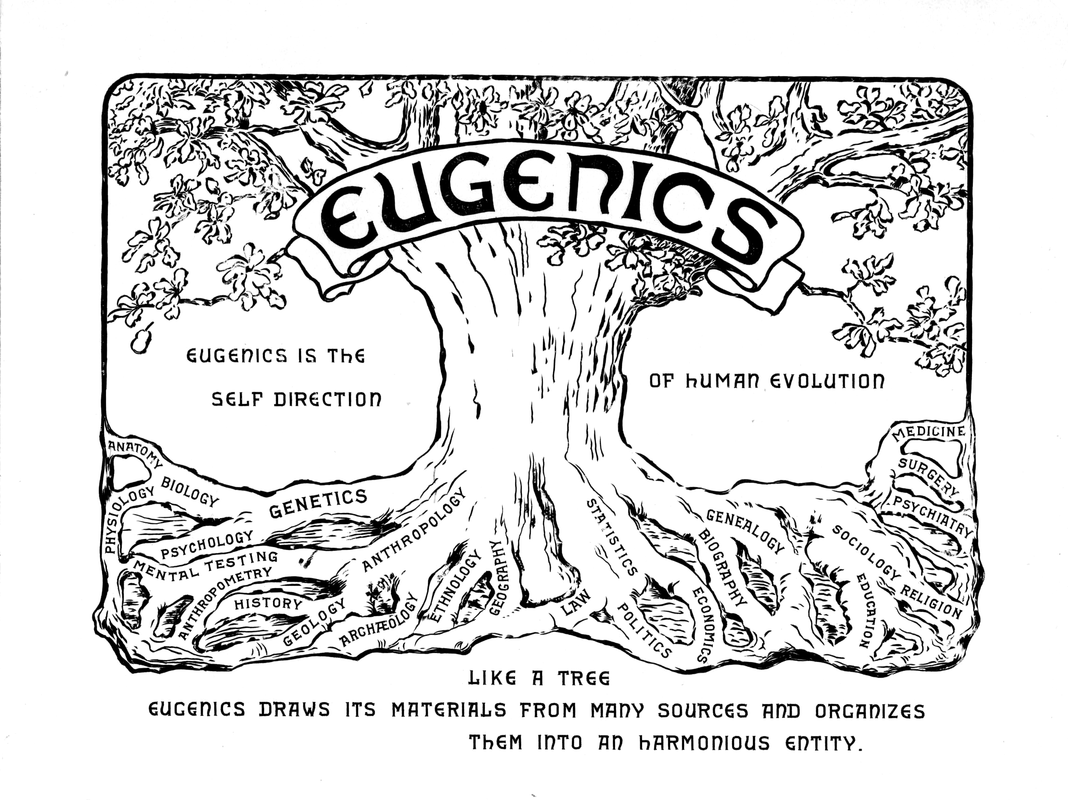
- Charles Darwin provided a scientific and material account of biological change and the development of human beings as a species, and inadvertently, a justification for racialist theories that became known as Social Darwinism.
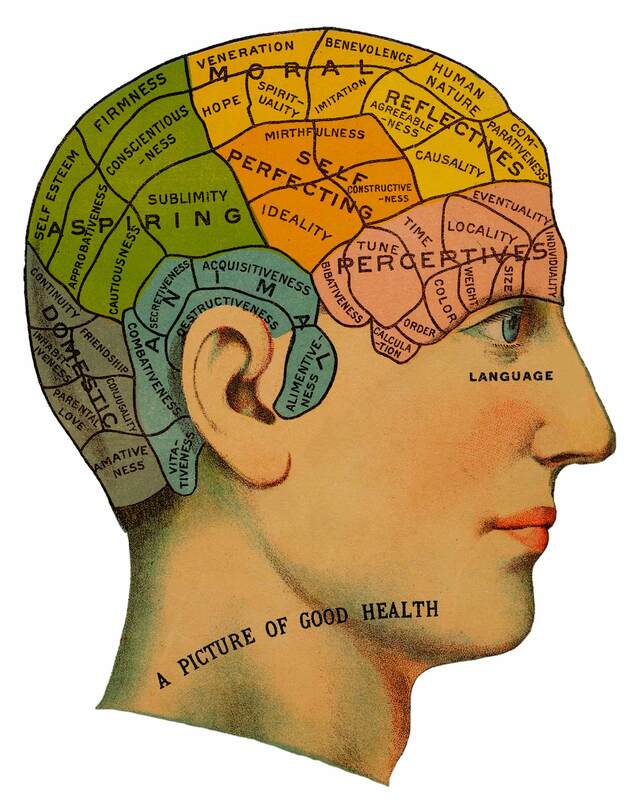
- Freudian psychology offered a new account of human nature that emphasized the role of the irrational and the struggle between the conscious and subconscious.
- Developments in the natural sciences, such as quantum mechanics and Einstein’s theory of relativity, undermined the primacy of Newtonian physics as an objective description of nature.
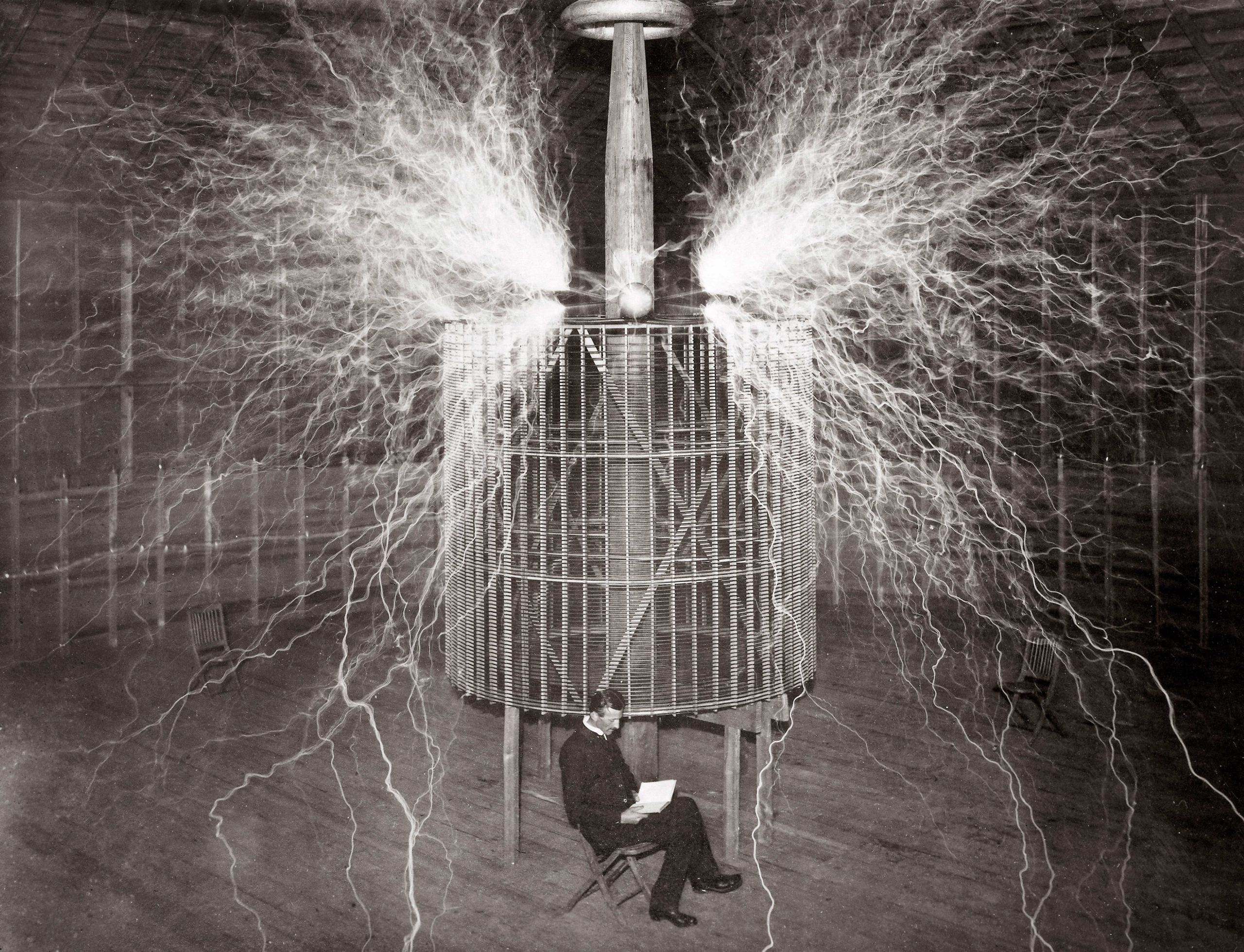
Electricity
Nikola Tesla sitting inside an active Faraday cage
Chemistry
Biology and Geology
Medicine
Social Sciences
Modern Physics
|
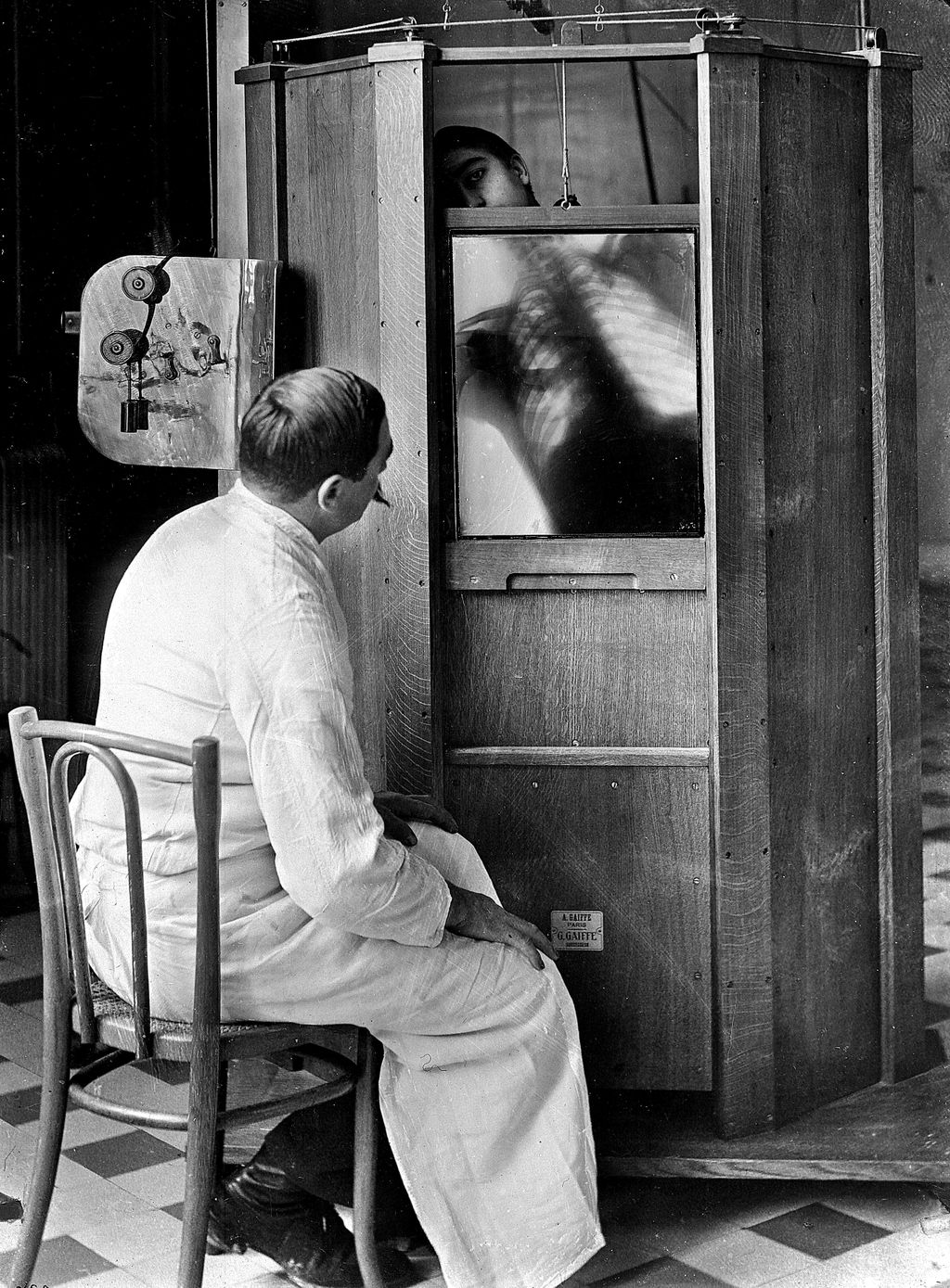
A chest X-ray in progress at Dr. Maxime Menard’s radiology department at the Cochin hospital in Paris, circa 1914. Mendard later lost his finger to side effects from operating the X-ray machine
|
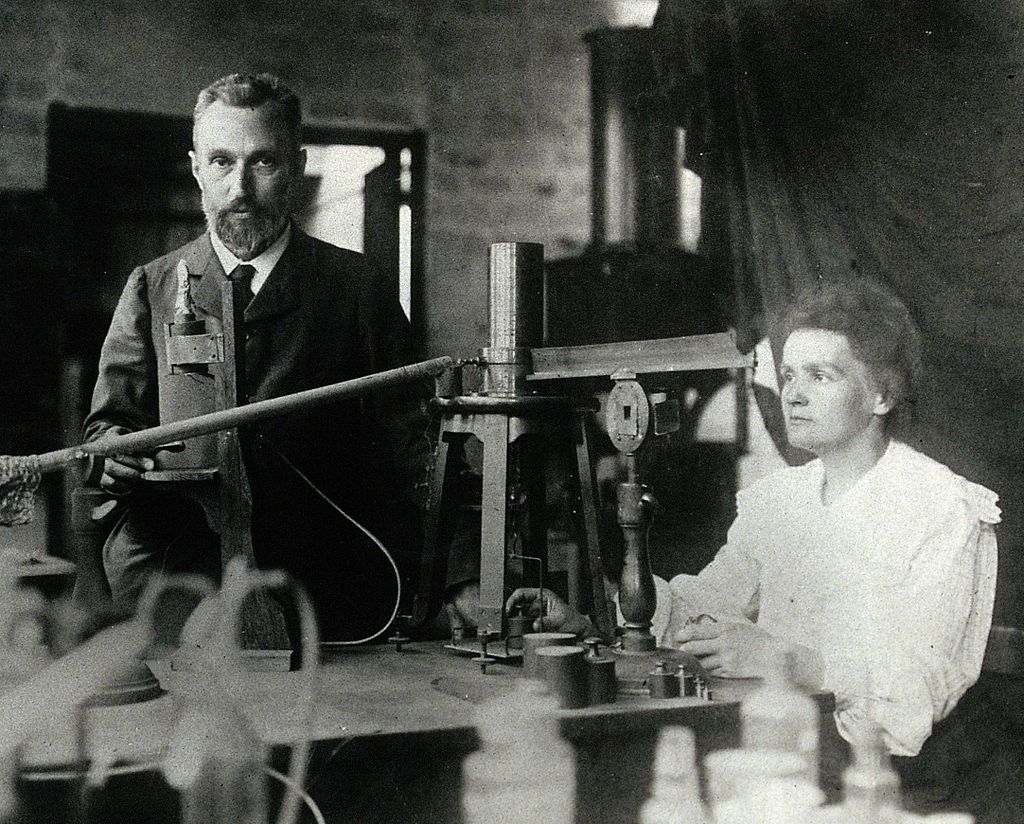
Marie Curie is one of the most celebrated female scientists. She and her husband Pierre Curie won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1903 for their discovery of radiation.
|
19th Century Philosophy
Objective: Explain how science and other intellectual disciplines developed and changed throughout the period from 1815 to 1914.
|
19th Century Religion
Objective: Explain how science and other intellectual disciplines developed and changed throughout the period from 1815 to 1914.
|
Kulturkampf caricature "Between Berlin and Rome", 1875
|
logo of the Theosophical Society
|
|
19th Century Science, Philosophy, and Religion Quizlet (comprehensive)
19th Century Science, Philosophy, and Religion Quizlet (abridged)
|