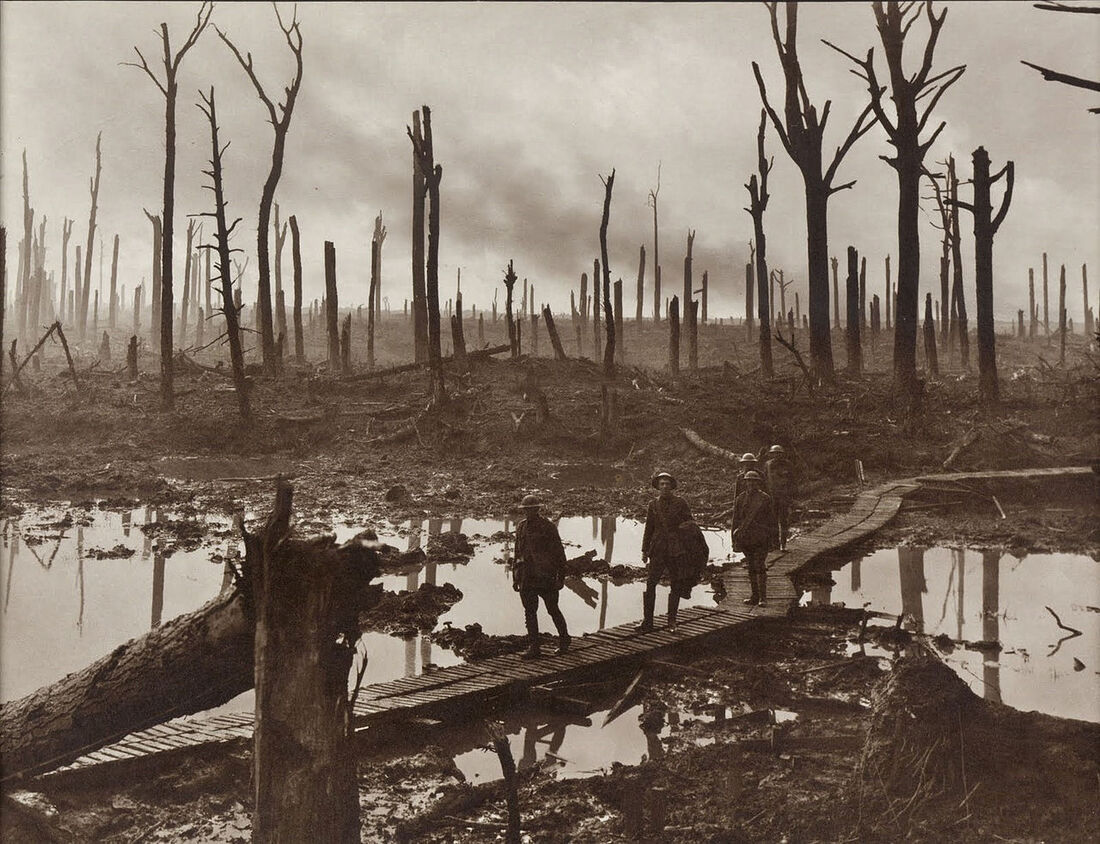
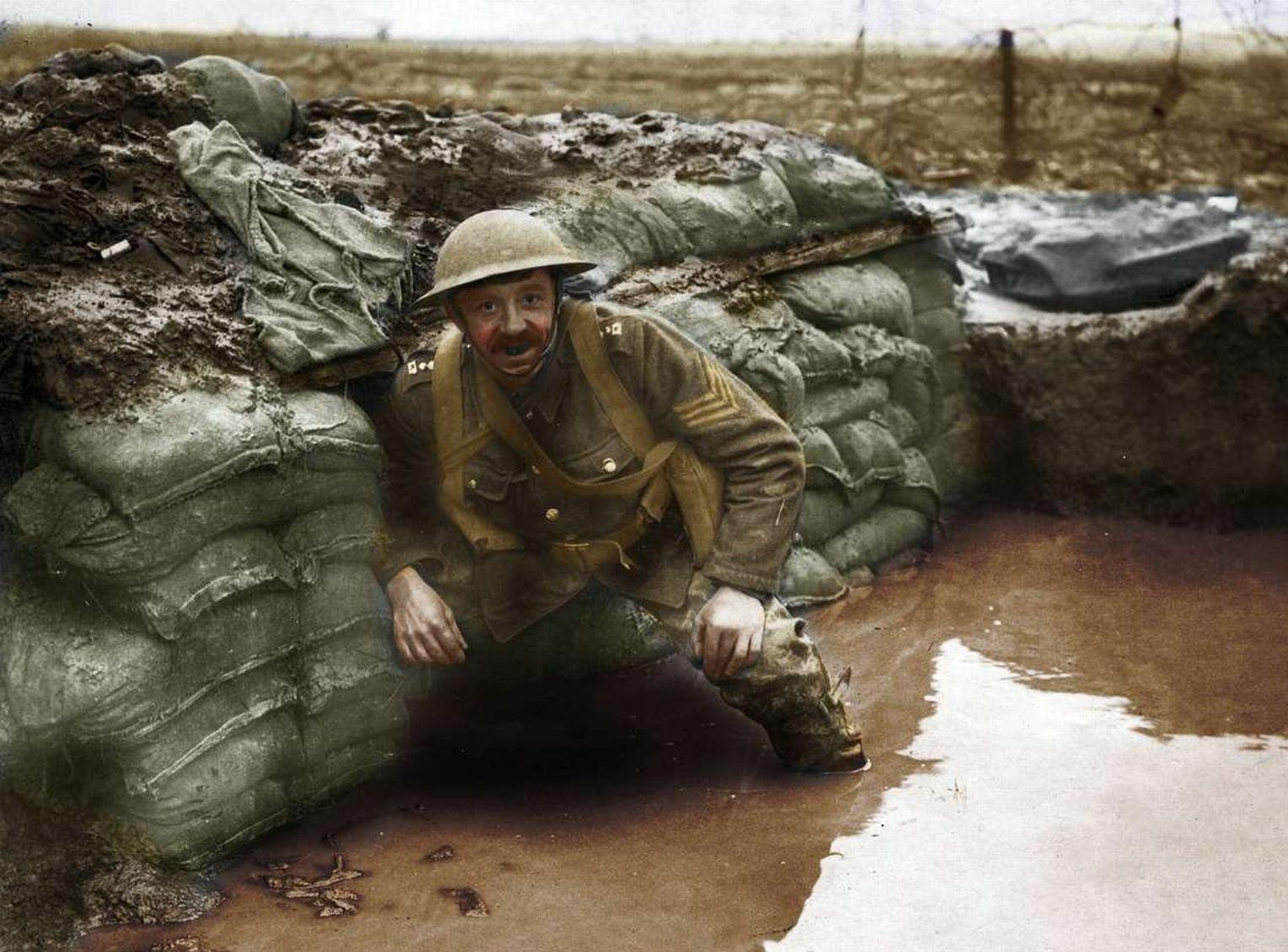
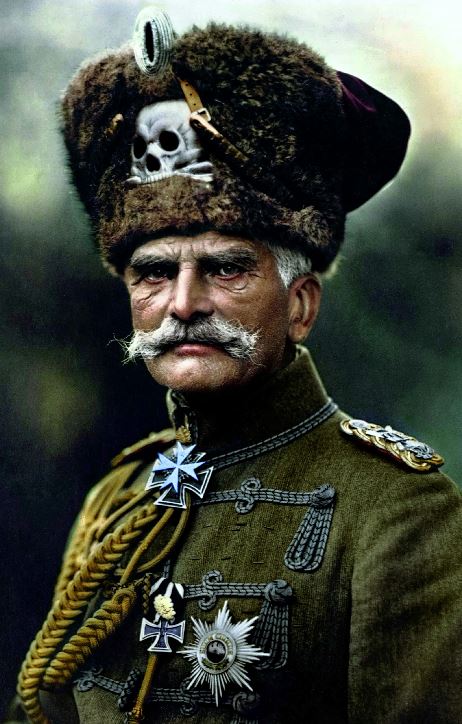
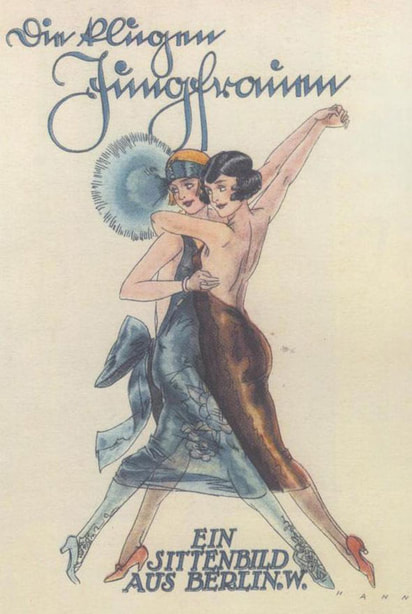World War I destroyed the balance of power, and the Treaty of Versailles, which ended the war, created unstable conditions in which extremist ideologies emerged that challenged liberal democracy and the postwar settlement.
The First World War,
c. 1914-1928 CE
Contents
European politics and diplomacy in the 20th century were defined by total war and its consequences. World War I destroyed the balance of power, and the Treaty of Versailles, which ended the war, created unstable conditions in which extremist ideologies emerged that challenged liberal democracy and the postwar settlement. In Russia, hardships during World War I gave rise to a revolution in 1917.
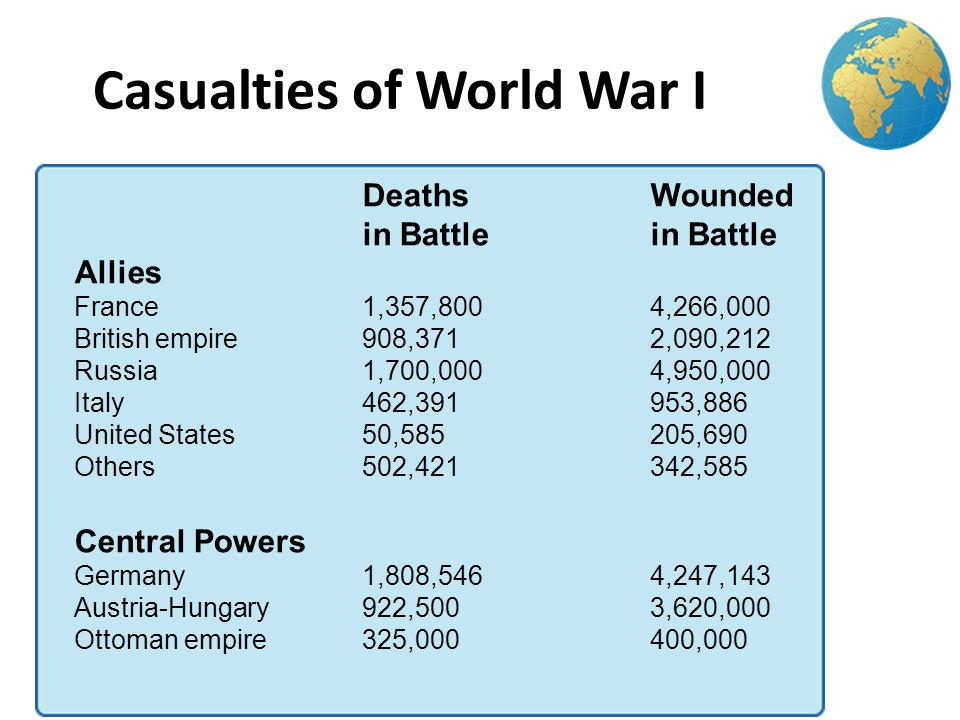
During World War I, states increased the degree and scope of their authority over their economies, societies, and cultures. The demands of total war required the centralization of power and the regimentation of the lives of citizens. During the war, governments sought to control information and used propaganda to create stronger emotional ties to the nation and its war effort. Ironically, these measures also produced distrust of traditional authorities. At the end of the war, four empires dissolved—the German, Austro-Hungarian, Ottoman, and Russian empires—but the democratic nations that arose in their place lacked a tradition of democratic politics and suffered from weak economies and ethnic tensions. Even before the end of the war, Russia experienced a revolution and civil war that created not only a new state, the USSR, but also a new conception of government and socioeconomic order based on communist ideals.
Source: https://apcentral.collegeboard.org/pdf/ap-european-history-course-and-exam-description.pdf
During World War I, states increased the degree and scope of their authority over their economies, societies, and cultures. The demands of total war required the centralization of power and the regimentation of the lives of citizens. During the war, governments sought to control information and used propaganda to create stronger emotional ties to the nation and its war effort. Ironically, these measures also produced distrust of traditional authorities. At the end of the war, four empires dissolved—the German, Austro-Hungarian, Ottoman, and Russian empires—but the democratic nations that arose in their place lacked a tradition of democratic politics and suffered from weak economies and ethnic tensions. Even before the end of the war, Russia experienced a revolution and civil war that created not only a new state, the USSR, but also a new conception of government and socioeconomic order based on communist ideals.
Source: https://apcentral.collegeboard.org/pdf/ap-european-history-course-and-exam-description.pdf
The Great War
Objectives:
- Explain the causes and effects of World War I.
- Explain how new technology altered the conduct of World War I.
- Explain the causes and effects of the Russian Revolution.
- World War I, caused by a complex interaction of long- and short-term factors, resulted in immense losses and disruptions for both victors and vanquished.
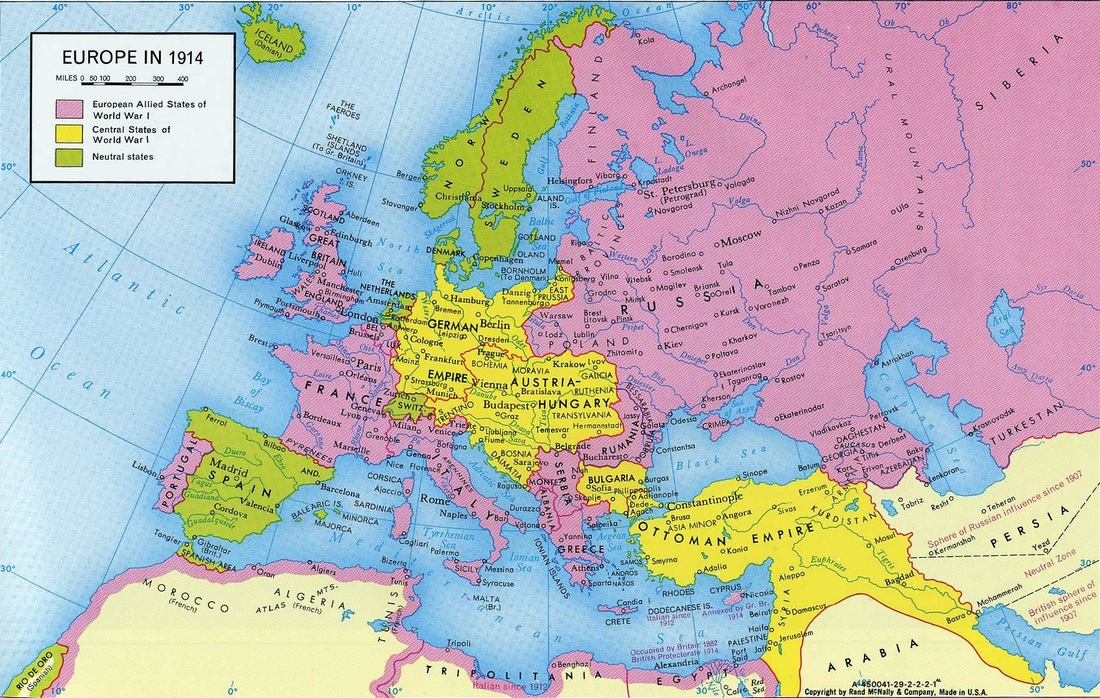
- A variety of factors—including nationalism, military plans, the alliance system, and imperial competition—turned a regional dispute in the Balkans into World War I.
- New technologies confounded traditional military strategies and led to trench warfare and massive troop losses.
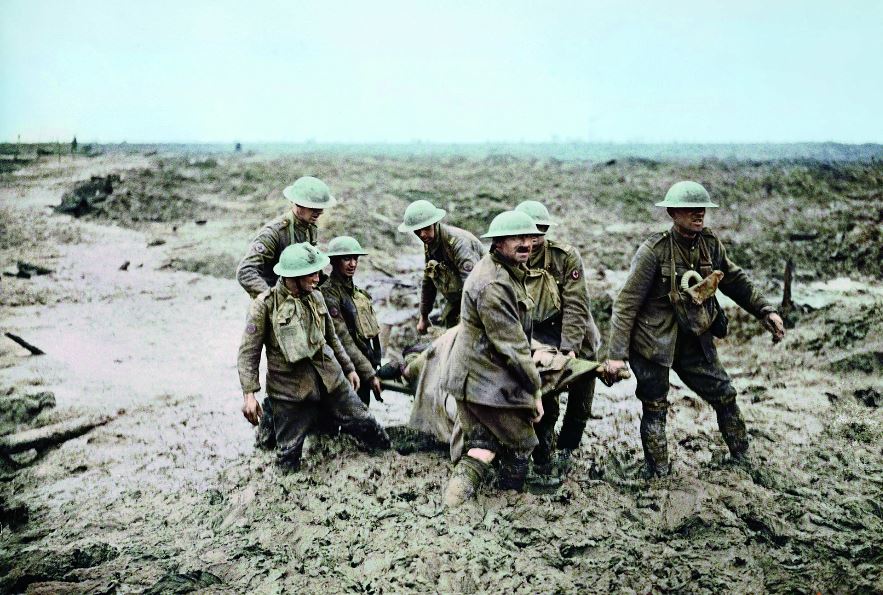
- The effects of military stalemate, national mobilization, and total war led to protest and insurrection in the belligerent nations and eventually to revolutions that changed the international balance of power.
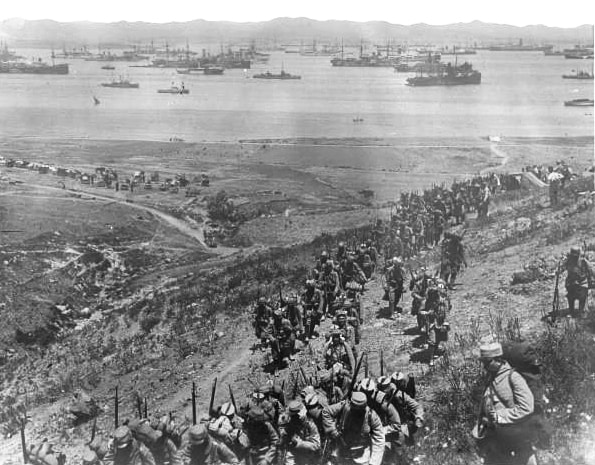
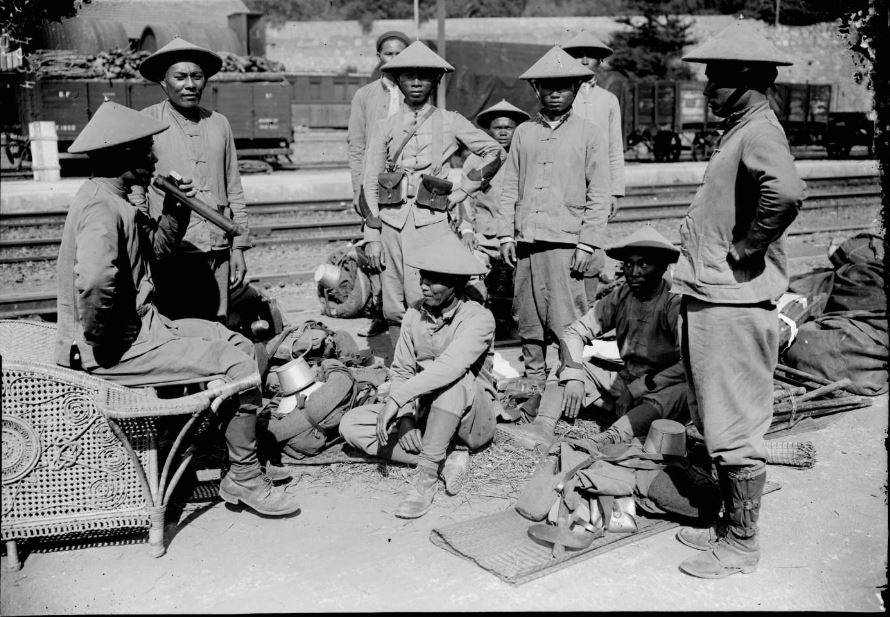
- The war in Europe quickly spread to non-European theaters, transforming the war into a global conflict.
- During the world wars, women became increasingly involved in military and political mobilization, as well as in economic production.
Causes
The Roads to World War I: Crash Course European History #32
Much has been written about what exactly caused World War I. As befits a true global war, the reality is that there isn't a single cause. There aren't even three causes. There are a vast array of causes. Today we'll get into just a few of those causes, including the complex system of alliances in Europe, the myriad military conflicts that played out in the years and decades leading up to the war, and the event that many point to as the beginning: the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand.
|
German Kaiser Wilhelm II's aggressive Weltpolitik foreign policy unnerved other Great Powers causing Britain and France to draw closer together after the Moroccan Crises.
|
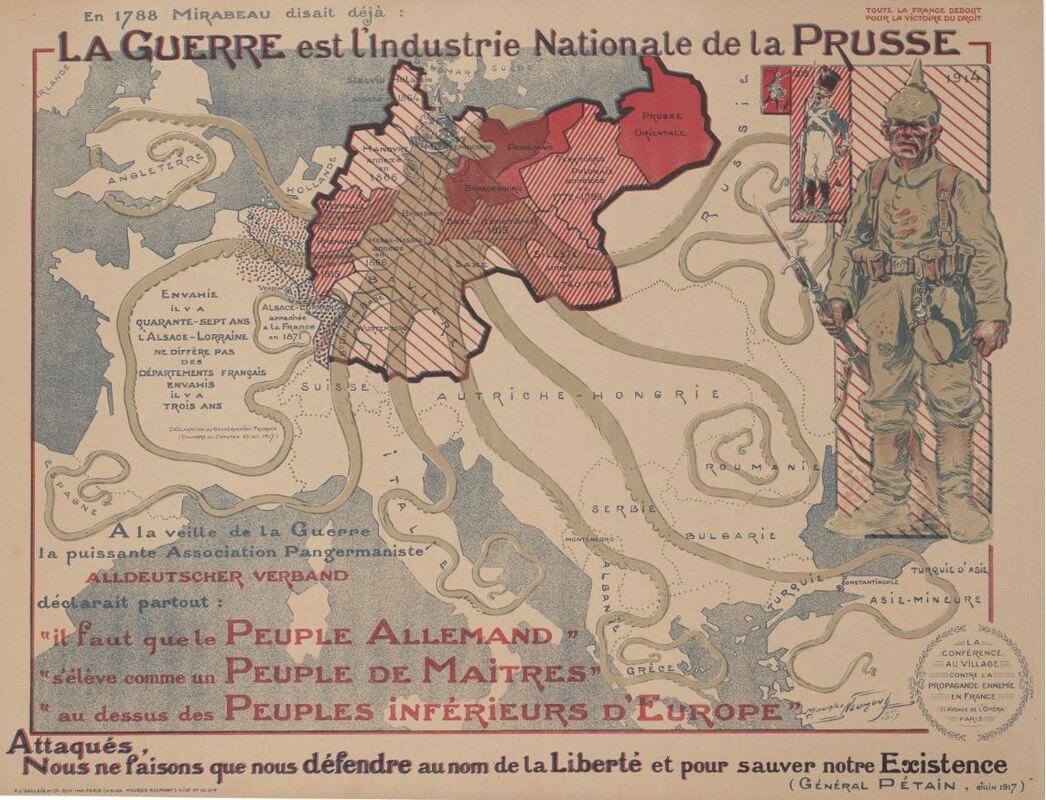
A brilliantly-designed and brutally-effective First World War propaganda map by Maurice Neumont, comparing Germany to a monstrous octopus threatening Europe. Germany is shown in different shadings of red, indicating its numerous annexations of surrounding territory since 1740, the most recent being the 1871 seizure of Alsace-Lorraine during the Franco-Prussian War.
World War I Battlefields: Crash Course European History #33
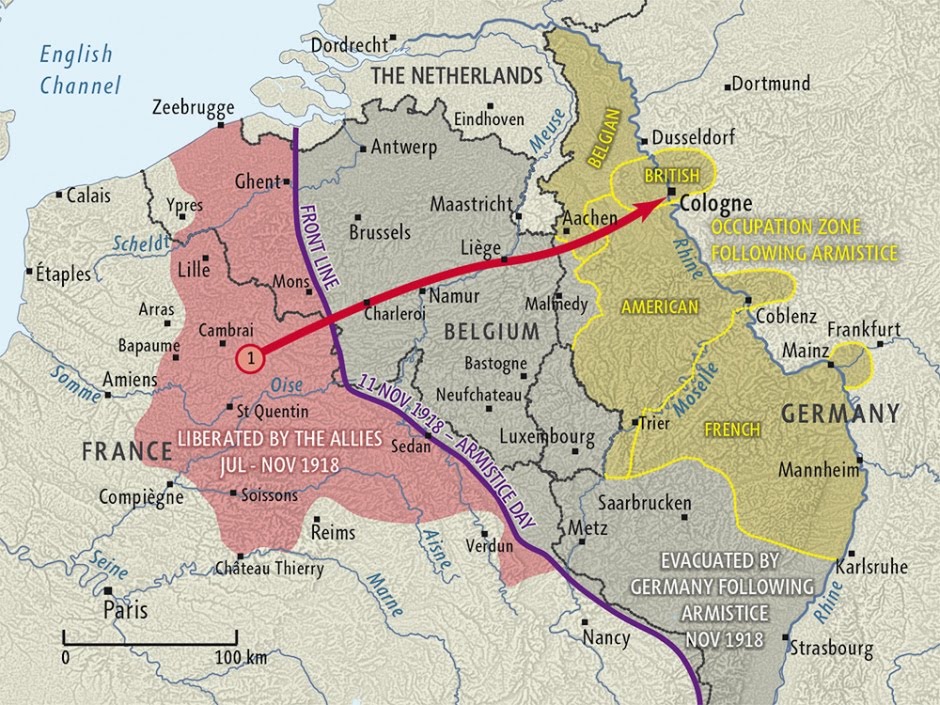
Europe's system of alliances and centuries-old tensions erupted into war in August of 1914. We'll take you from the guns of August through gruesome battles like Verdun and the Somme and follow the thread all the way through to the Armistice in 1918. It didn't turn out to be the War to End All Wars, sadly, but there is a lot to learn from it.
1914
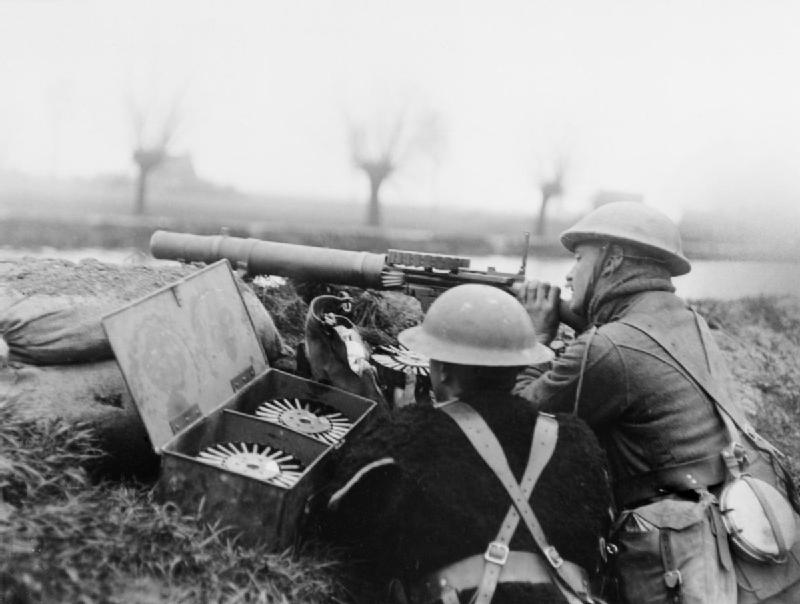
British machine gunners
|
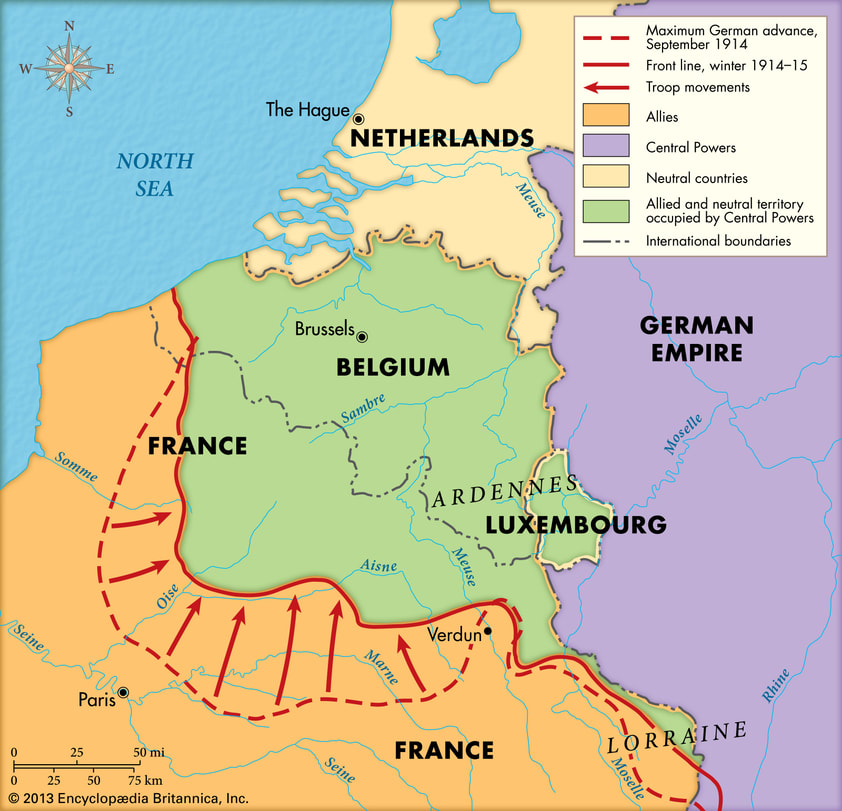
The heroic French defense at the First Battle of the Marne halted the German advance.
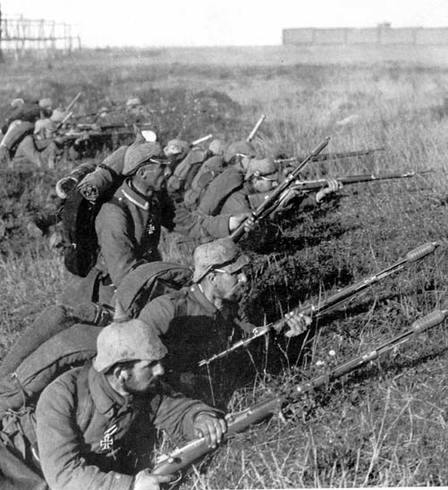
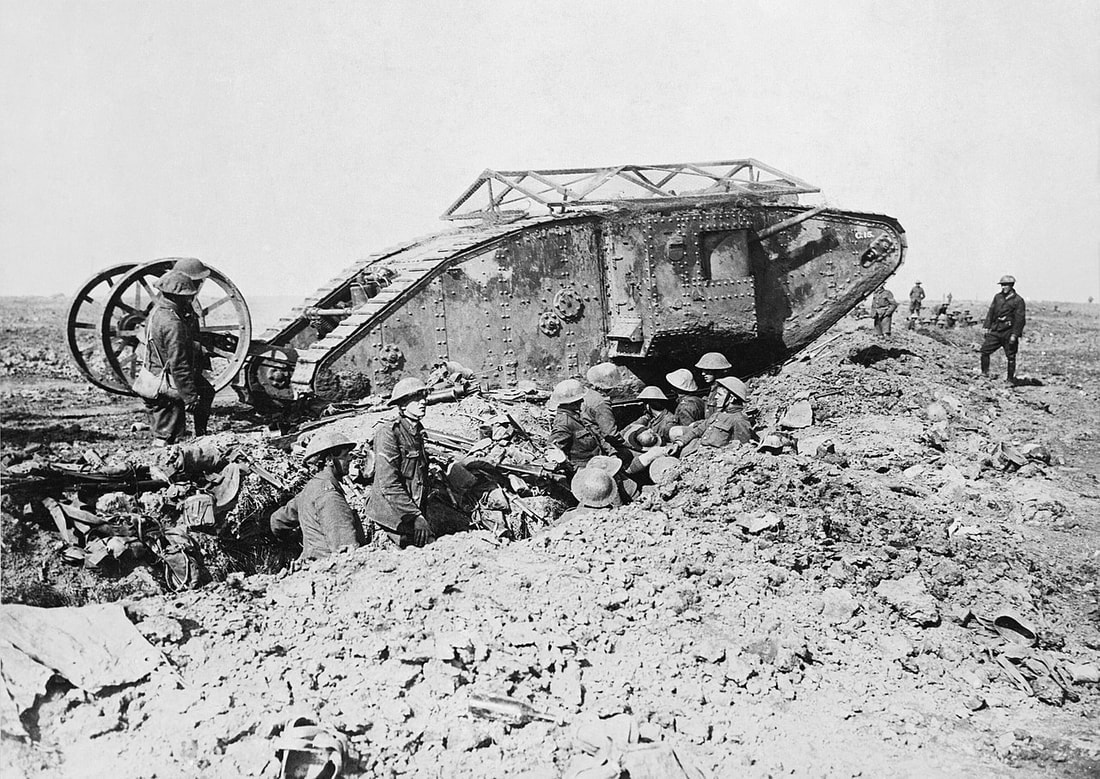
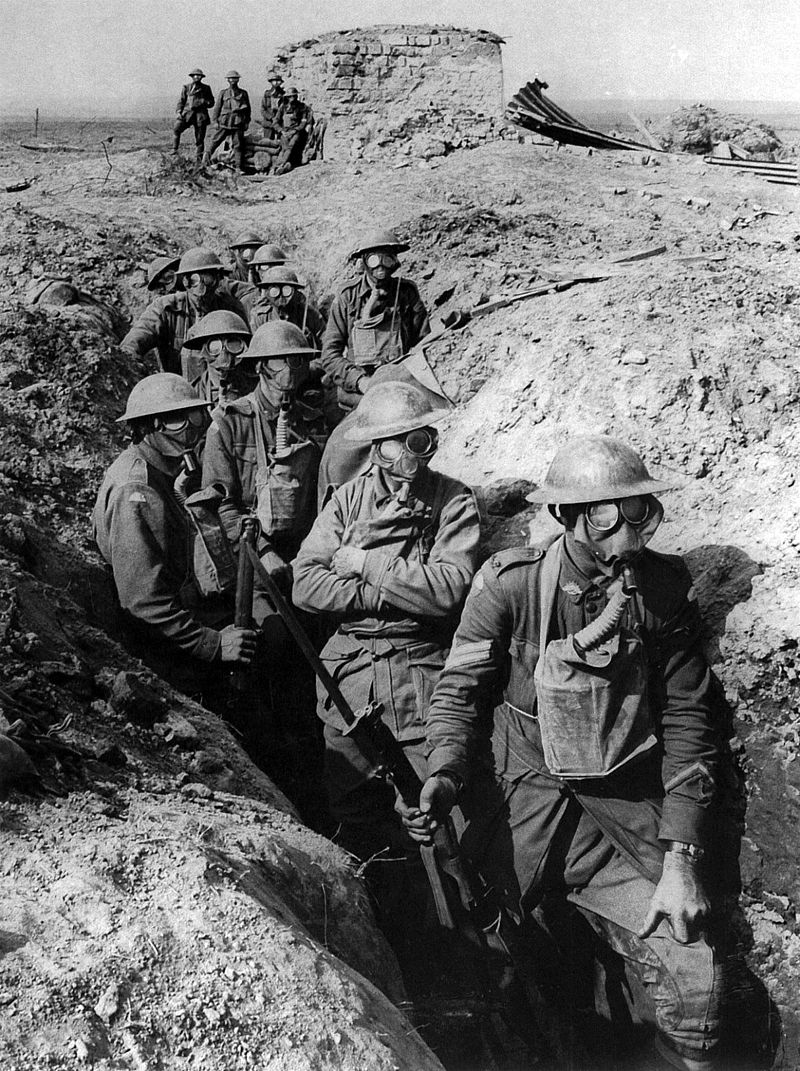
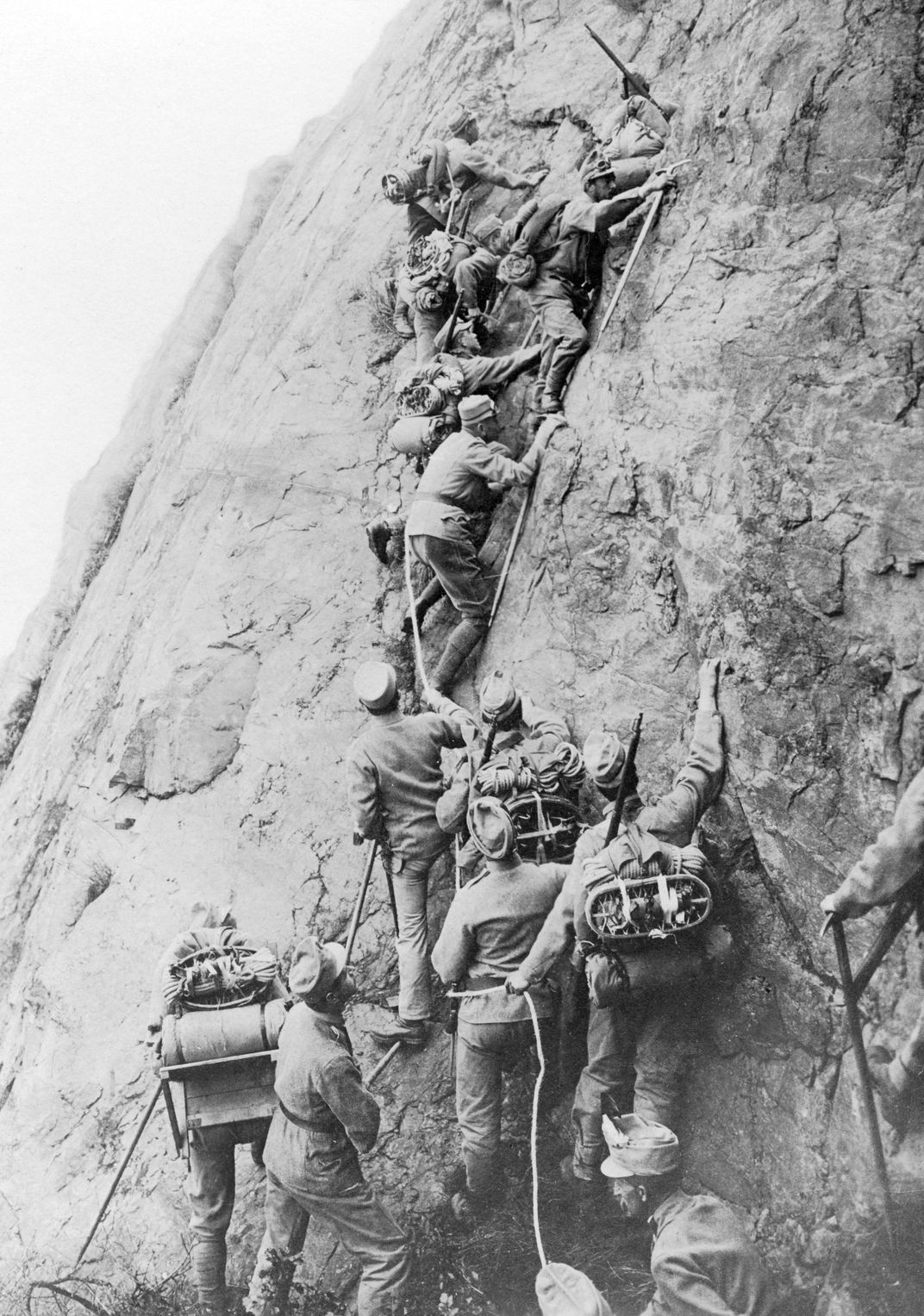
Fighting along the Western Front quickly bogged down in horrific trench warfare as Germany was forced to divide its forces in a protracted two-front war.
|
|
German Field Marshal August von Mackensen in 1914
|
Lord Kitchener, the popular Secretary of State for War, encourages British men to enlist in this well-known propaganda poster.
|
WWI's Civilians, the Homefront, and an Uneasy Peace: Crash Course European History #34
World War I was a total war for millions of people in Europe. Many men were enlisted in the fighting, but the war work had implications for the daily lives of a huge number of Europeans. Women entered the workforce in huge numbers, and for a lot of people, the battles raged through their towns, cities, and even their homes.
1915-1916
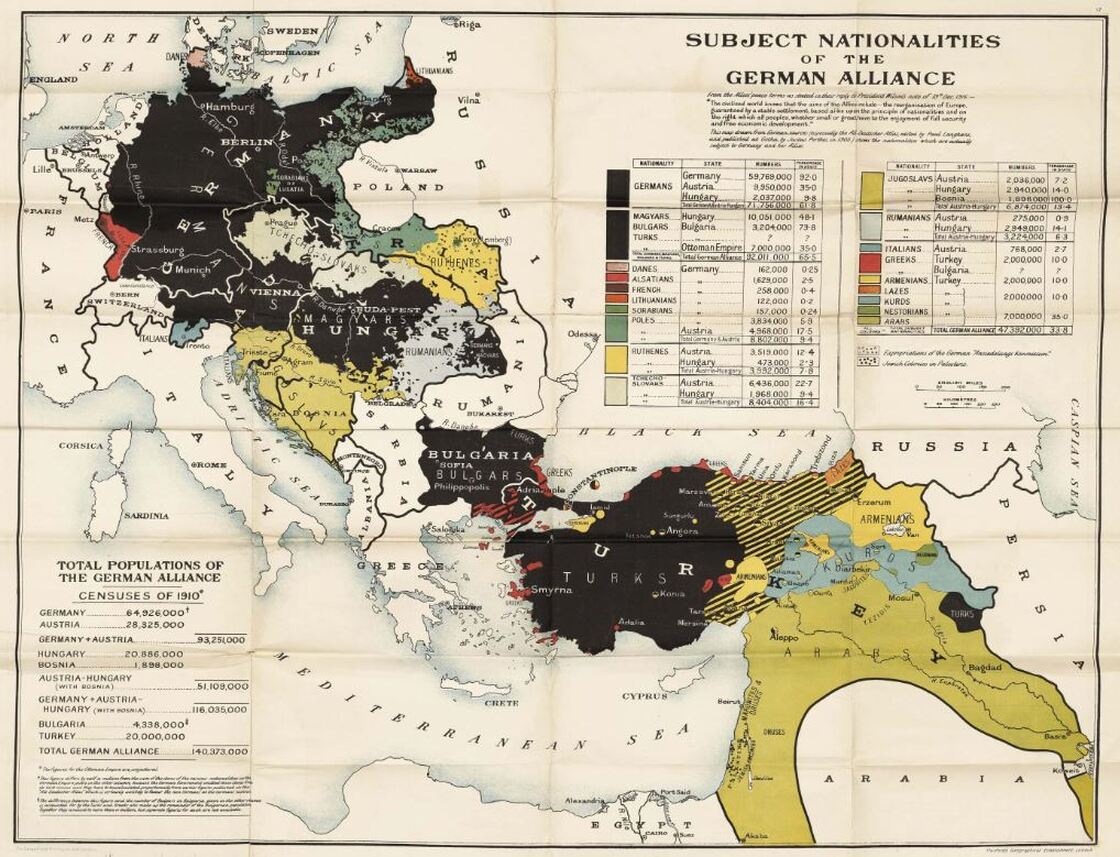
Allied study of the ethnic groups of the Central Powers
|
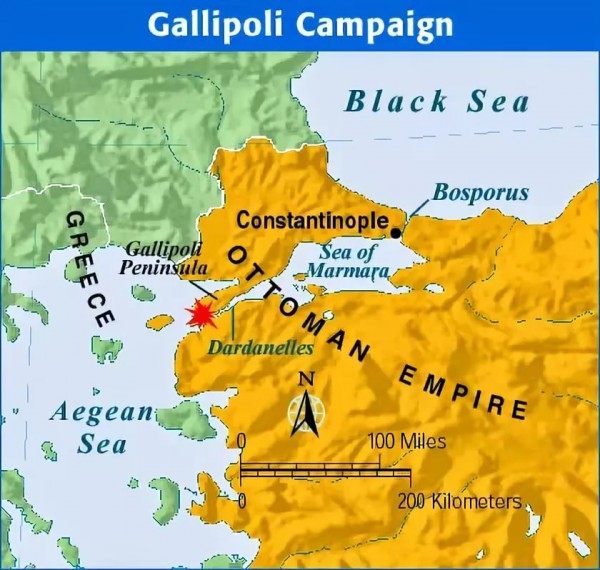
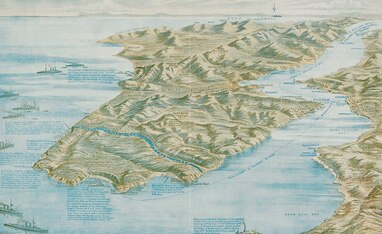
Article: Six unexpected WW1 battlegrounds
|
|
The Great War. 1914-1916 Quizlet (comprehensive)
The Great War. 1914-1916 Quizlet (abridged)
|
Russian Revolution and Civil War: Crash Course European History #35
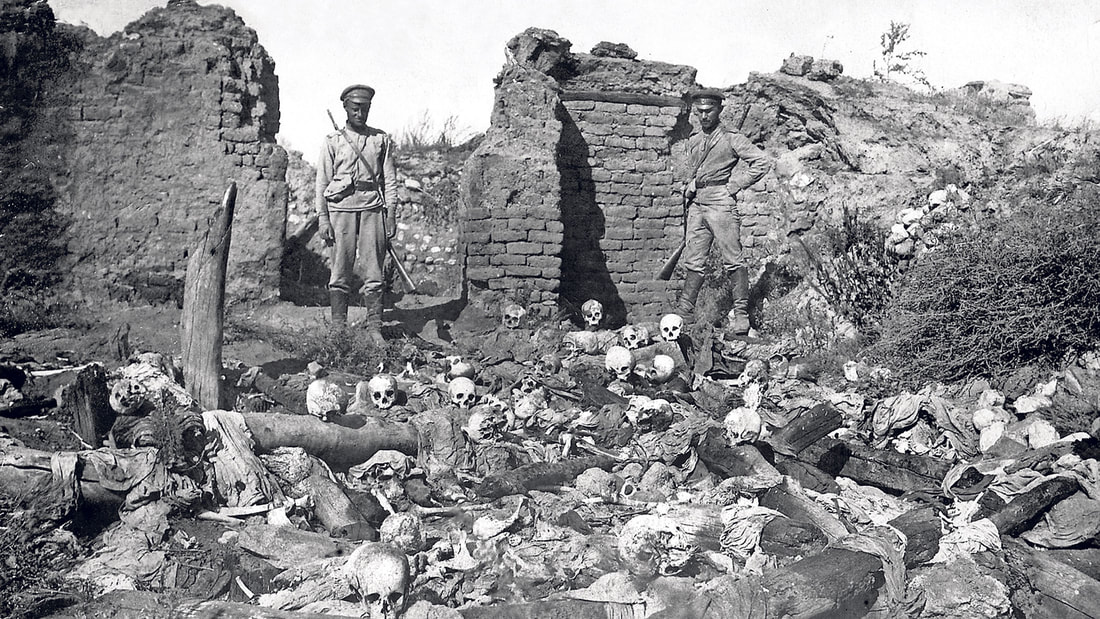
World War I was very hard on the Russian Empire. So hard, in fact, that it led to the end of the Russian Empire. As the global conflict ground on, Tsar Nicholas II faced increasing unrest at home. Today we'll learn about the Revolutions of 1917, the rise of Lenin, Trotsky, and the Bolsheviks, and the Russian Civil War and the creation of the Soviet Union.
1917
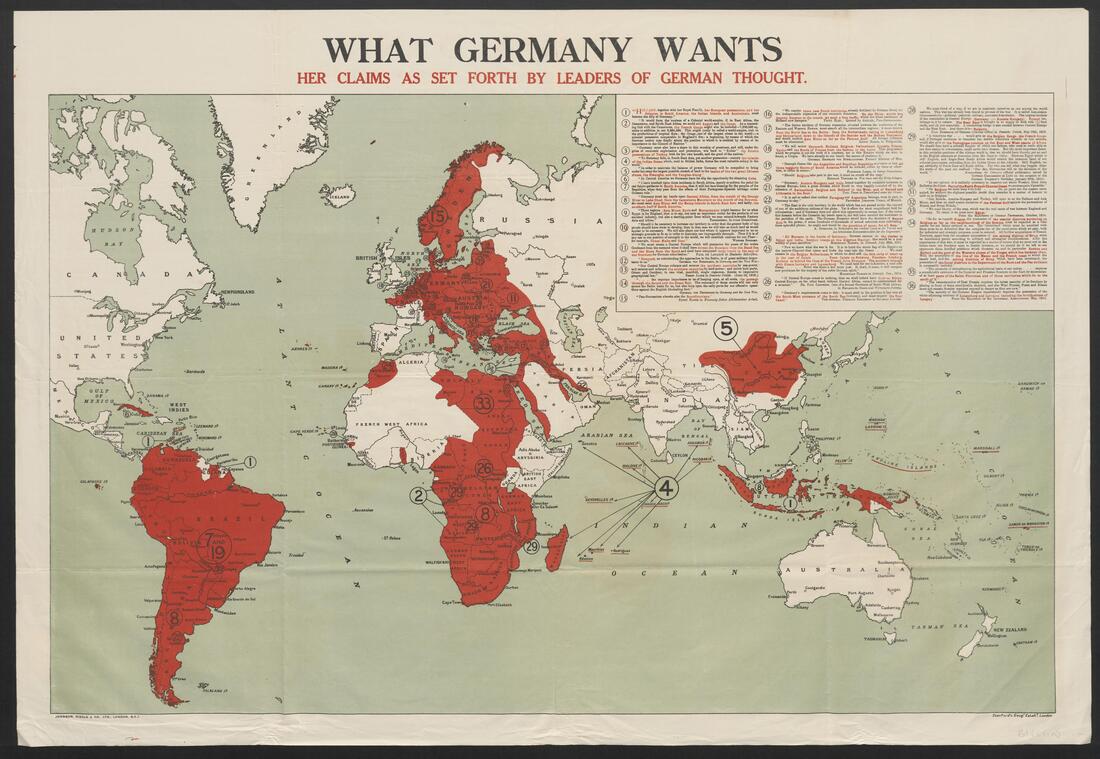
This British propaganda map includes a table at upper right with 36 statements from German politicians, military officers and intellectuals meant to demonstrate Germany’s aggressive imperial intentions.
“We will annex Denmark, Belgium, Holland, Switzerland, Livonia, Trieste, Venice, and the North of France from the Somme to the Loire. This programme which we propose is not the work of a madman, nor is this Empire which we wish to found, a Utopia. We have already in our hands the means of realising it." - General Bronsart von Schellendorf, Minister of War.”
“We will annex Denmark, Belgium, Holland, Switzerland, Livonia, Trieste, Venice, and the North of France from the Somme to the Loire. This programme which we propose is not the work of a madman, nor is this Empire which we wish to found, a Utopia. We have already in our hands the means of realising it." - General Bronsart von Schellendorf, Minister of War.”
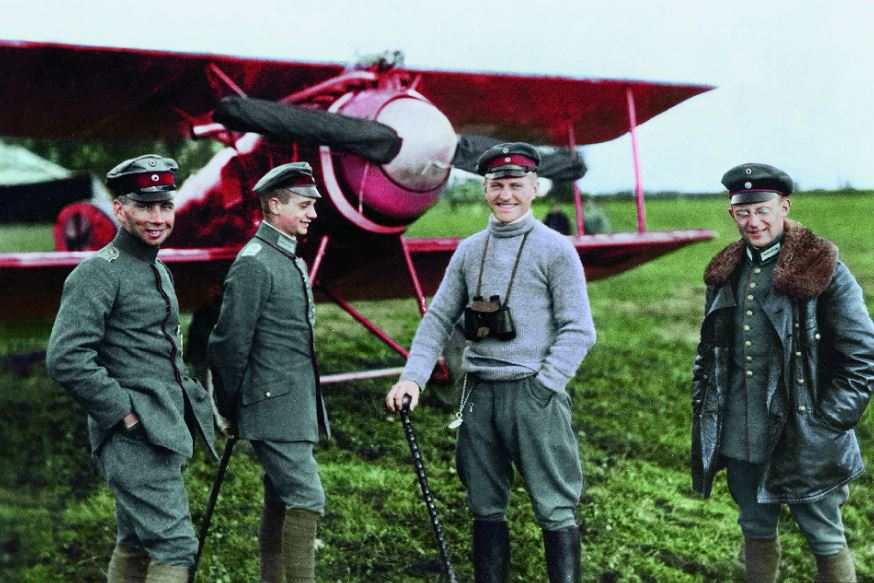
Manfred Albrecht Freiherr von Richthofen, the Red Baron, and members of his Flying Circus
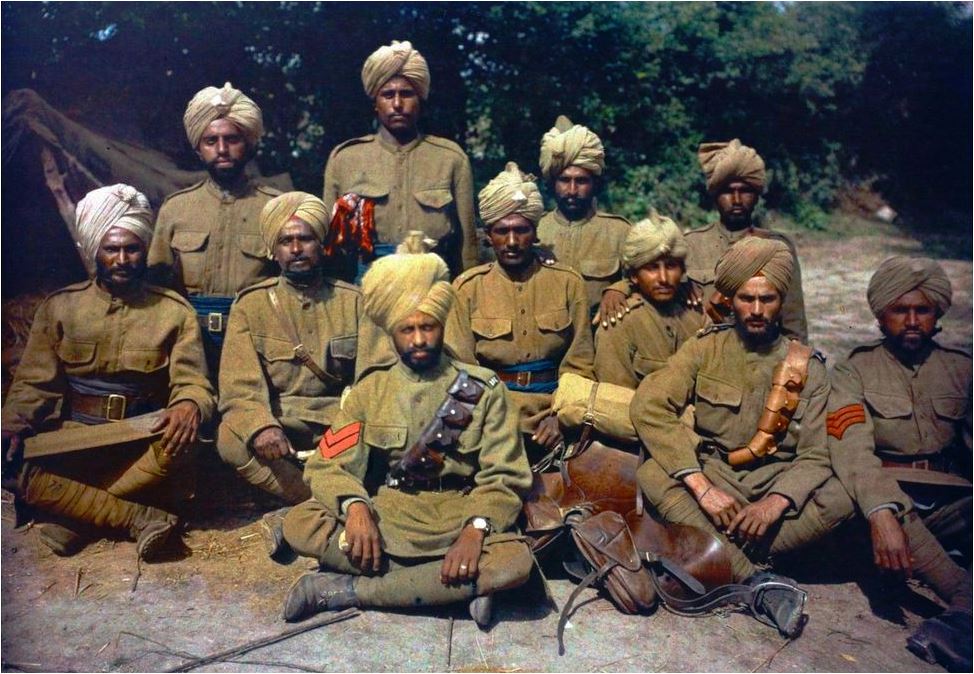
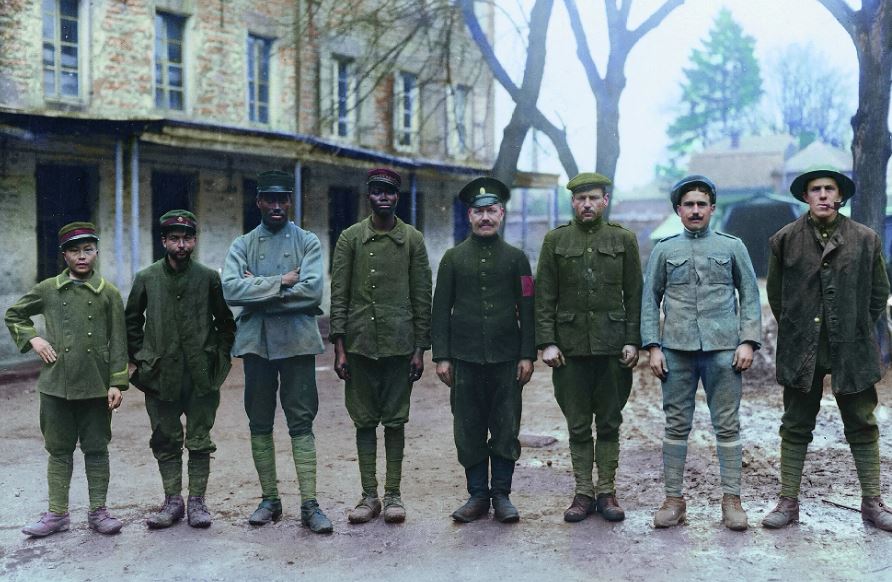
Indian troops from Punjab in France, 1917
|
Australian soldiers at Ypres, France during the battle of Passchendaele.
|
slogging through mud during the battle of Passchendaele
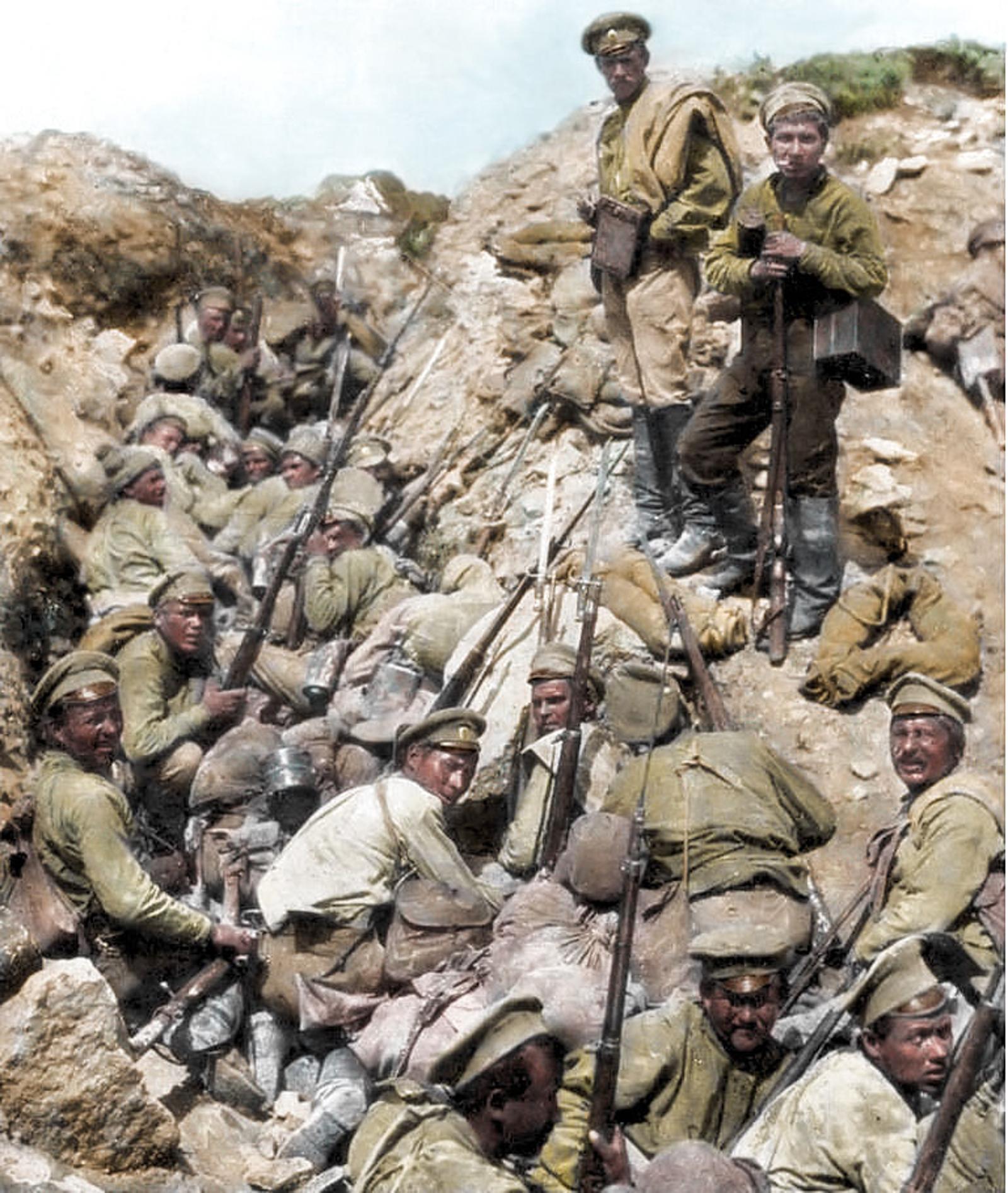
Russian soldiers during the Kerensky Offensive
|
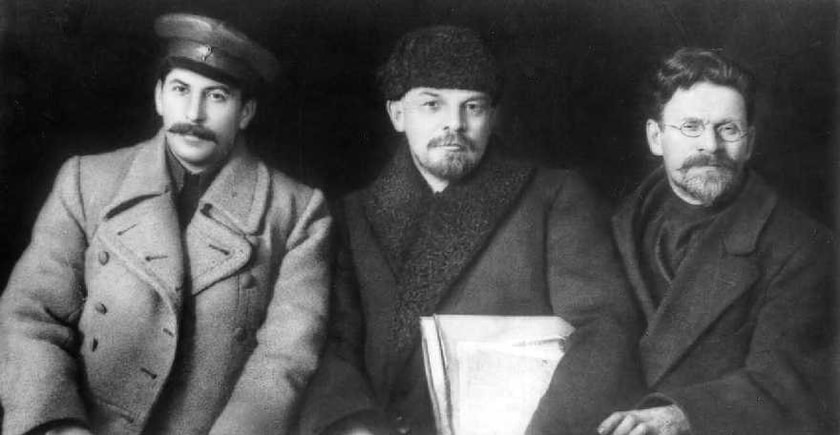
Joseph Stalin (left), Vladimir Lenin (center), and Leon Trotsky (right) led the Bolshevik Revolution and founded the Soviet Union.
|
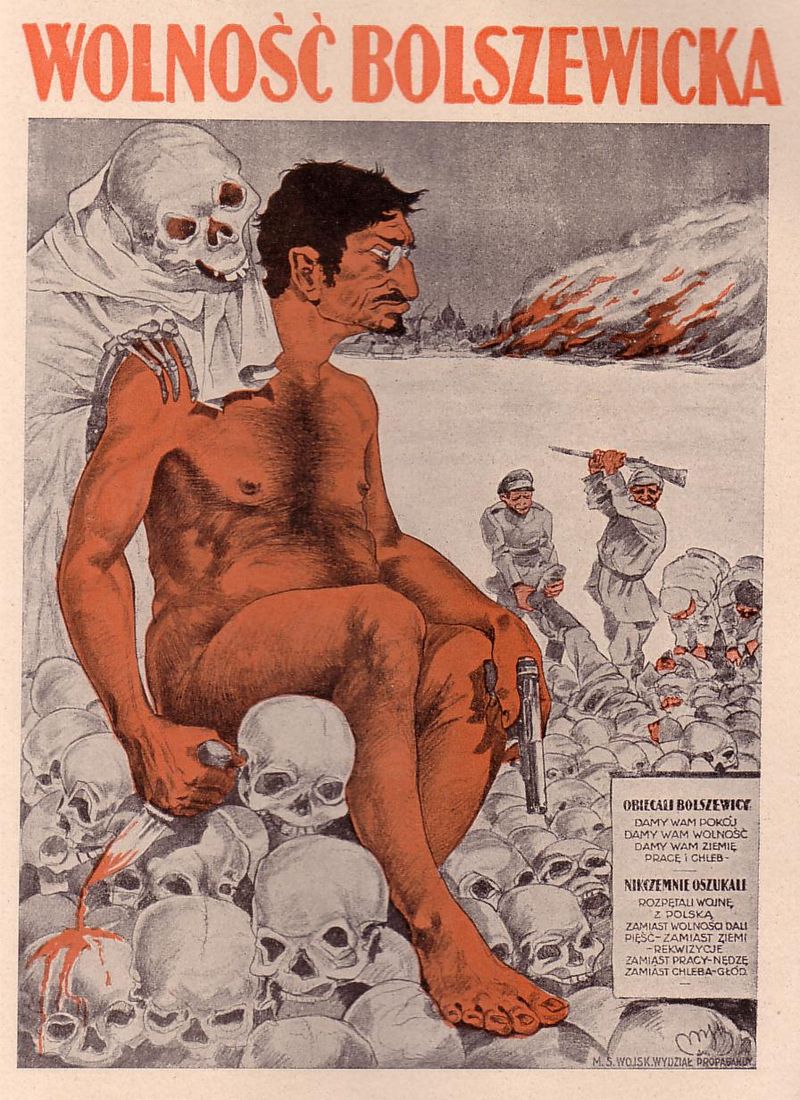
White coalition propaganda depicted the horrors of the Red Terror.
|
1918
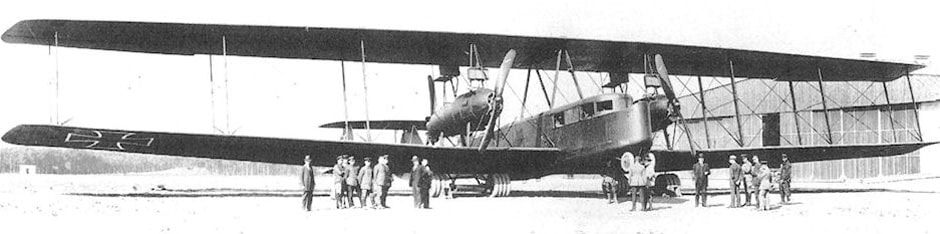
German Zeppelin-Staaken R.VI giant bomber
prisoners of war from various Allied nations
|
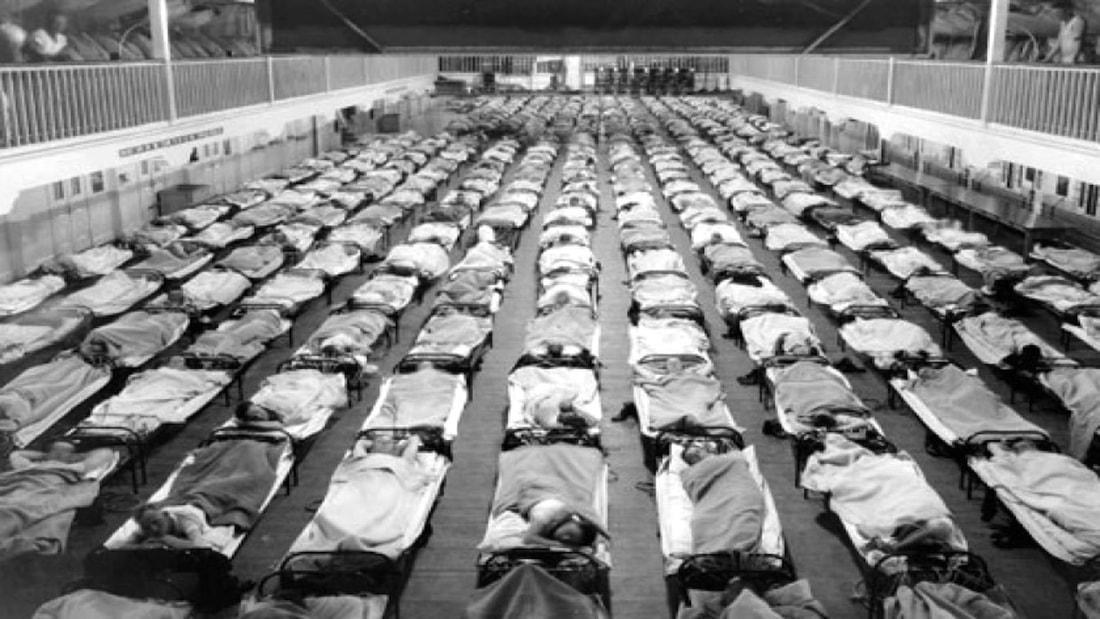
Soldiers suffering during the 1918 "Spanish" flu pandemic that killed up to 100 million people worldwide, or approximately 5% of the global population.
|
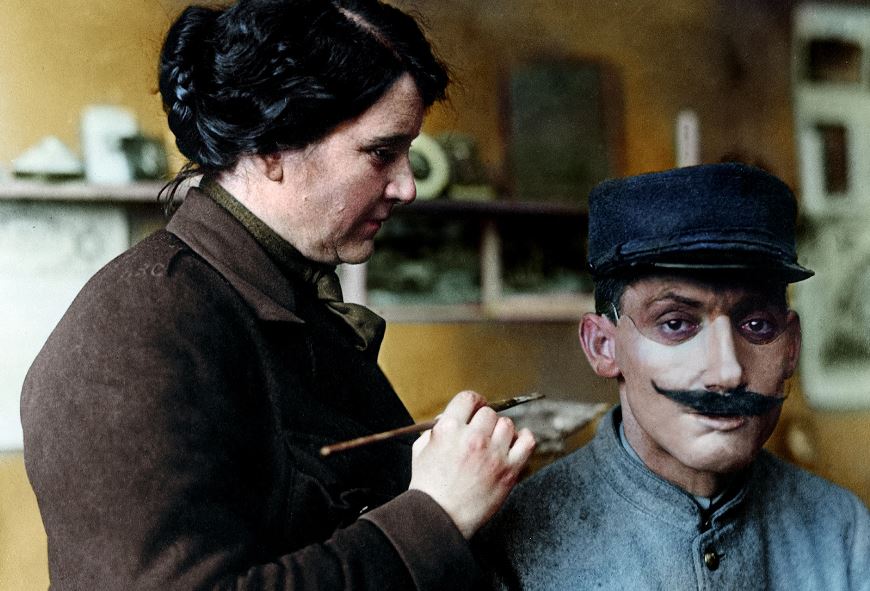
fitting for a prosthetic face covering
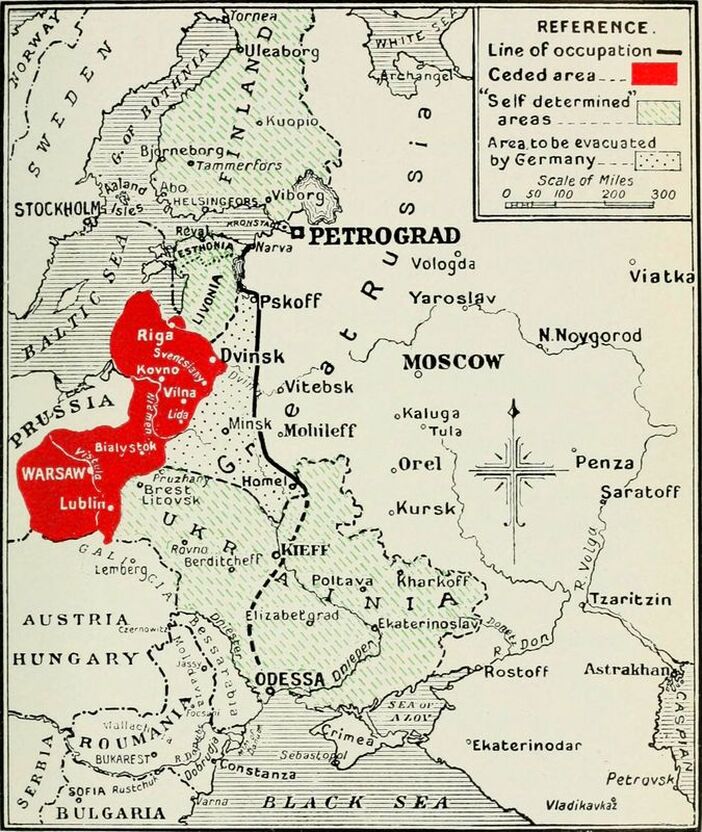
Russia surrendered in the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk following the November 1917 Bolshevik Revolution allowing Germany to turn its full might against the Western Front during the 1918 Spring Offensive.
|
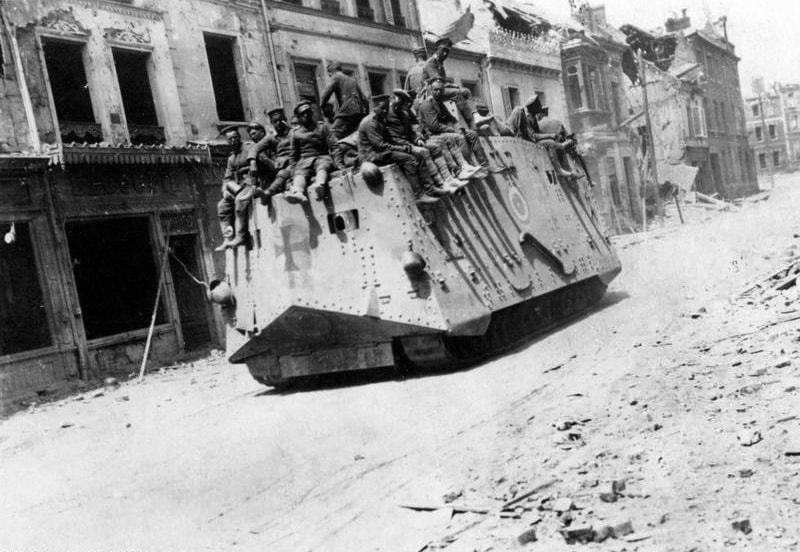
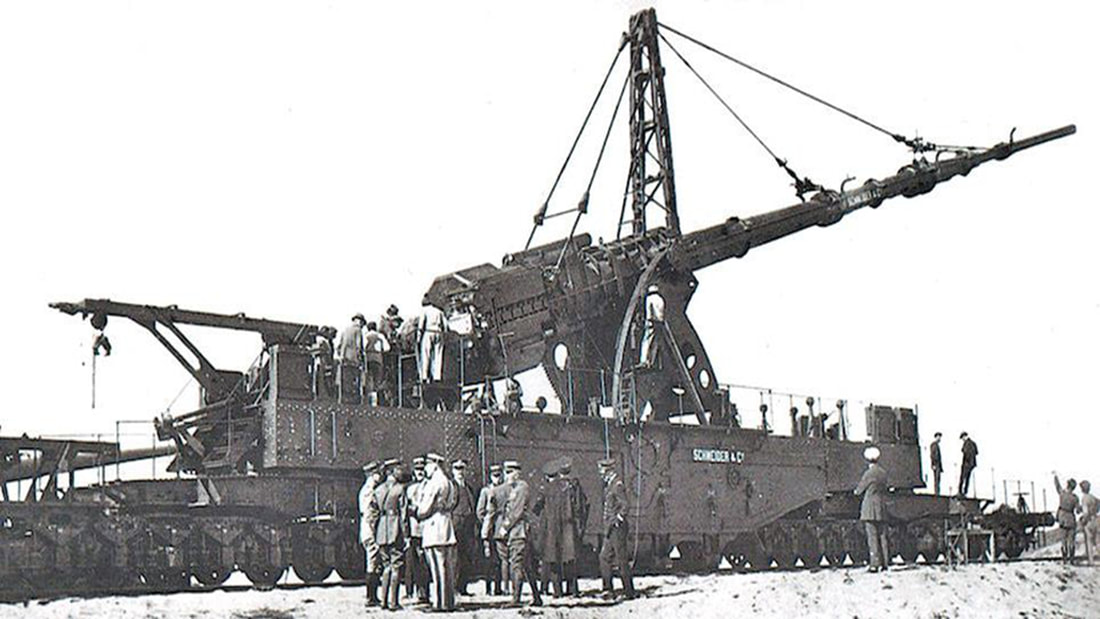
Despite immense fire power from weapons like the Paris Gun and the A7V tank, the Germans failed to breakthrough Allied defenses. In summer 1918, they fell back to the defensive Hindenburg Line as the Allies, fresh with American reinforcements, went on the Hundred Days Offensive. By November, the Germans were exhausted and asked for an Armistice after the German Revolution overthrew the Kaiser.
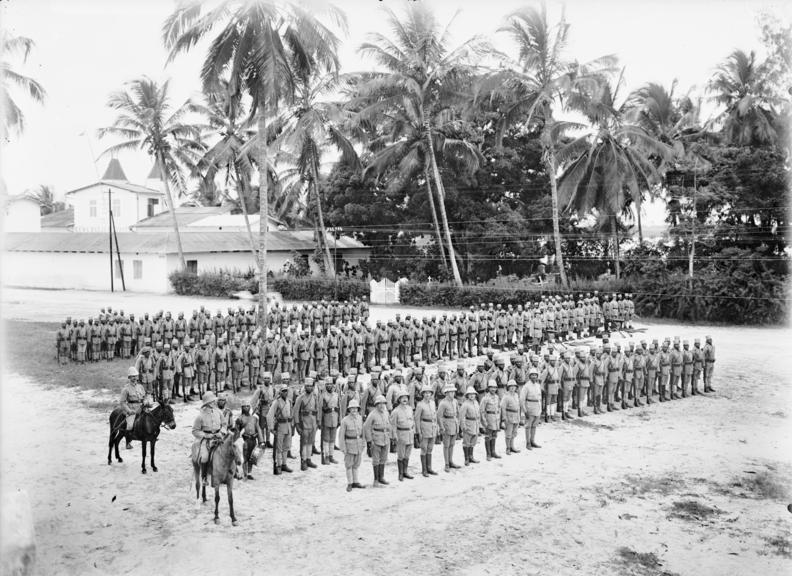
German General Paul von Lettow-Vorbeck, the Lion of Africa, harassed 300,000 Allied troops in East Africa with just 14,000 guerrilla fighters. He surrendered two weeks after the war ended in Europe.
|
The Great War, 1917-1918 Quizlet (comprehensive)
The Great War, 1917-1918 Quizlet (abridged)
|
Peace
Objectives:
- Explain how the developments of World War I changed political and diplomatic interactions between and among nations.
- Explain how and why the settlement of World War I failed to effectively resolve the political, economic, and diplomatic challenges of the early 20th century.
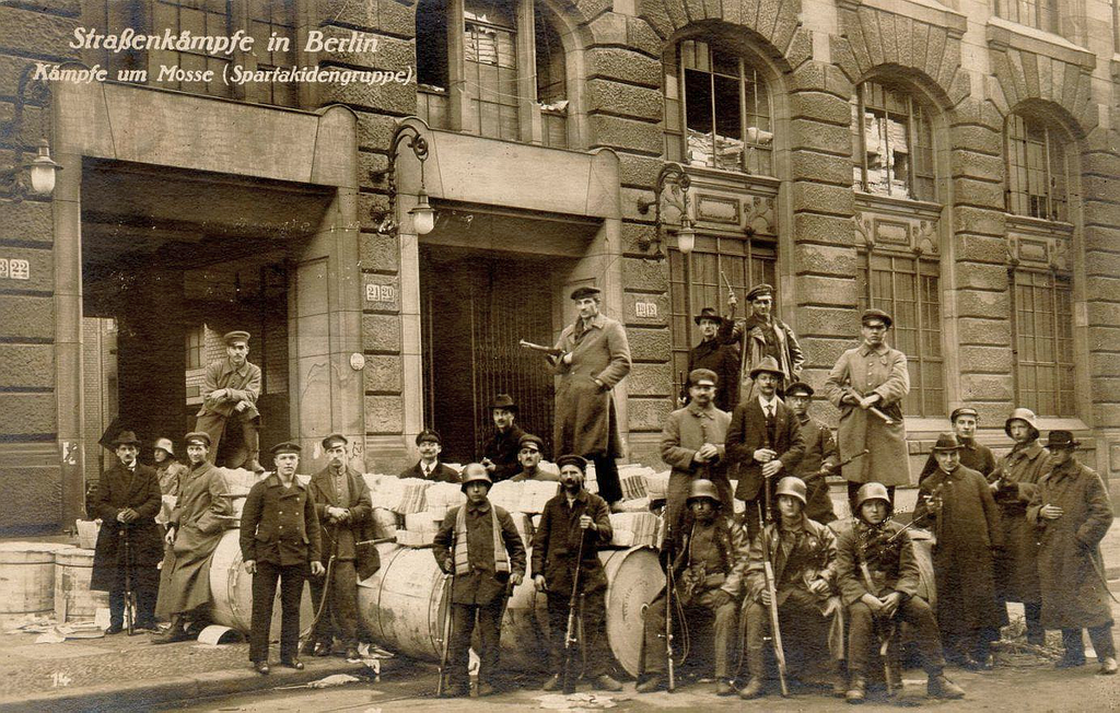
In January 1919, communists tried to seize power in Germany during the failed Spartacist Uprising.
|
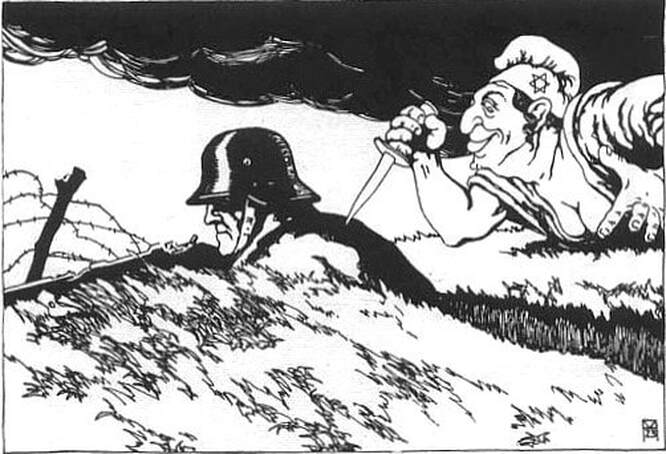
When the fighting ended, the stab-in-the-back myth emerged among German right-wing militants, a dangerous narrative that the German armed forces were not defeated in the field but were betrayed by communists, socialists, and Jews at home - the so-called "November criminals."
|
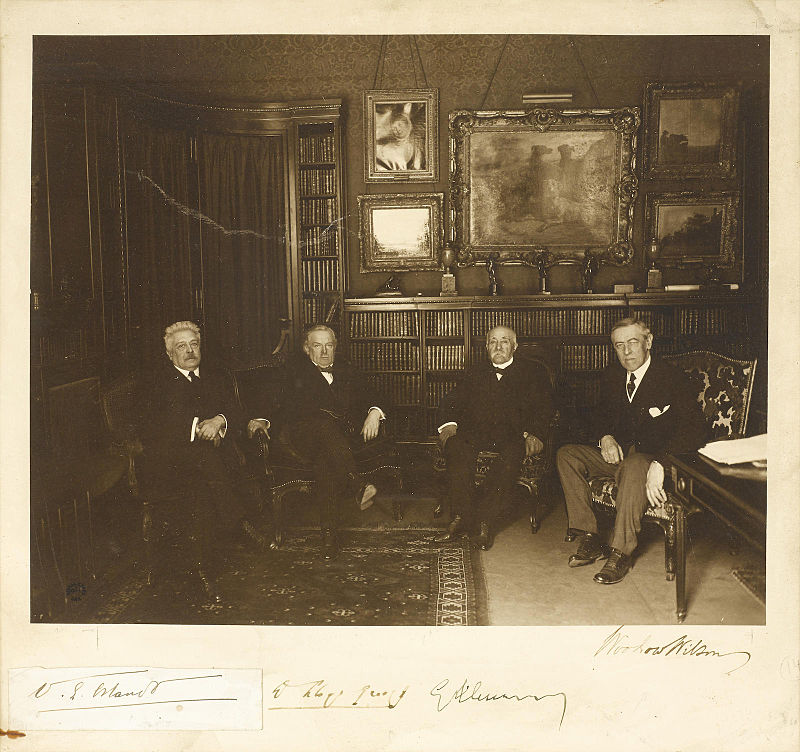
"The Big Four" - David Lloyd George of Britain, Vittorio Orlando of Italy, Georges Clemenceau of France, and Woodrow Wilson of the U.S. - made all the major decisions at the Paris Peace Conference.
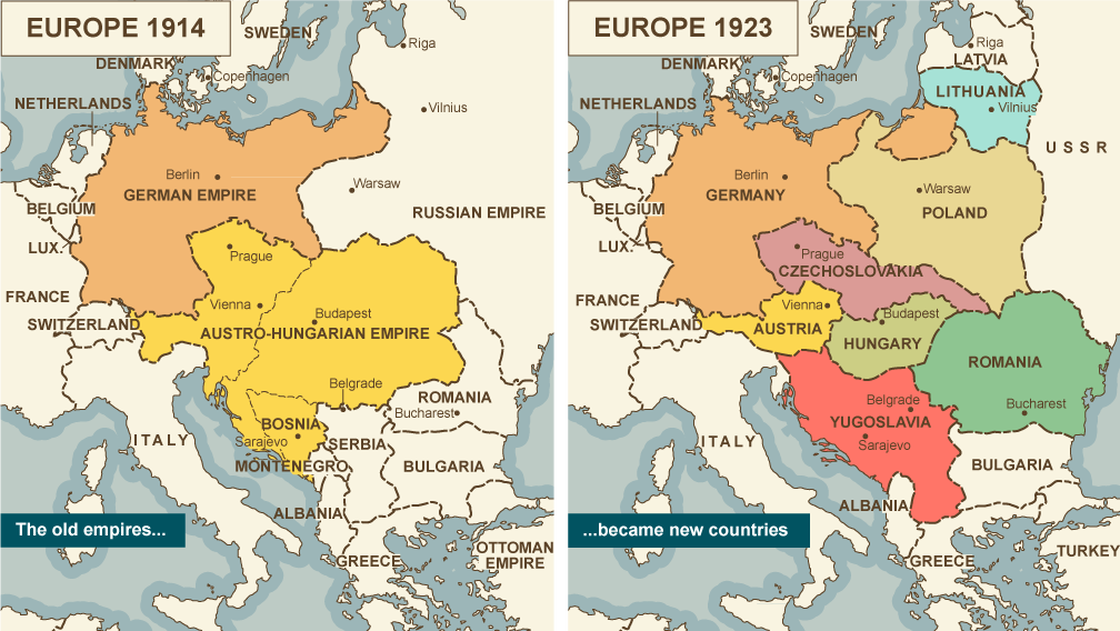
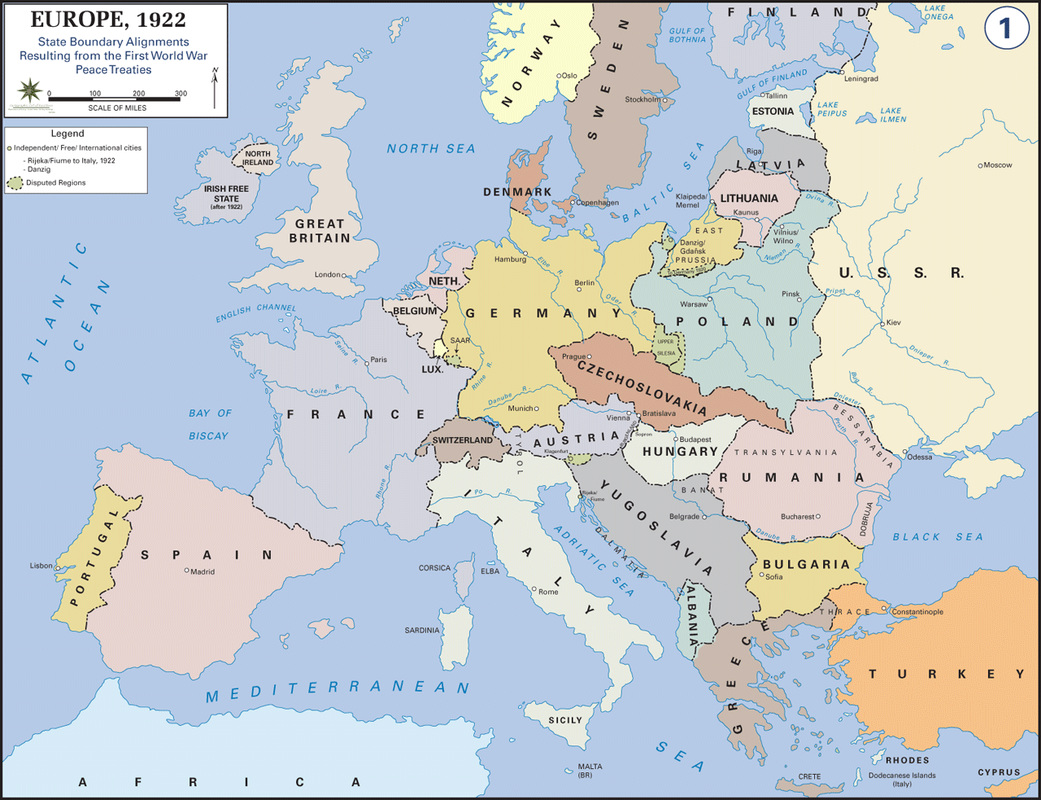
The German, Austro-Hungarian, Russian, and Ottoman Empires collapsed. Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Czechoslovakia, and Hungary emerged as new nation-states. Serbia was awarded control of Bosnia, Montenegro, Croatia, and Slovenia to become the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. Romania invaded newly-independent Hungary and seized much of its territory. In the Middle East, Syria, Lebanon, Iraq, Palestine, and Transjordan became League of Nations mandates. Britain, France, and Belgium took control of Germany's African colonies while Japan took control of Germany's Pacific islands.
|
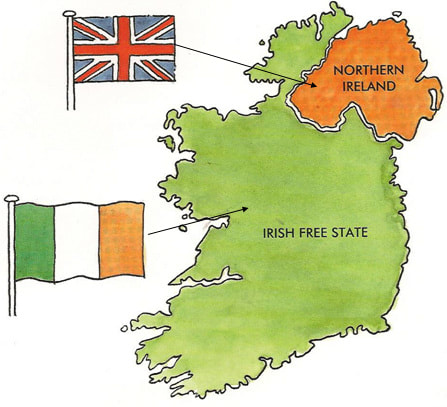
Fighting during the Irish Civil War. In 1922, majority-Catholic southern Ireland won independence as the Irish Free State. Majority-Protestant Northern Ireland remained part of the United Kingdom.
|
|
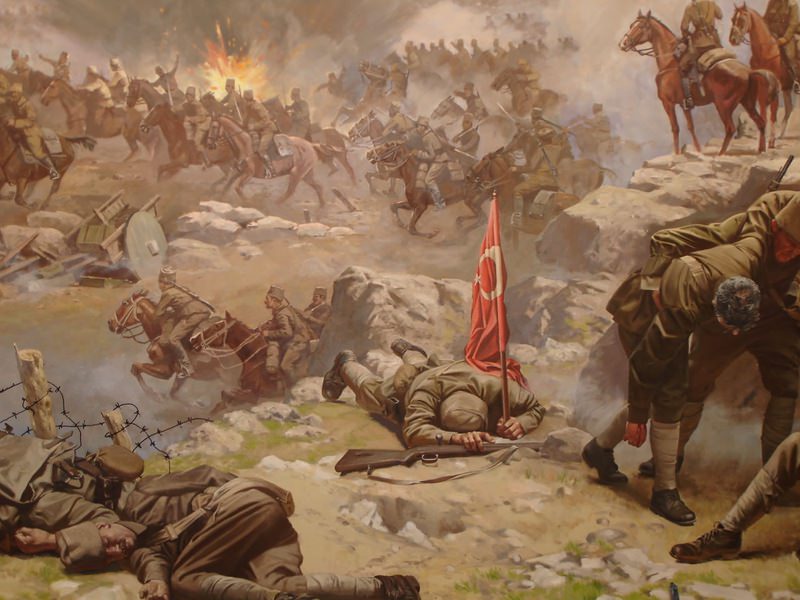
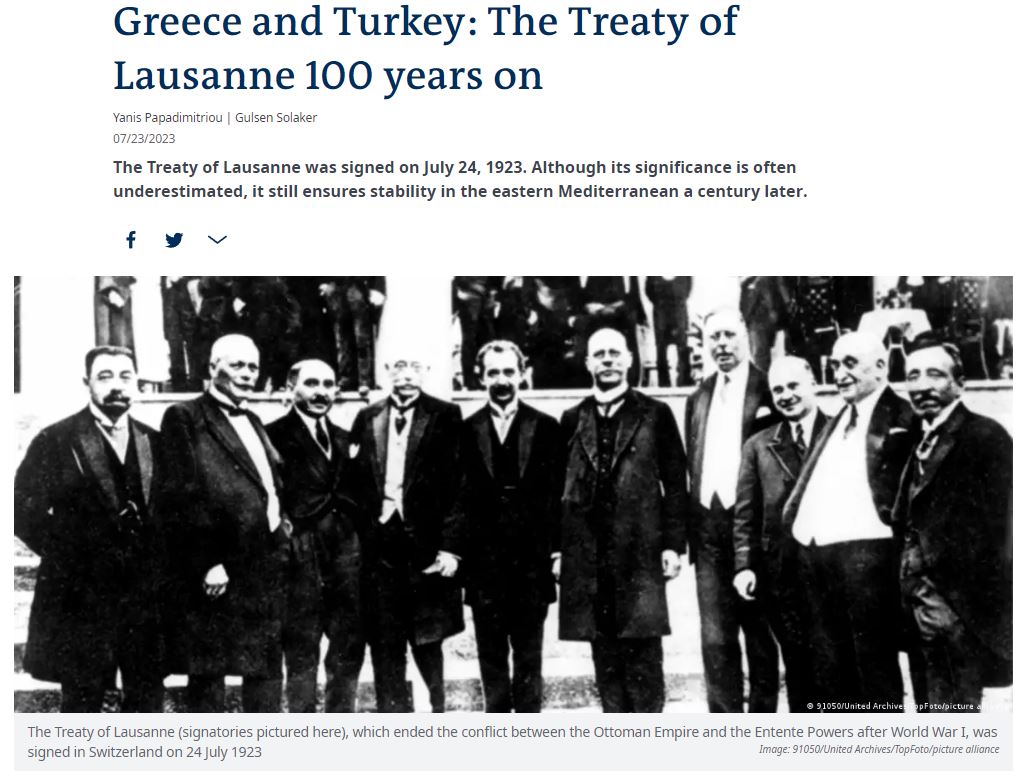
The Allies carved Turkey up in the Treaty of Sèvres. Allied occupation forces were defeated during the Turkish War of Independence.
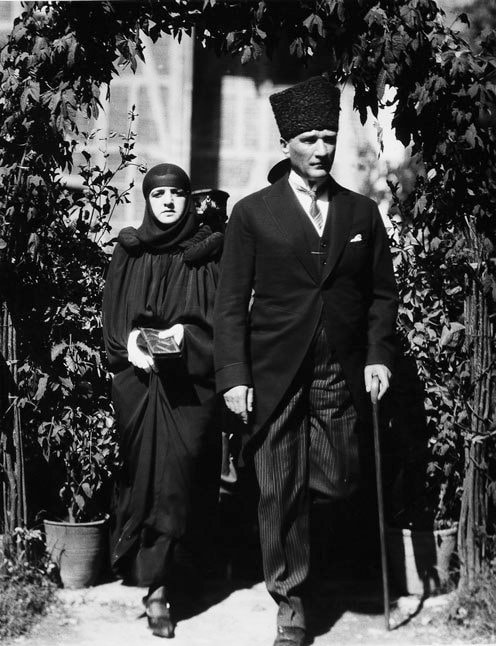
Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, founder and first president of the Republic of Turkey (1923-1938) transformed Turkey into a progressive, secular, industrial nation.
|
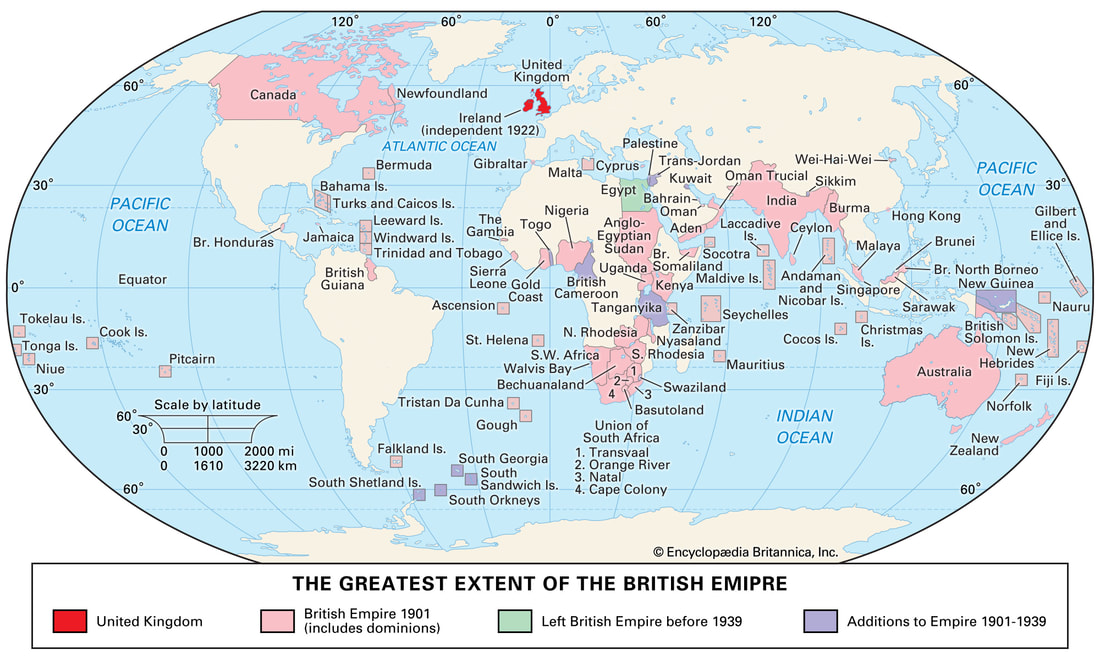
Though greatly weakened by the First World War, the British Empire reached its greatest territorial size afterward.
|
Peace Quizlet (comprehensive)
Peace Quizlet (abridged)
|
The Lost Generation
Objective: Explain how the events of the first half of the 20th century challenged existing social, cultural, and intellectual understandings.
- The widely held belief in progress characteristic of much of 19th-century thought began to break down before World War I.
- When World War I began, Europeans were generally confident in the ability of science and technology to address human needs and problems despite the uncertainty created by the new scientific theories and psychology.
- The challenge to the certainties of the Newtonian universe in physics opened the door to uncertainty in other fields by undermining faith in objective knowledge while also providing the knowledge necessary for the development of nuclear weapons and power.
- World War I created a “lost generation” and fostered disillusionment and cynicism, while it transformed the lives of women, and democratized societies
Literature
Architecture
Visual Arts
Music and Dance
|
Berlin cabarets captured the wild, decadent spirit of the 1920s.
|
The Blue Angel (1930) made Marlene Dietrich one of the earliest international movie stars.
|
The Machine Age
The Graf Zeppelin traveled more than a million miles during 590 flights around the world during the 1920s and 1930s.
|
In 1944 the German V-2 became the first long-range ballistic missile.
|
|
The Lost Generation Quizlet (comprehensive)
The Lost Generation Quizlet (abridged)
|