AP World History: Modern
Course Overview
|
Dave Phillips
email: [email protected] website: www.accordingtophillips.com office hours: 2:30-3:30 PM Tuesdays and Thursdays Google Classroom:
Remind: @kgkd83 |
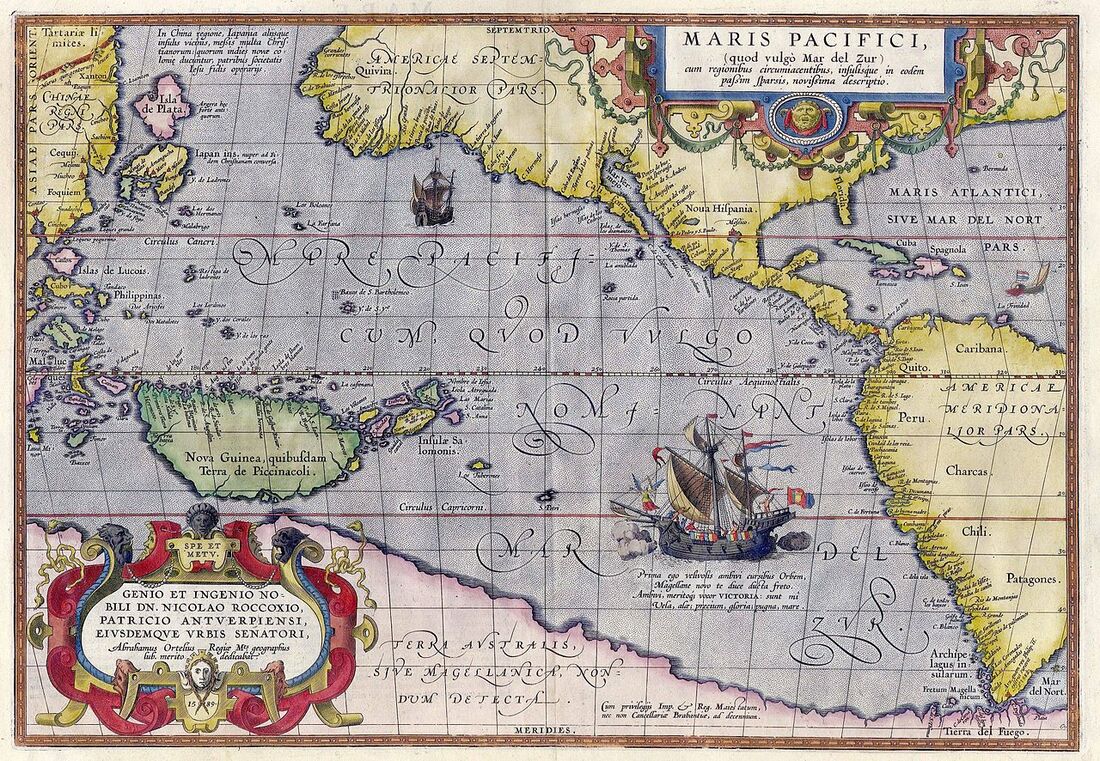
AP World History: Modern is an introductory college-level survey of modern world history. It investigates significant events, individuals, developments, and processes from 1200 to the present.
The course focuses on cultural developments, political and economic systems, social interactions, technological innovation, and people and their environments. Students develop and use skills used by historians, analyze sources, build arguments, make connections, and think about continuity and change over time. Students should be able to read a college-level textbook and write grammatically correct, complete sentences. College Board AP Exam Information
See here for details about the College Board AP World History Exam. |
Contents
Course Goals
|
Course Outline
The course covers four time periods organized into 14 units.
Global Regions, c. 1200-1450
Global Interactions, c. 1450-1750
|
|
Global Empires, c. 1750-1900
|
|
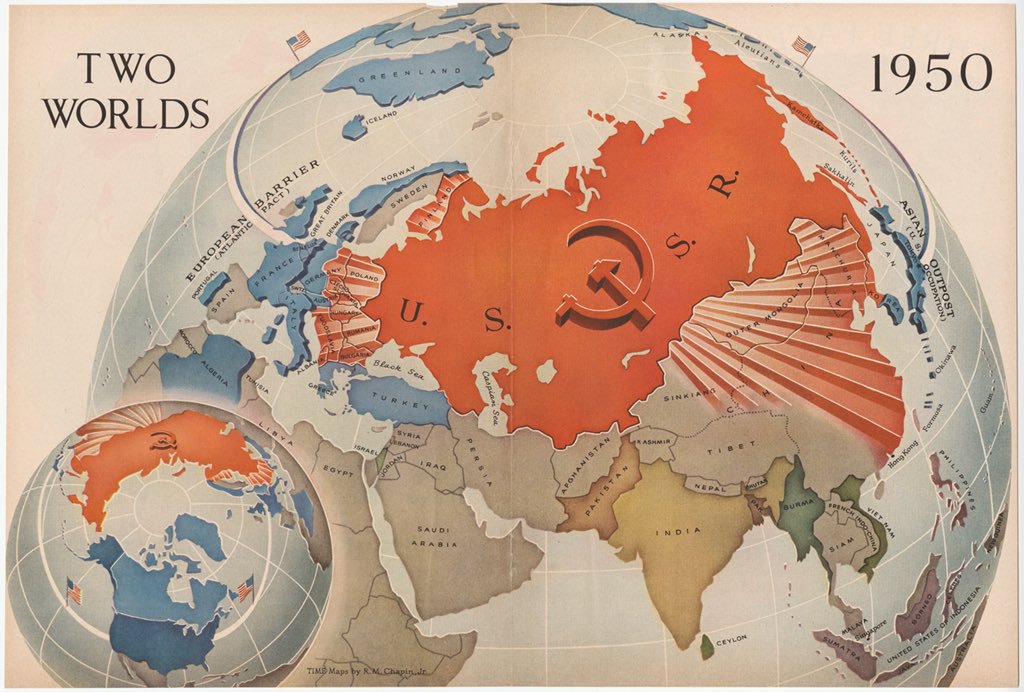
Global Challenges, c. 1900-Today
|
|
Course Themes
Politics
|
Thematic Overview Worksheet
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| thematic_overview_worksheet.pdf | |
| File Size: | 92 kb |
| File Type: | |
Historical Thinking Skills
Chronological Reasoning
Comparison and Contextualization
Crafting Historical Arguments from Historical Evidence
Historical Interpretation
|
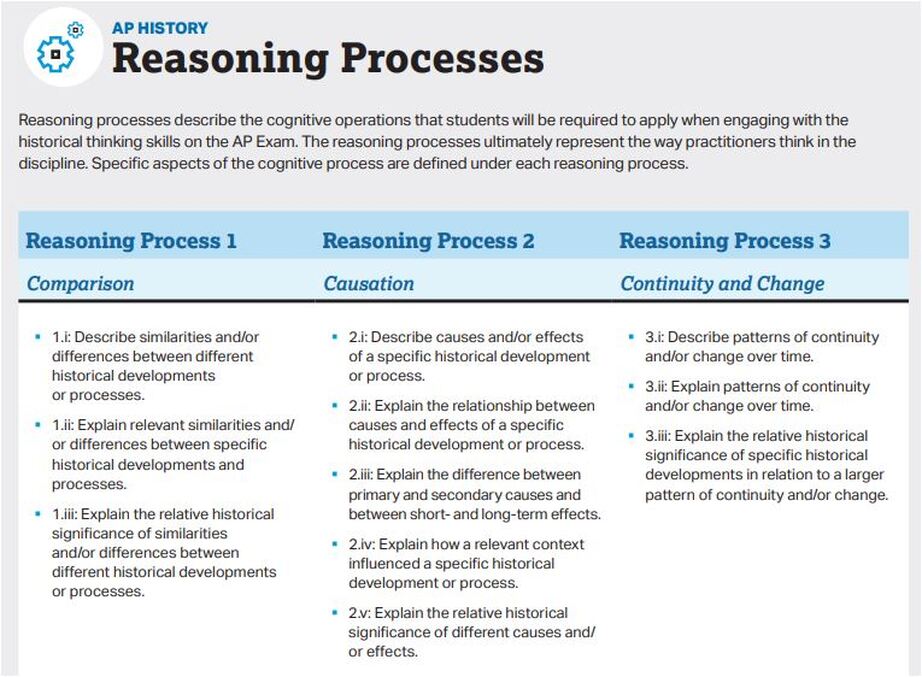
The table below presents the historical reasoning processes students should develop in AP history courses. Every AP history exam question will assess one or more of these skills.
The table below presents the historical thinking skills students should develop in AP history courses. Every AP history exam question will assess one or more of these skills.