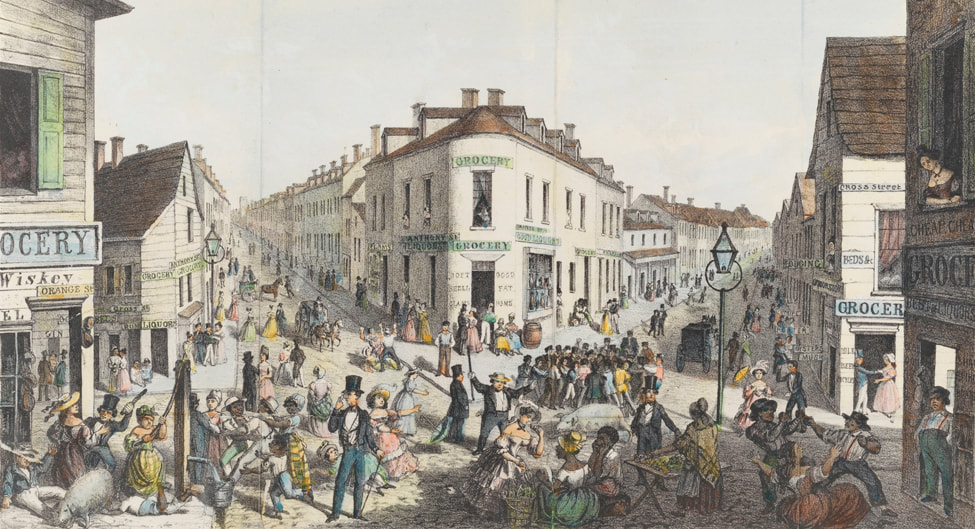Industrialization
c. 1750-1900
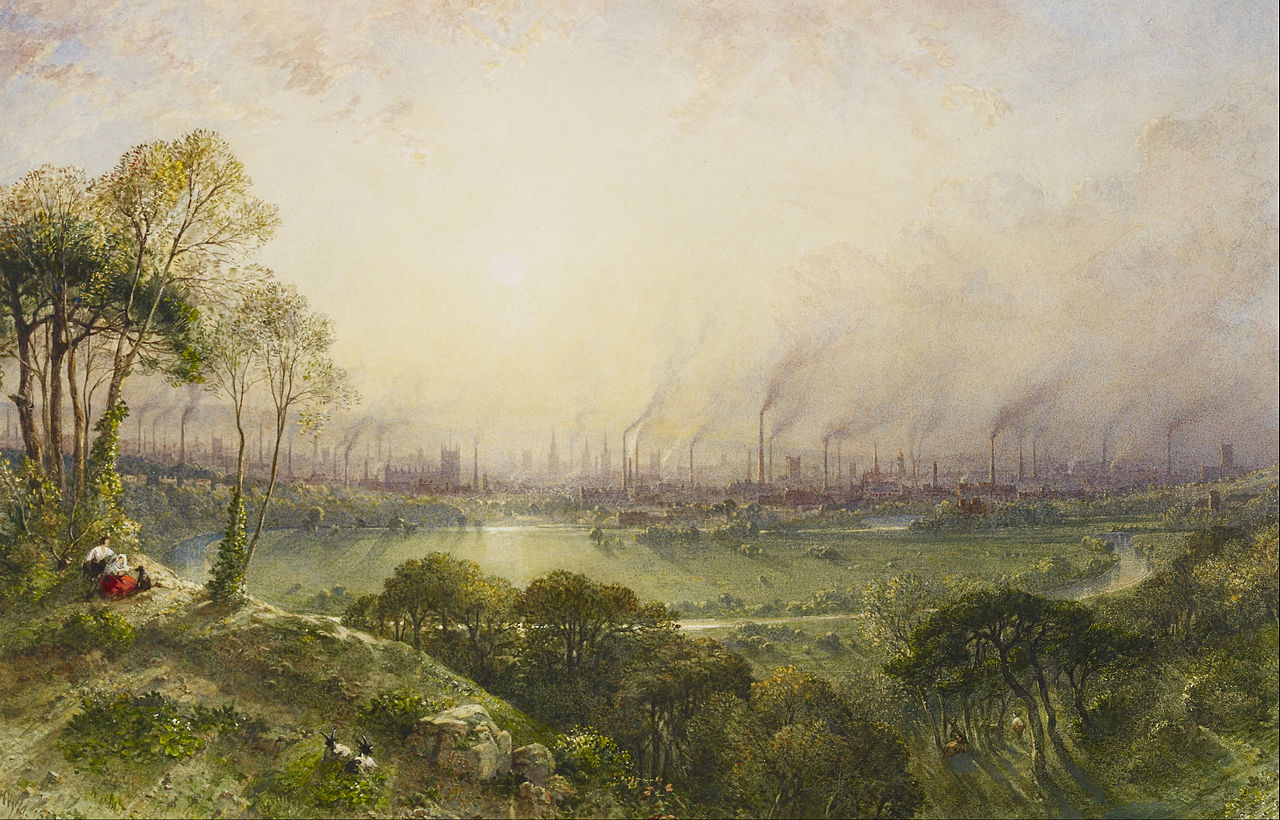
Manchester from Kersal Moor, by William Wyld in 1857, a view dominated by chimney stacks as a consequence of the Industrial Revolution.
Contents
Industrialization, c. 1750-1900:
Objectives
- Explain how environmental factors contributed to industrialization from 1750 to 1900.
- Explain how different modes and locations of production have developed and changed over time.
- Explain how technology shaped economic production over time.
- Explain the causes and effects of economic strategies of different states and empires.
- Explain the development of economic systems, ideologies, and institutions and how they contributed to change in the period from 1750 to 1900.
- Explain the causes and effects of calls for changes in industrial societies from 1750 to 1900.
- Explain how industrialization caused change in existing social hierarchies and standards of living.
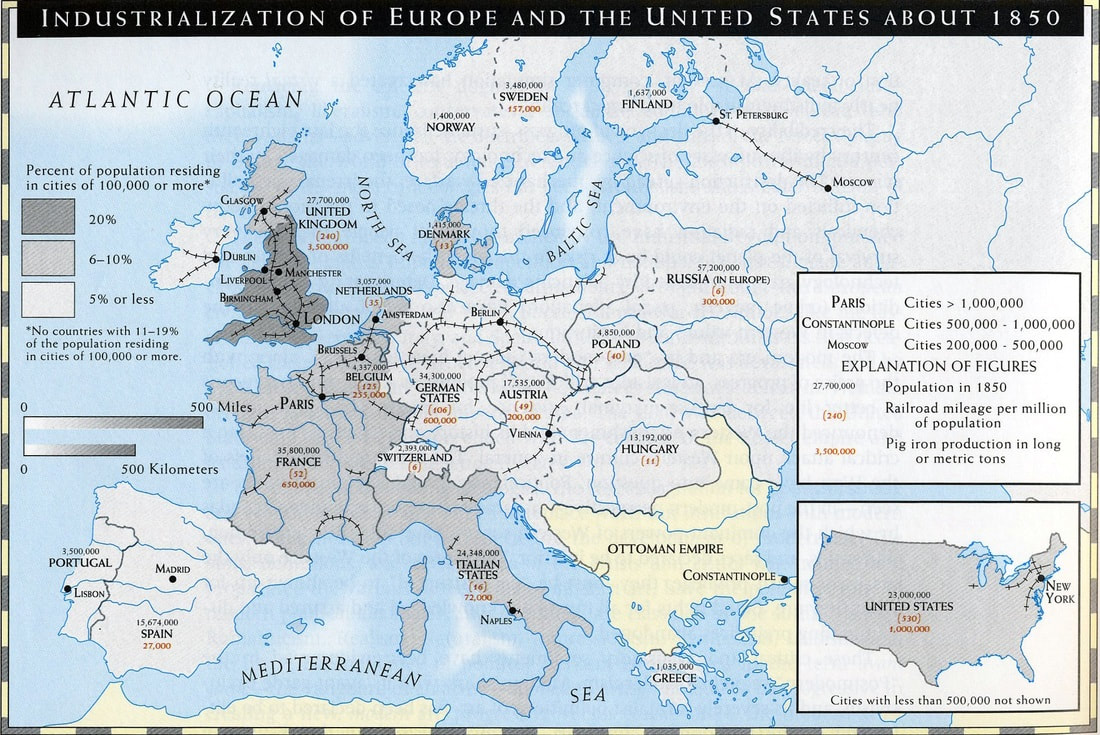
The Factory System
The first World's Fair, the Great Exhibition of the Works of Industry of All Nations held at the Crystal Palace, London in 1851, housed 14,000 displays of industrial equipment from 25 countries.
|
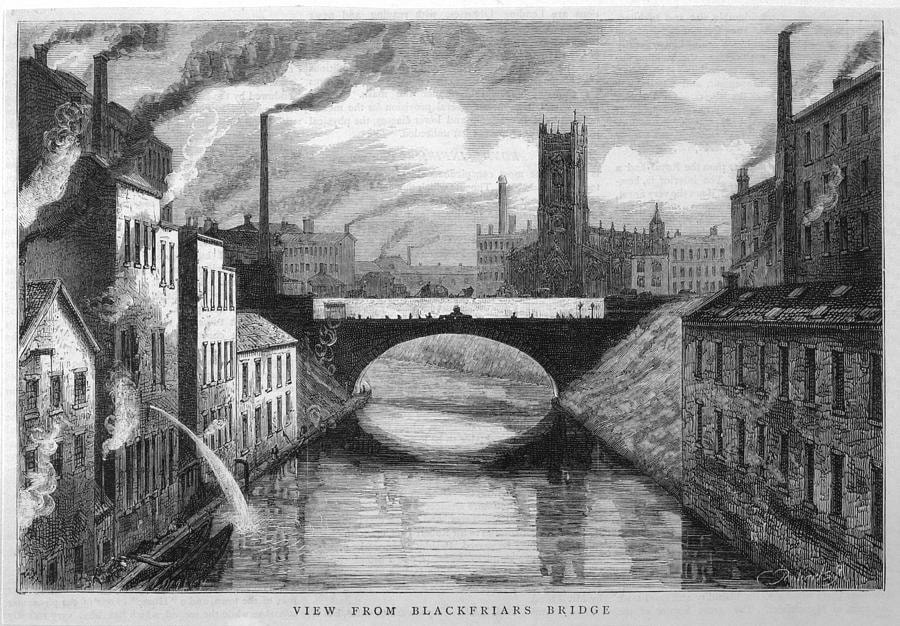
Industrial Manchester, England, c. 1844
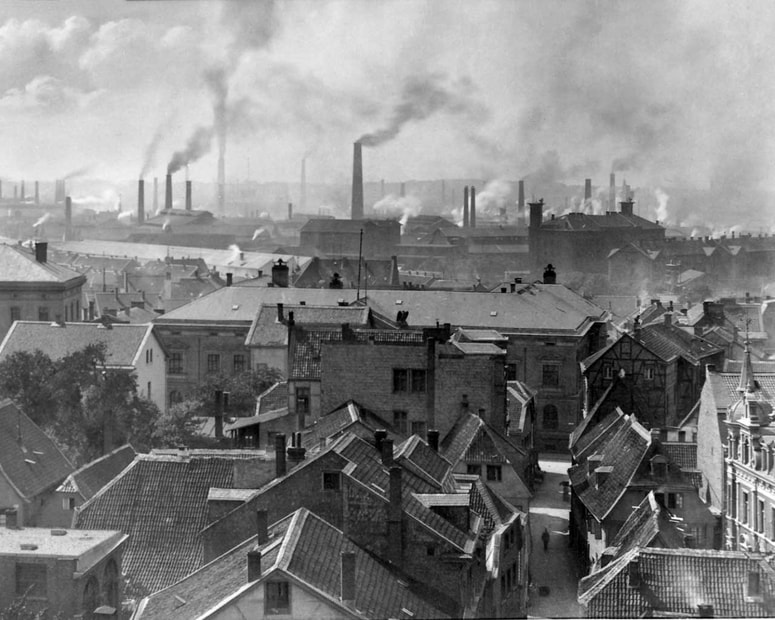
Essen, Germany, 1890
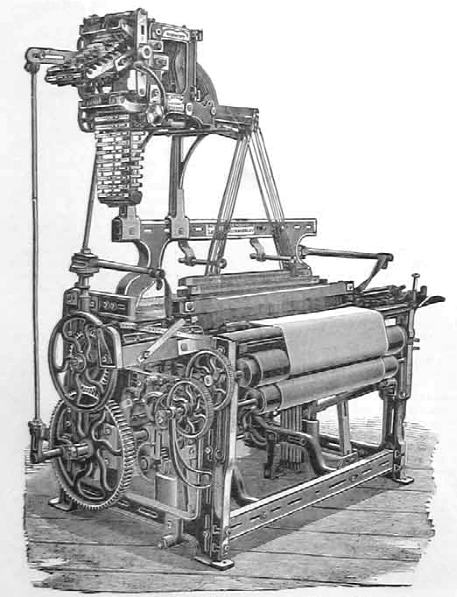
1890s loom
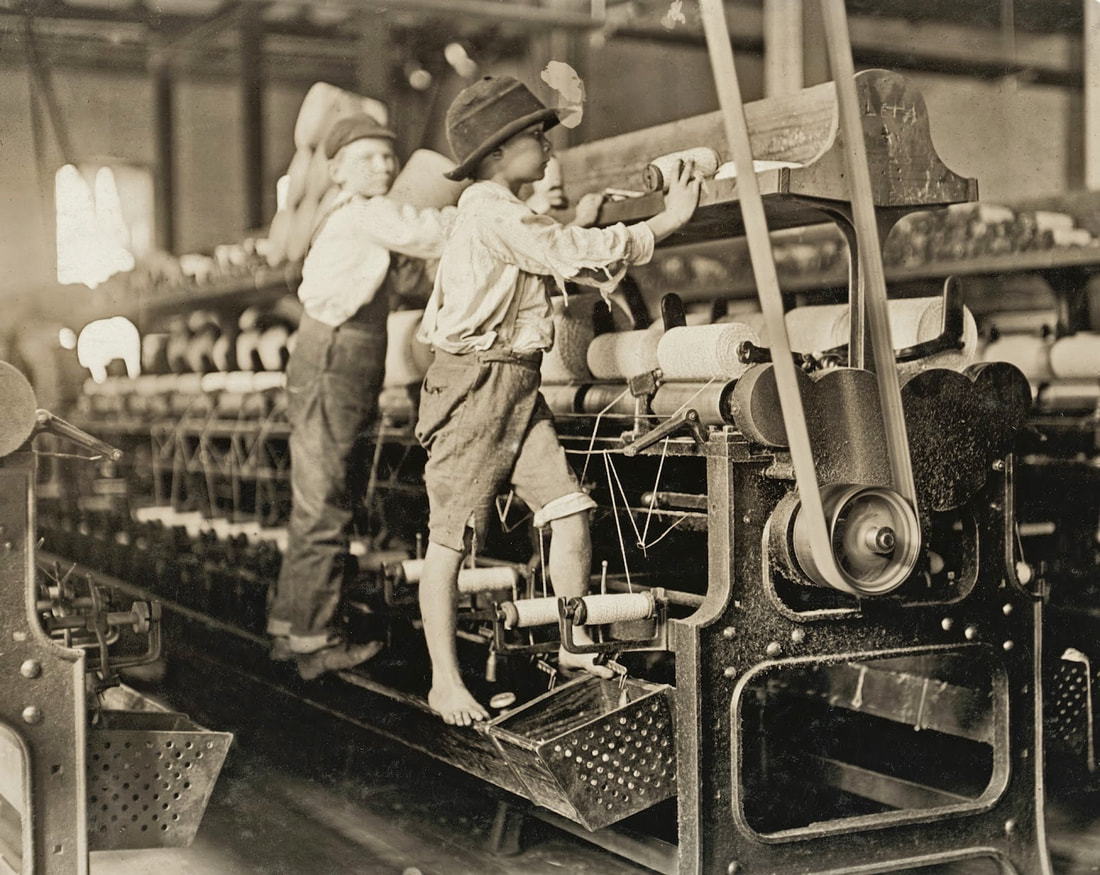
child workers in a textile mill, Macon, Georgia, 1909
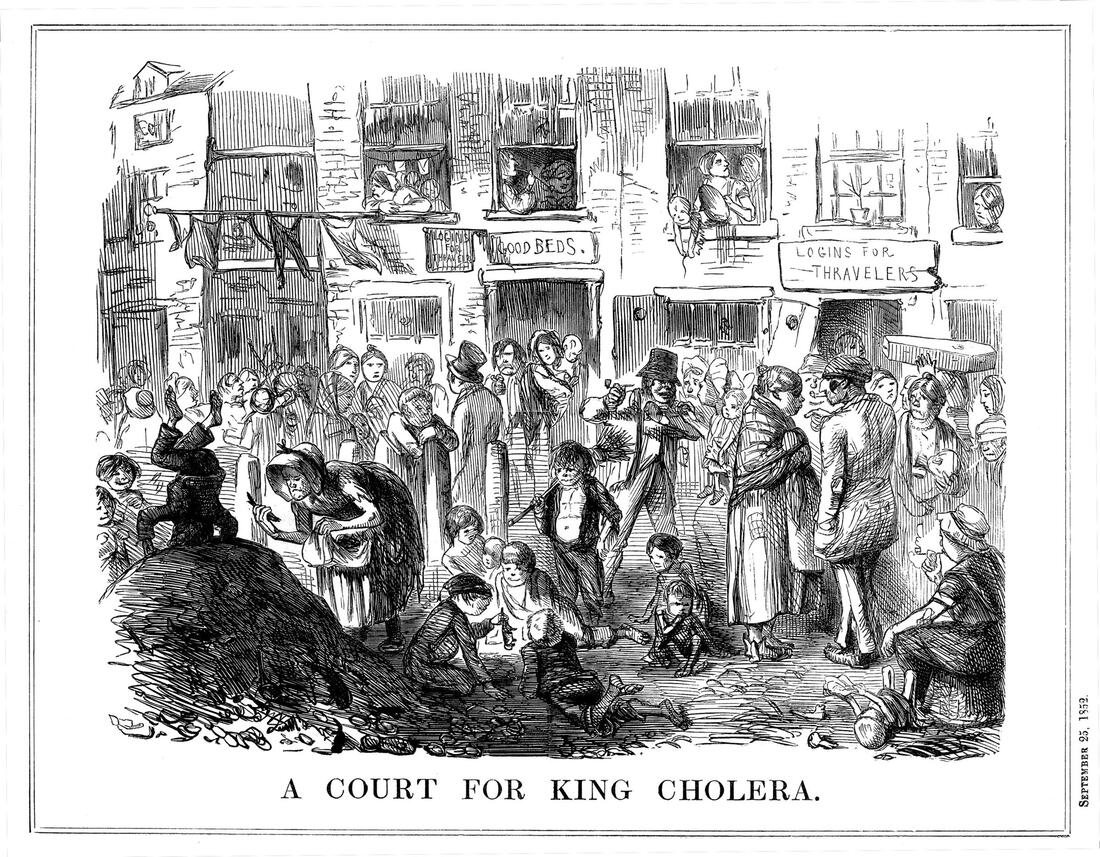
Five Points, New York City was one of the slummiest slums that ever slummed.
|
audio pronunciation guide:
|
|
The Factory System (comprehensive)
The Factory System (abridged)
|
The Second Industrial Revolution
|
Skyscrapers designed by William Le Baron Jenney, Louis Sullivan, and Daniel Burnham transformed American cities.
|
Assembly line production at Ford Motor Company plants greatly increased efficiency of manufacturing.
|
|
The Second Industrial Revolution (comprehensive)
The Second Industrial Revolution (abridged)
|
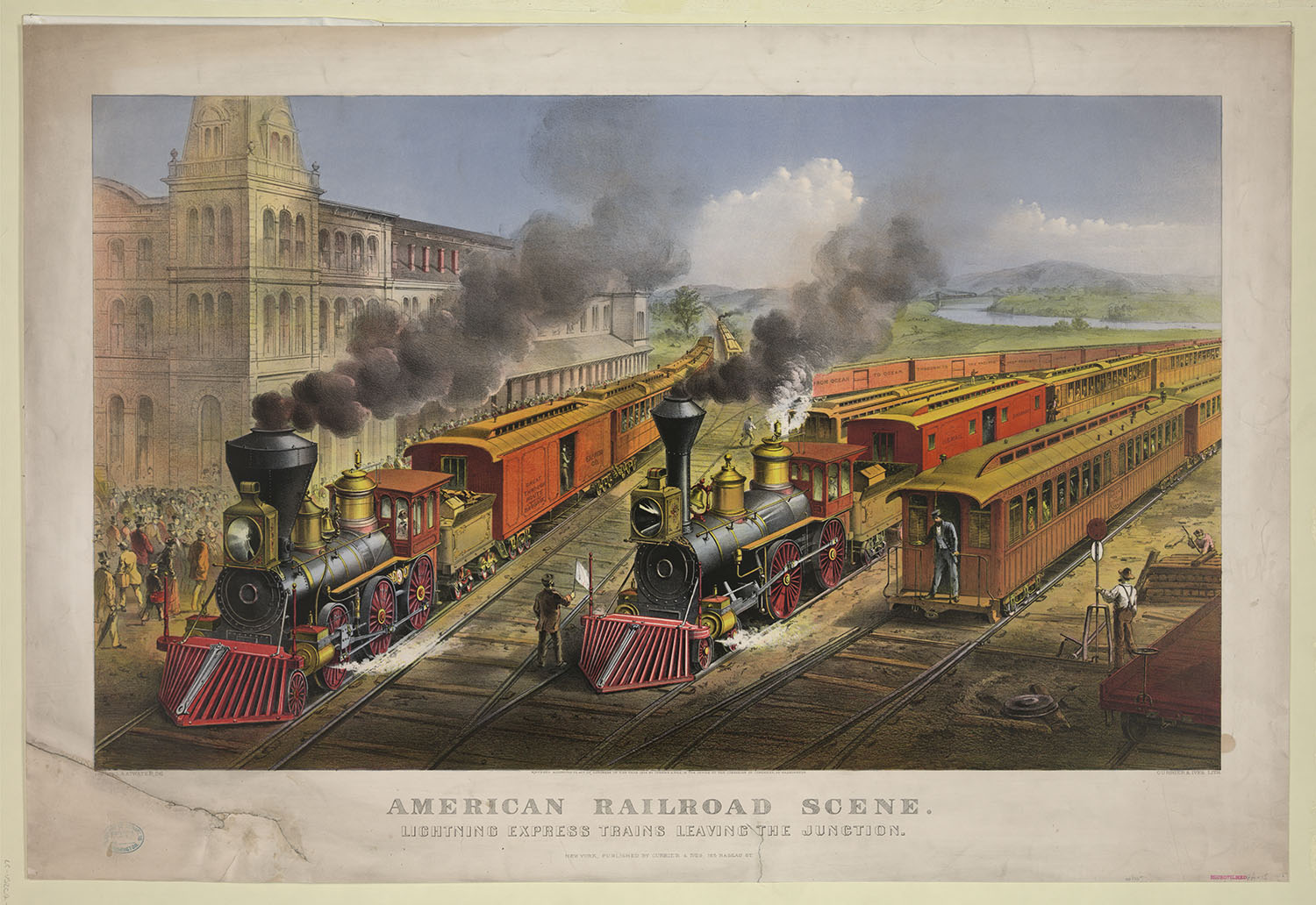
Transportation, Communication, and Financial Networks
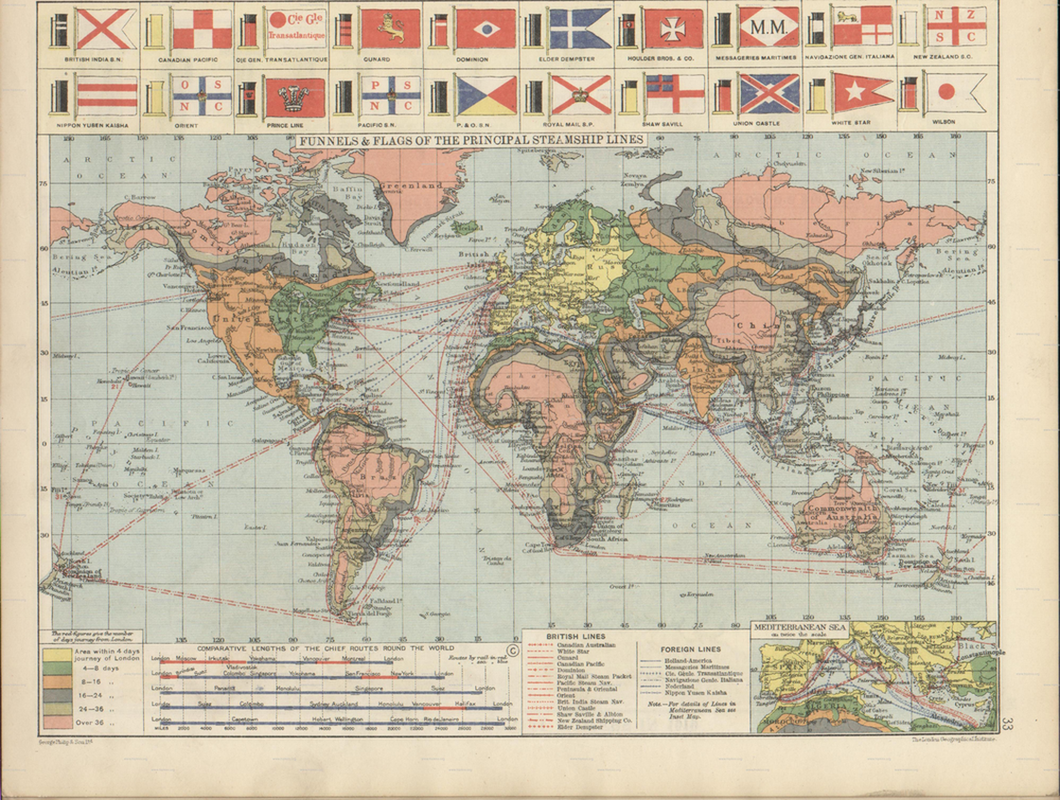
global steamship routes, c. 1920
|
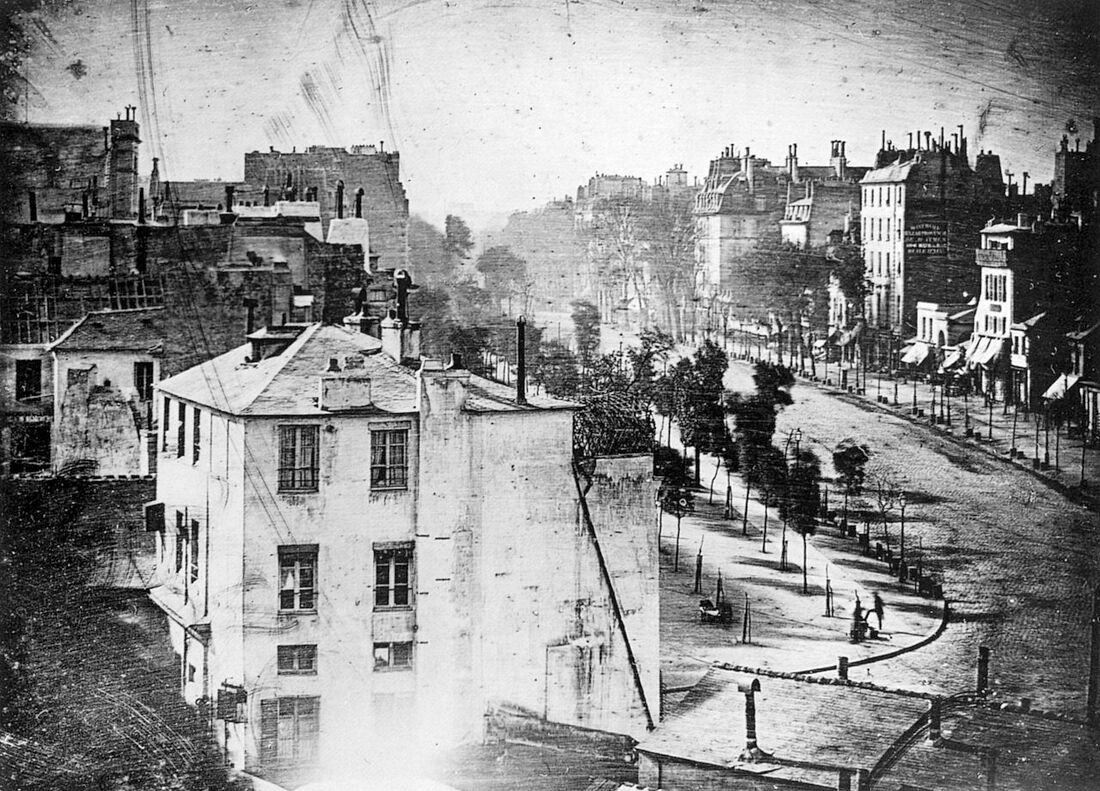
View of the Boulevard du Temple, taken by Daguerre in 1838 in Paris, includes the earliest known photograph of a person.
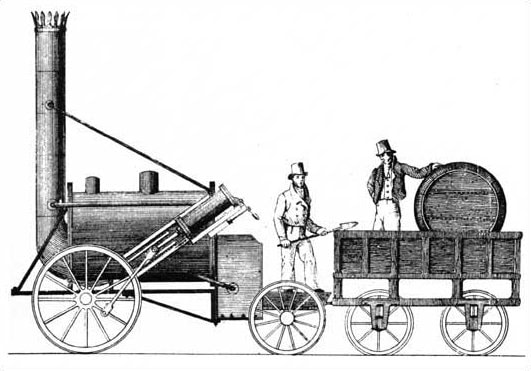
George Stephenson's Rocket amazed onlookers when it sped along the Liverpool and Manchester Railway at 16 miles per hour in 1829.
Brazilian aviation pioneer Alberto Santos Dumont circling the Eiffel Tower in 1901.
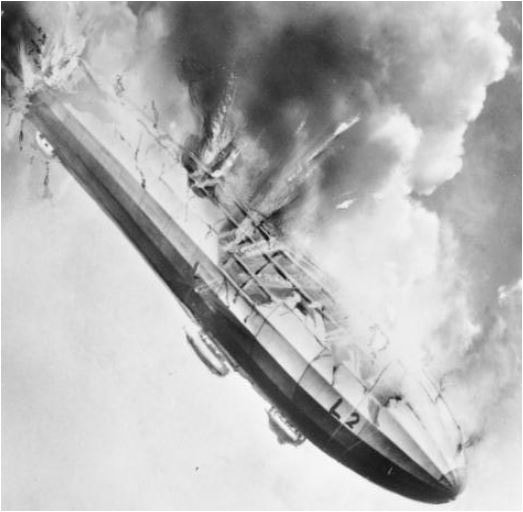
Early airships like the German Zeppelin LZ 18 (L 2), pictured here in 1913, were filled with highly flammable hydrogen gas.
Guglielmo Marconi demonstrates radio.
Thomas Cook & Co. guided tourists around the world.
|
audio pronunciation guide:
France during La Belle Epoque at the turn of the 20th century
|
|
Transportation, Communication, and Financial Networks (comprehensive)
Transportation, Communication, and Financial Networks (abridged)
|
Social Class and Labor Movements
|
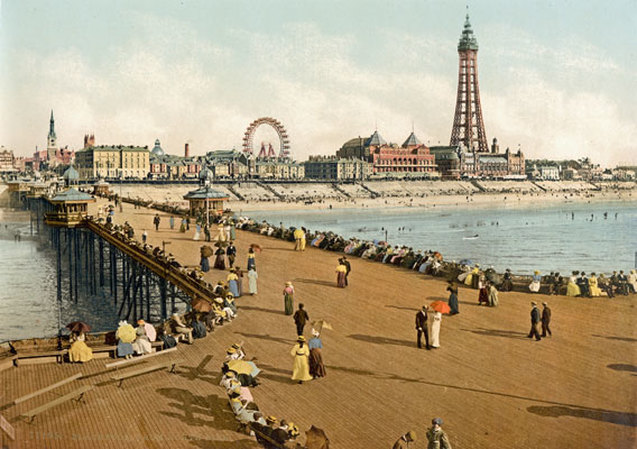
Blackpool was a Victorian-era beach side resort which offered the middle and working classes all the entertaining marvels of the Modern Age.
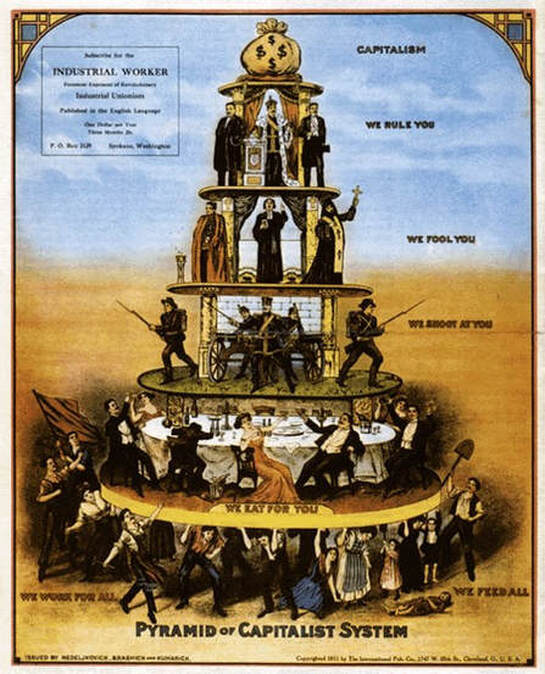
Socialists despised capitalism as unjust suppression of the working class masses.
|
audio pronunciation guide:
|
|
Social Class and Social Reform (comprehensive)
Social Class and Social Reform (abridged)
|