Asia
c. 1200-1450
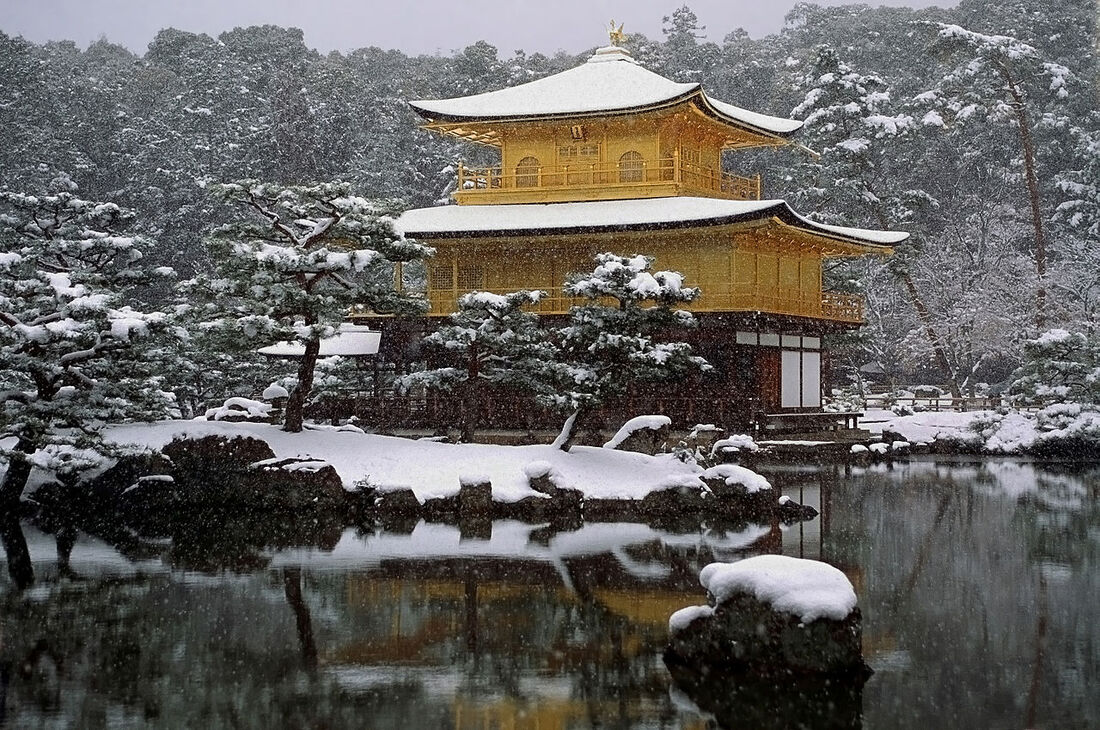
Kinkakuji Zen Buddhist temple in Kyoto, Japan
Contents
Asia, c. 1200-1450:
Objectives
- Explain how systems of belief and their practices affected society in the period from c. 1200 to c. 1450.
- Explain the systems of government employed by Chinese dynasties and how they developed over time.
- Explain the effects of Chinese cultural traditions on East Asia over time.
- Explain the effects of innovation on the Chinese economy over time.
- Explain how the various belief systems and practices of South and Southeast Asia affected society over time.
- Explain how and why various states of South and Southeast Asia developed and maintained power over time.
- Explain the causes and effects of the rise of Islamic states over time.
- Explain the effects of intellectual innovation in Dar al-Islam.
- Explain the process of state building and decline in Eurasia over time.
- Explain how the expansion of empires influenced trade and communication over time.
- Explain the significance of the Mongol Empire in larger patterns of continuity and change.
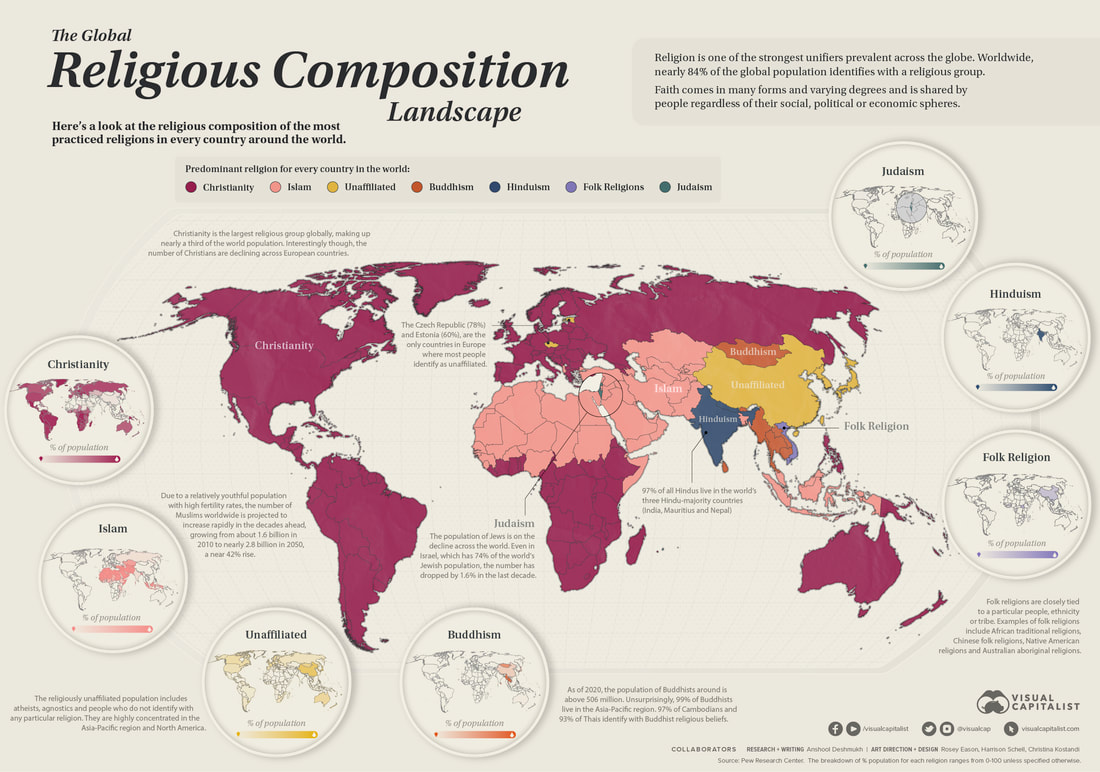
Religious Traditions
Hinduism, Buddhism, Confucianism, Daoism, and Shinto, and their core beliefs and practices, continued to shape societies in South and East Asia.
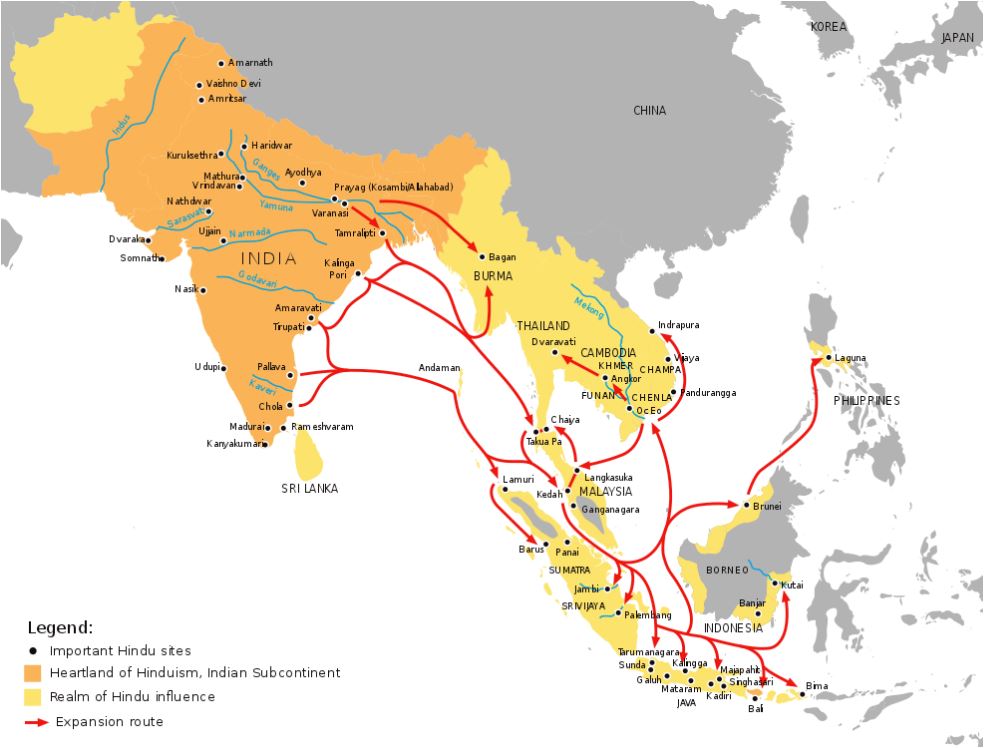
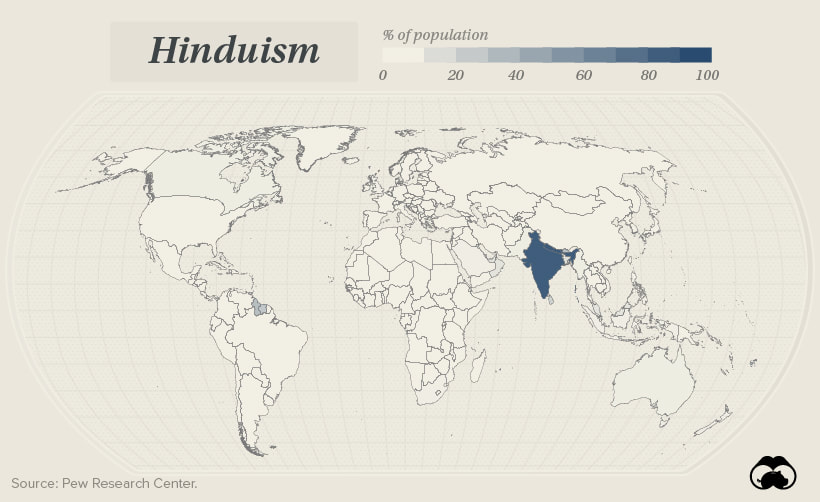
Hinduism
Spread of Hindu cultural influence
|
Hinduism in the world today
|
audio pronunciation guide:
|
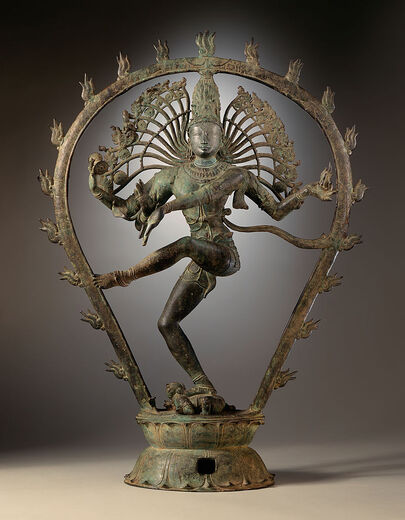
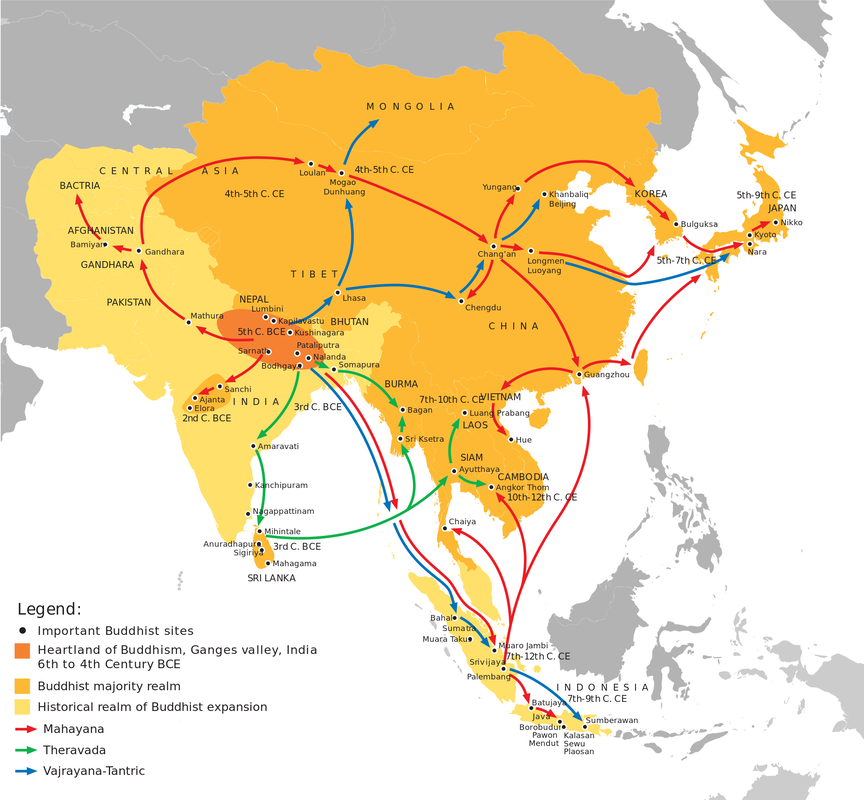
Buddhism
Spread of Buddhism
|
The Tibetan Buddhist bhavachakra, representing saṃsāra, helps ordinary people understand Buddhist teachings.
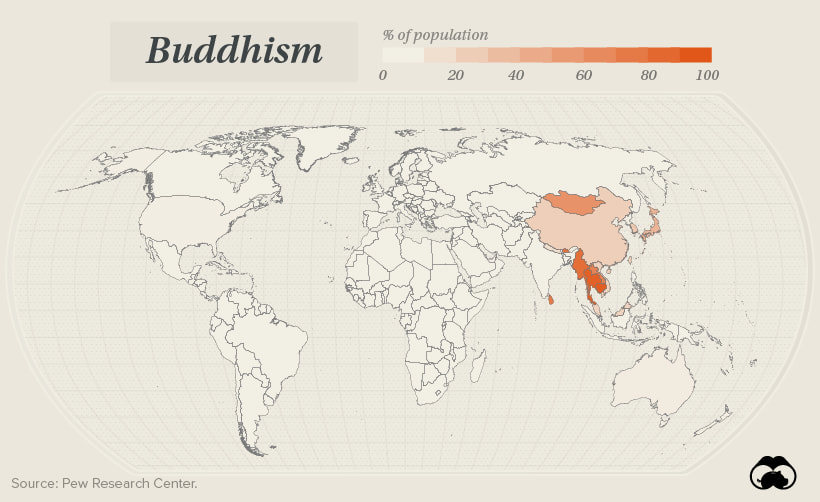
Buddhism in the world today
|
audio pronunciation guide:
|
Confucianism
|
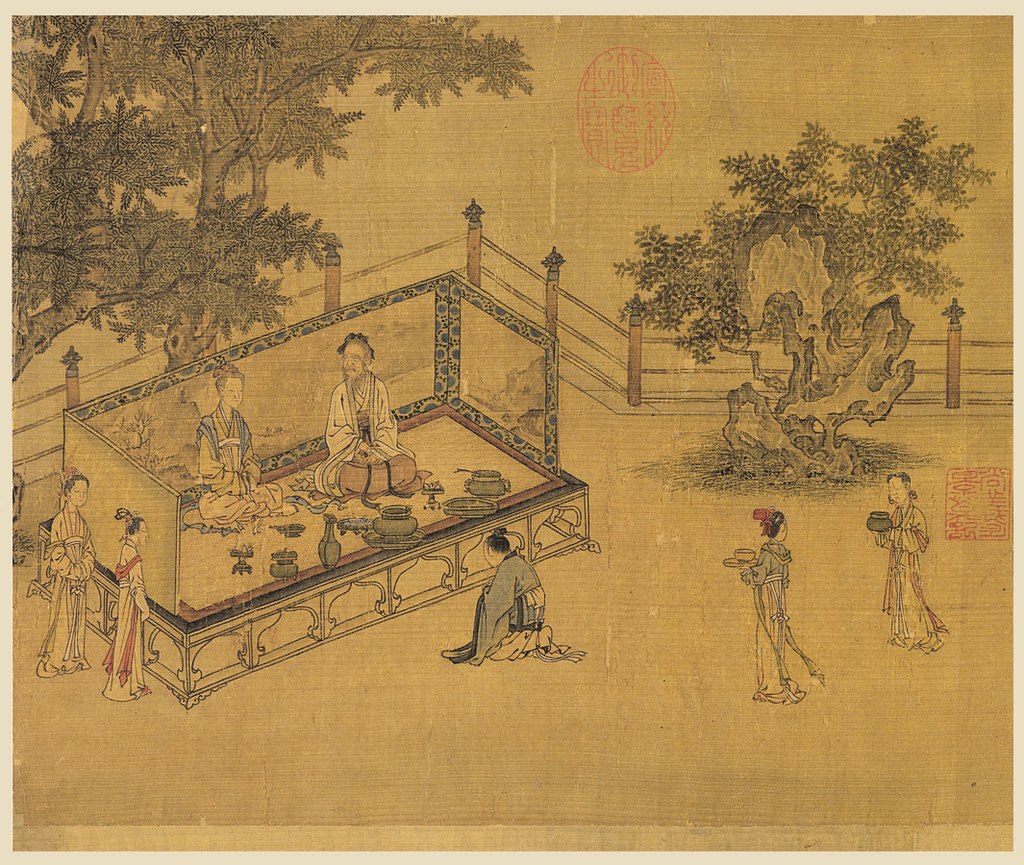
Scene from the Song Dynasty Illustrations of the Classic of Filial Piety (detail), depicting a son kneeling before his parents
|
audio pronunciation guide:
|
Daoism
Shinto
|
Amaterasu, one of the central kami in the Shinto faith
Article: Core stories of Shinto
|
audio pronunciation guide:
torii gate at the Itsukushima Shine
|
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
Asian Religious Traditions (comprehensive)Asian Religious Traditions (abridged)
|
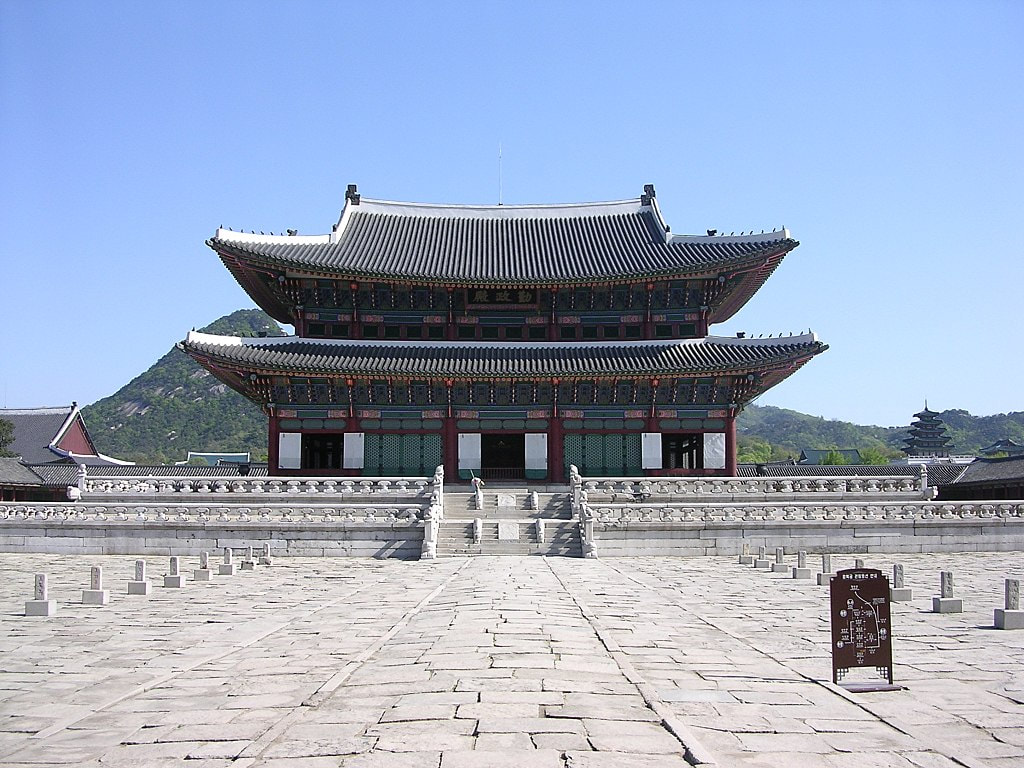
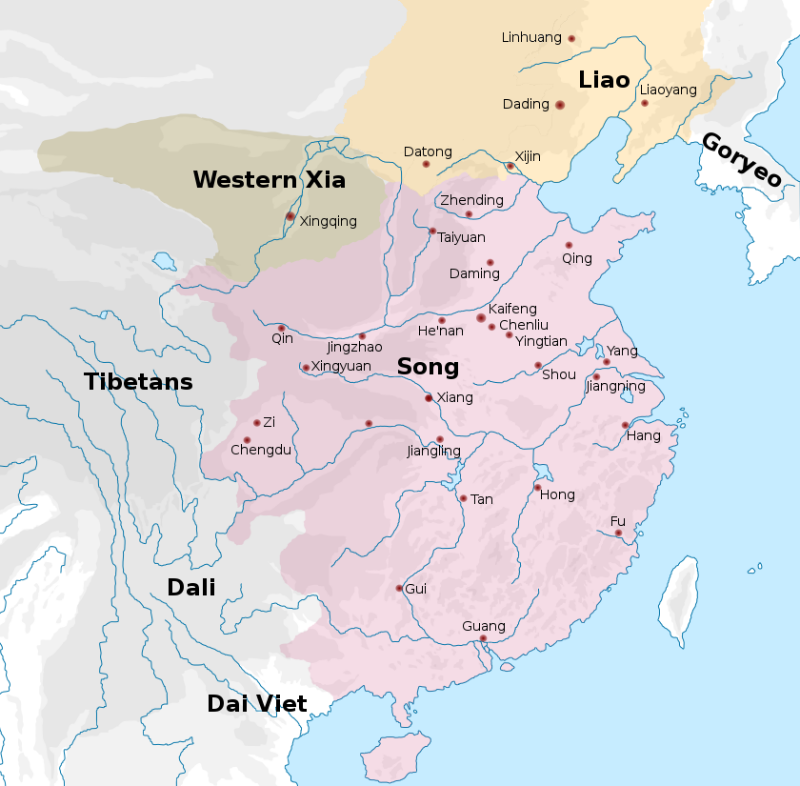
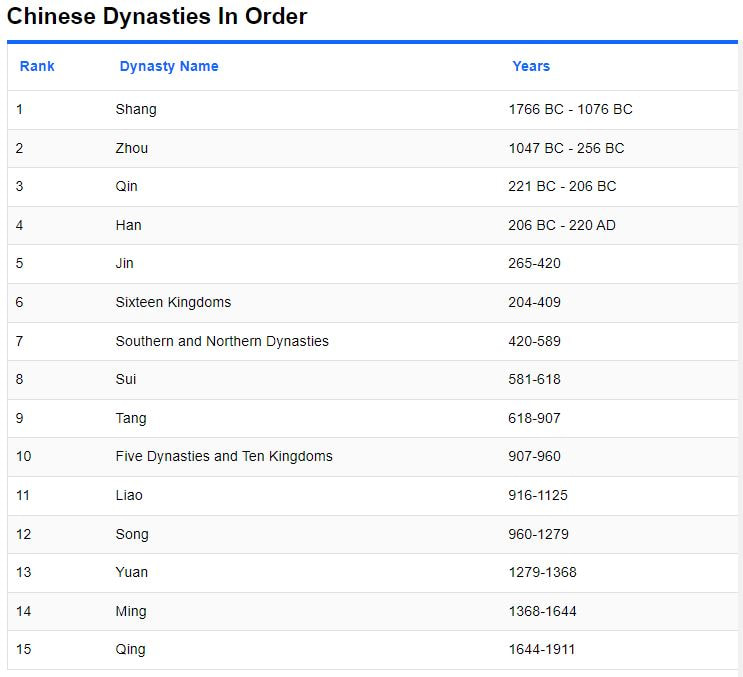
East Asia
|
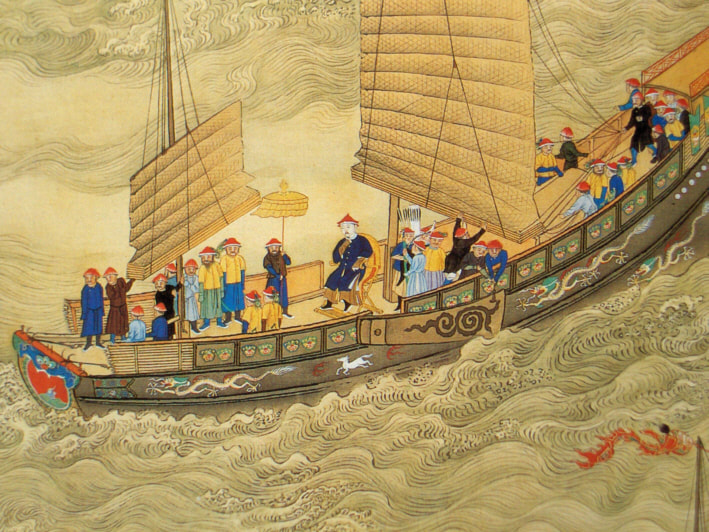
Kangxi Emperor aboard a Chinese junk
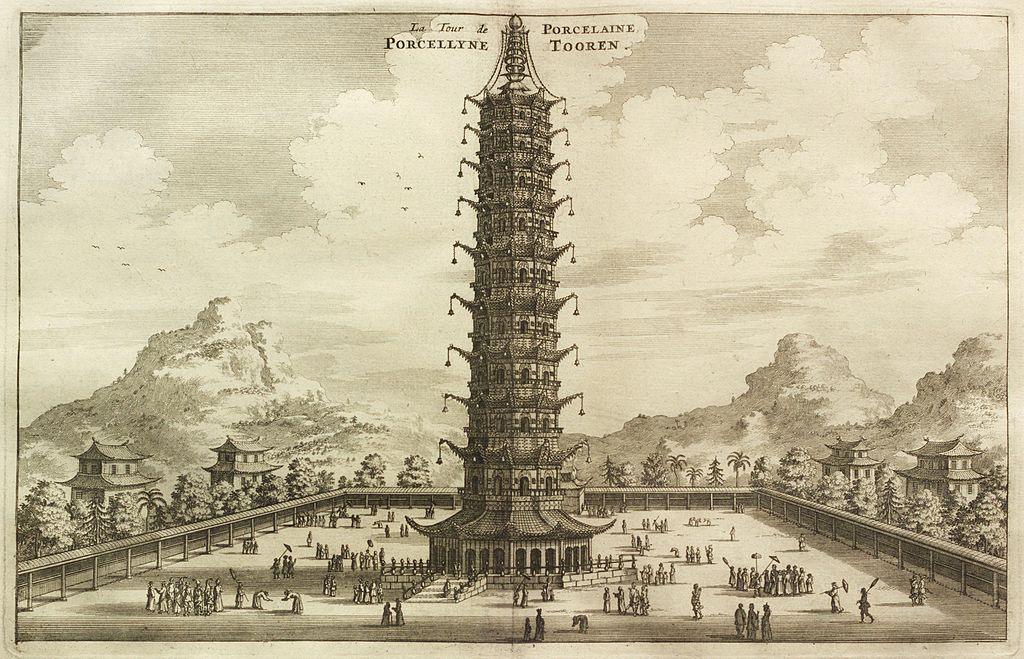
European illustration of the Porcelain Tower
The 1,104 mile long Beijing–Hangzhou Grand Canal, the world's oldest and longest artificial river, links northern and southern China.
|
audio pronunciation guide:
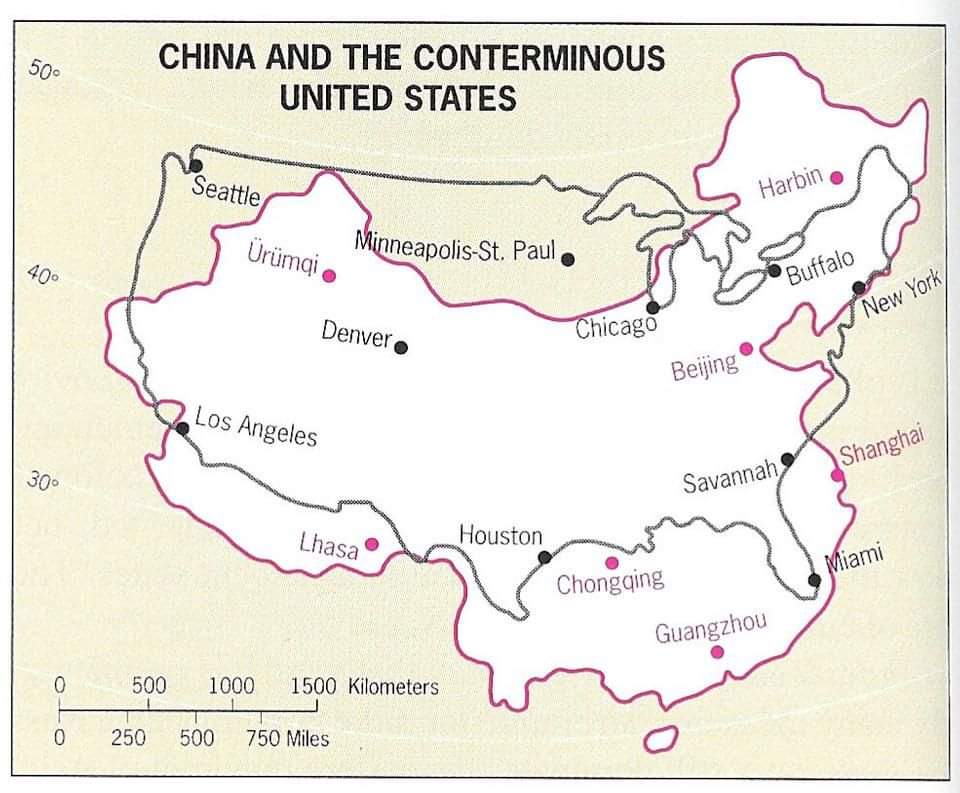
A size comparison of China and the lower 48 states of the United States
|
|
audio pronunciation guide:
|
| korea_japan_and_vietnam_c._1200-1450_ce.pdf | |
| File Size: | 12790 kb |
| File Type: | |
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
East Asian Civilizations (comprehensive)East Asian Civilizations (abridged)
|
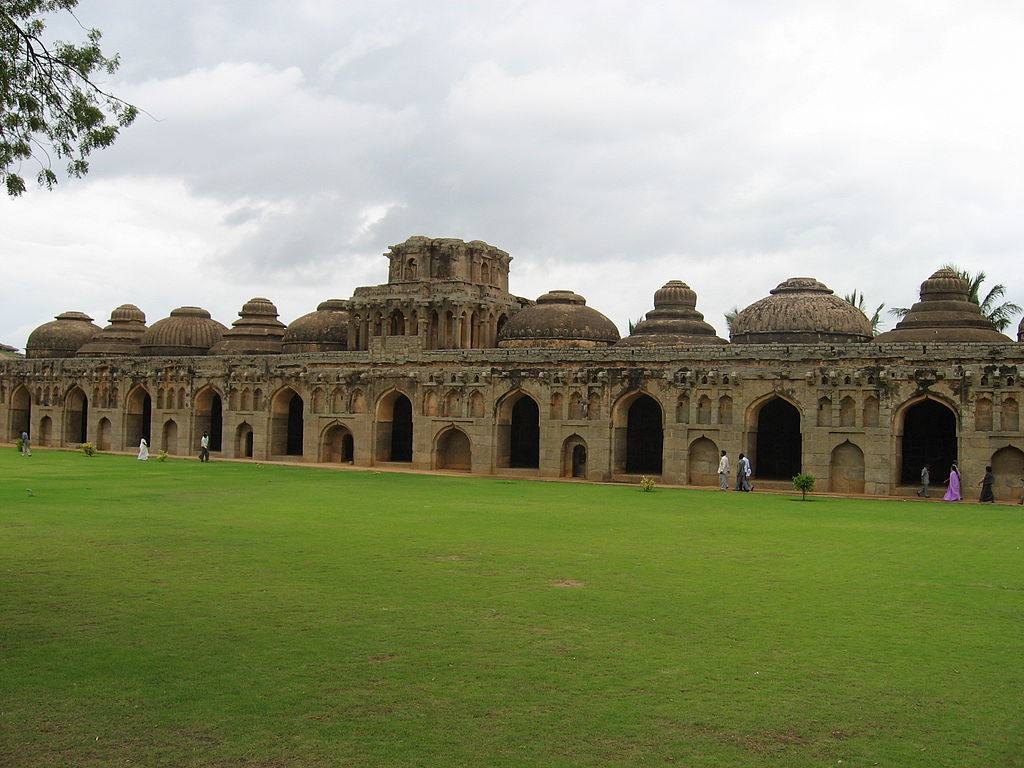
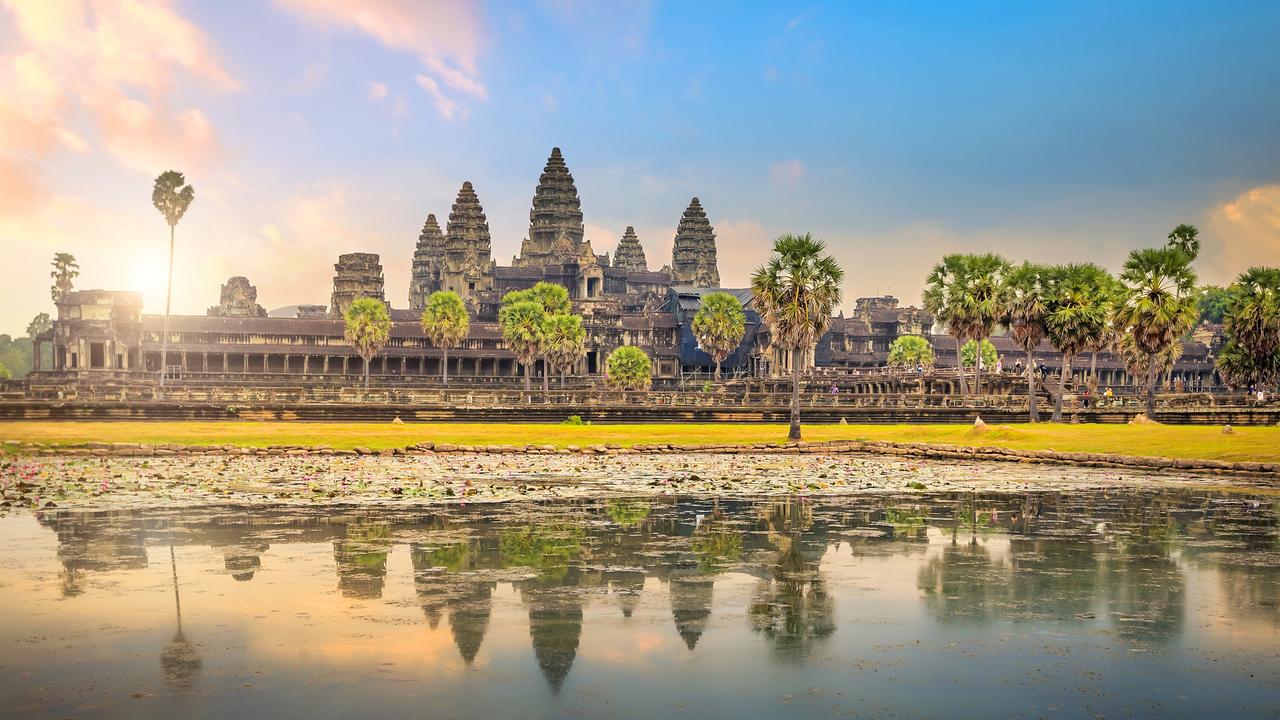
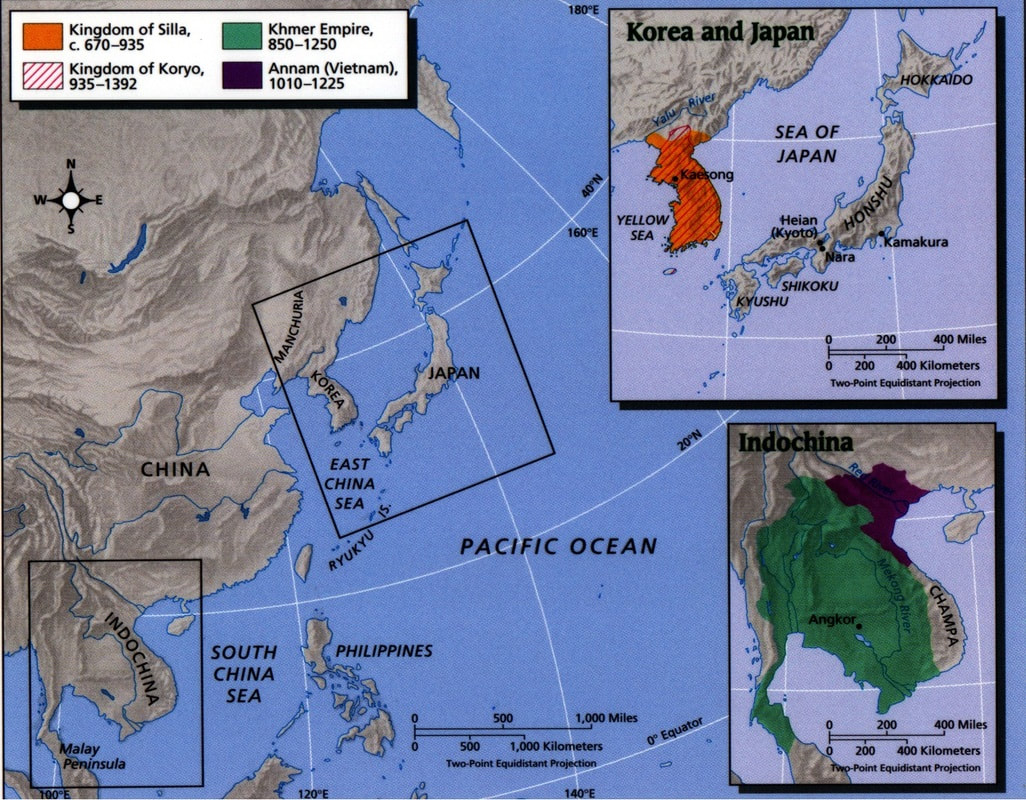
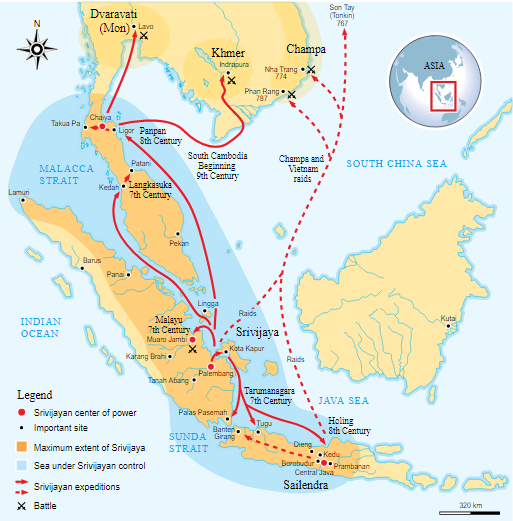
South and Southeast Asia
|
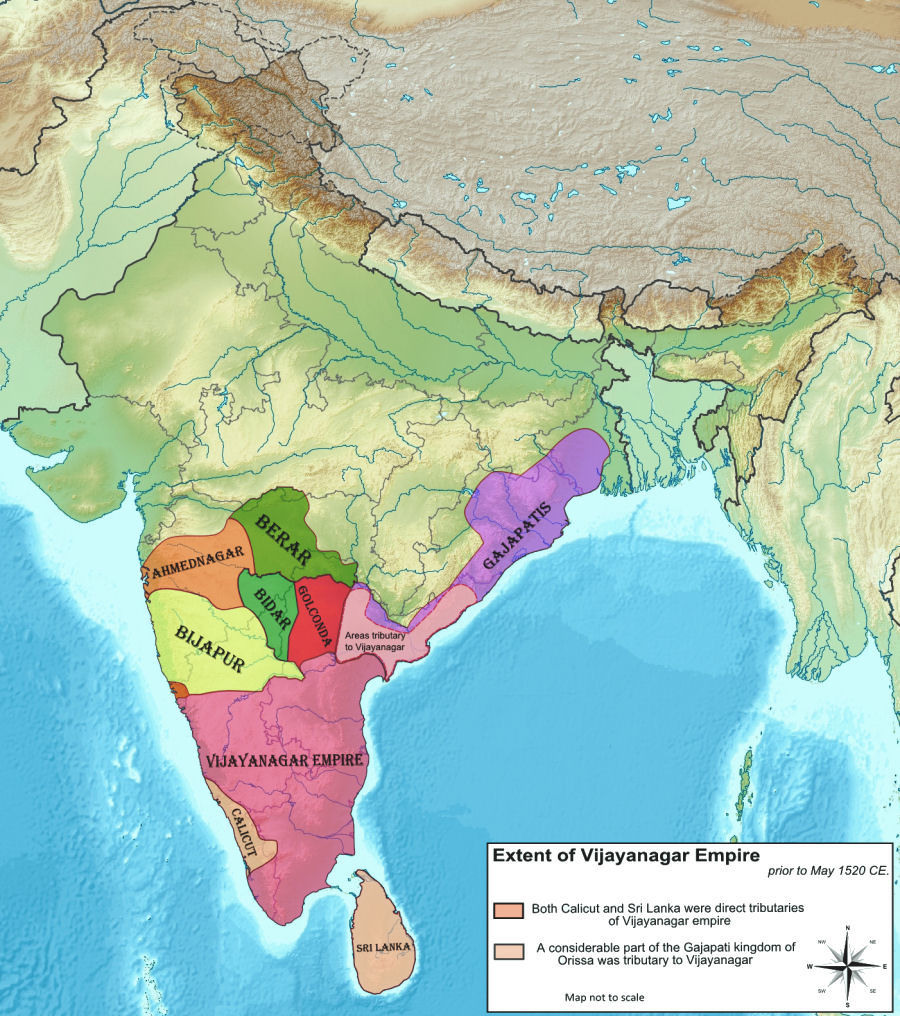
stable for Vijayanagara war elephants
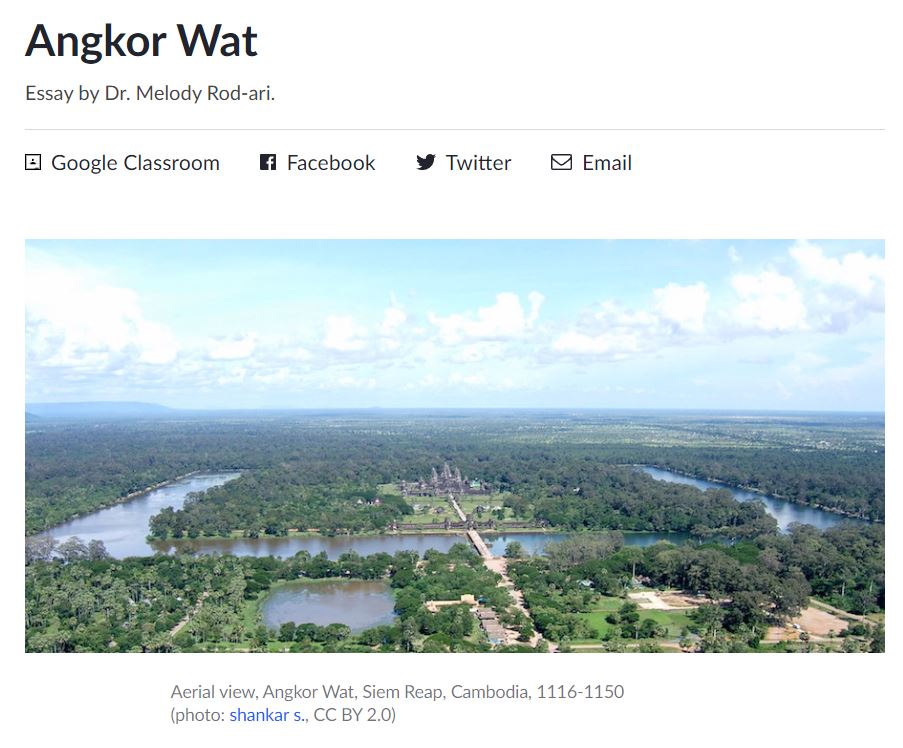
Angkor Wat, 12th century Hindu (later Buddhist) temple, Cambodia
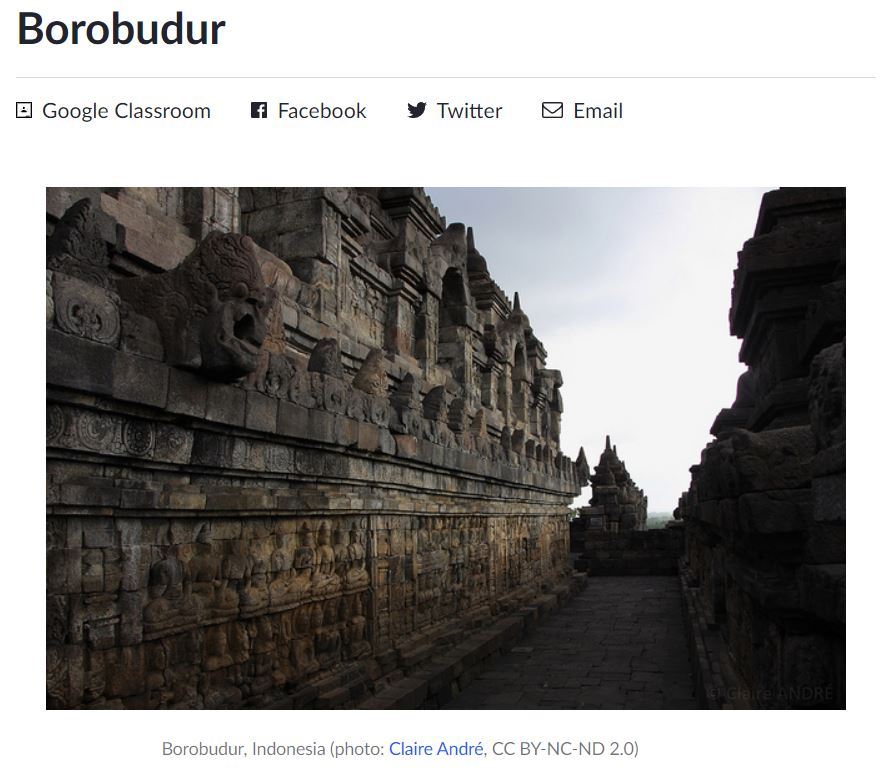
Borobudur on the island of Java in Indonesia is the world's largest Buddhist temple. It was constructed during the 9th-century.
|
State formation and development demonstrated continuity, innovation, and diversity, including the new Hindu and Buddhist states that emerged in South and Southeast Asia.
audio pronunciation guide:
|
|
Article: Angkor Wat
|
Article: The Lost City of Cambodia
|
|
Article: Borobudur
|
Oceania
|
Australasia comprises Australia, New Zealand, and some neighboring islands.
|
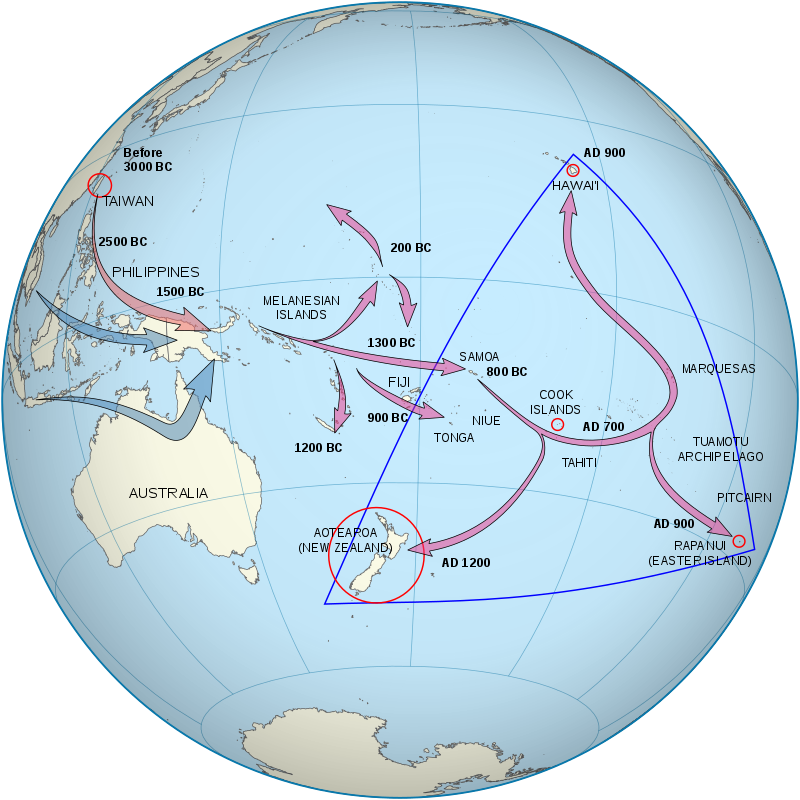
area of Polynesian colonization between 700-1200 CE
|
|
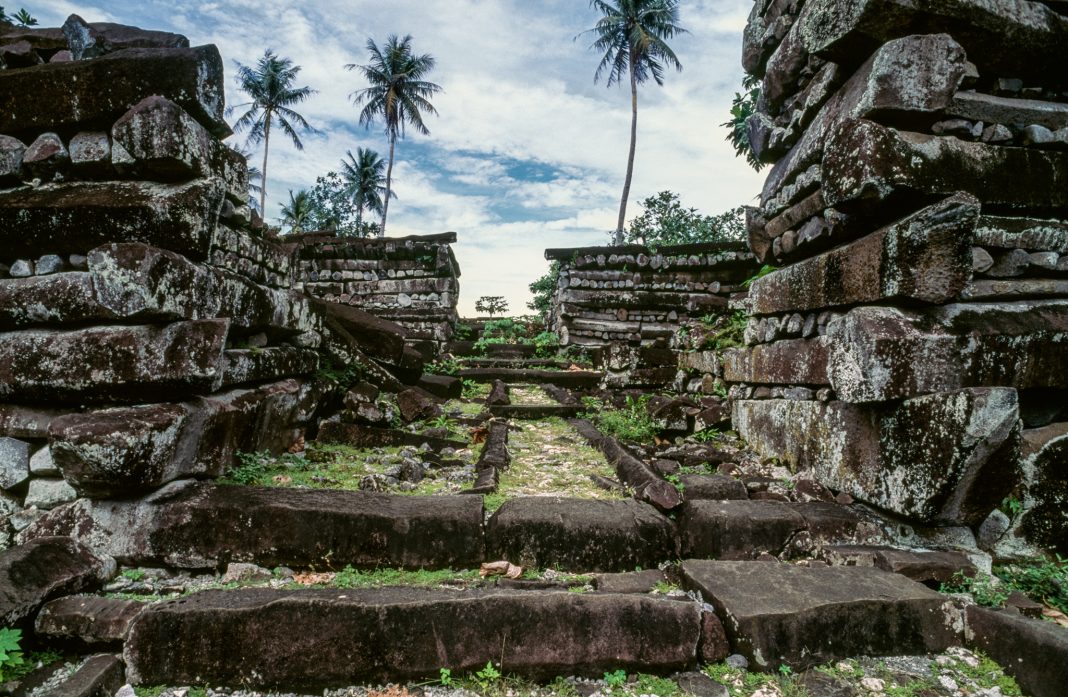
ruins of Nan Madol on Pohnpei Island
|
audio pronunciation guide:
|
Civilizations of SE Asia & Oceania (comprehensive)Civilizations of SE Asia & Oceania (abridged)
|
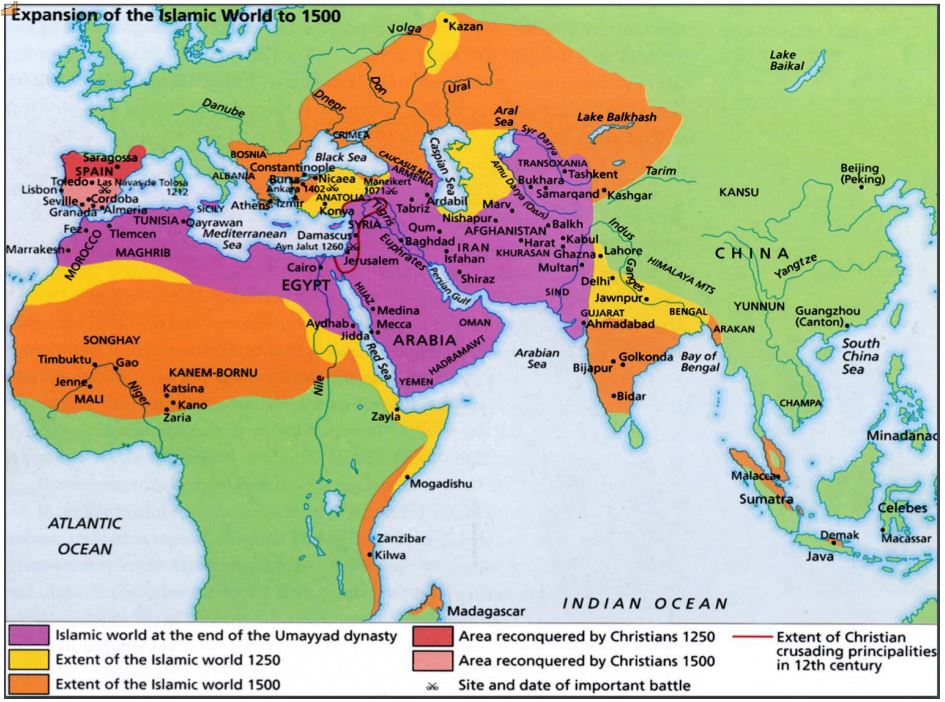
Dar al-Islam
|
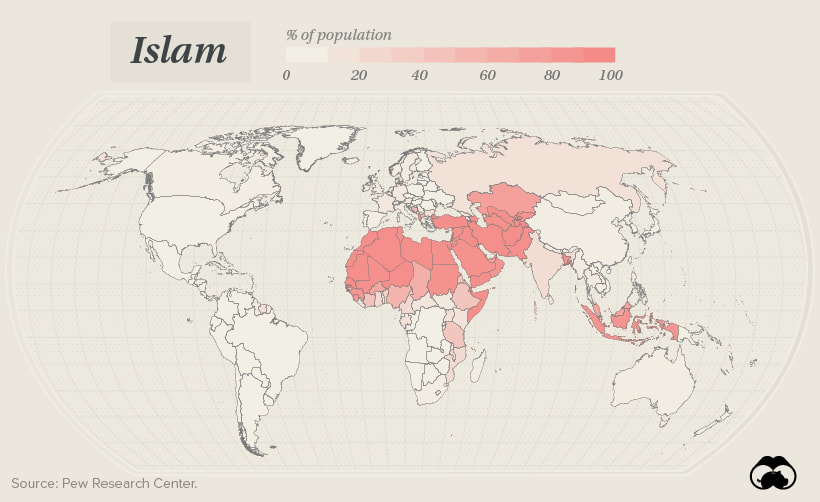
Islam in the world today
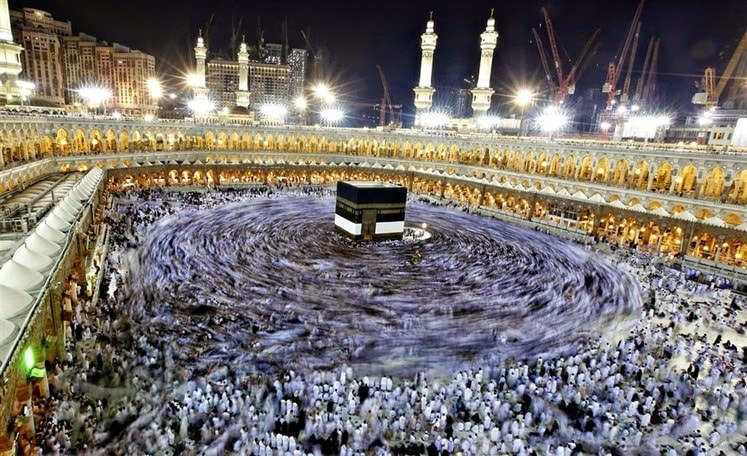
In this time-elapsed photo, Muslims circle the Ka’aba in Mecca during hajj, the pilgrimage to Islam's holy city.
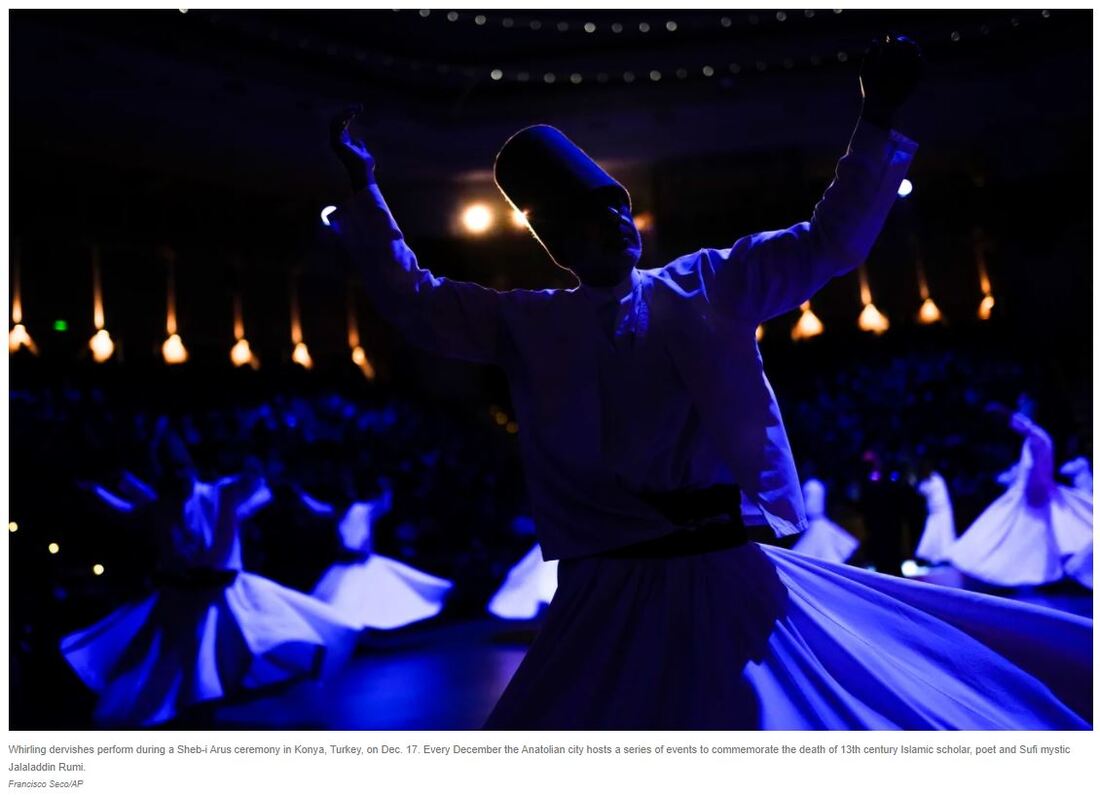
Sufi mystic dervishes dancing
Article: Arab Conquests and Sasanian Iran
|
audio pronunciation guide:
|
Dar al-Islam (comprehensive)Dar al-Islam (abridged)
|
Mongol Empire
|
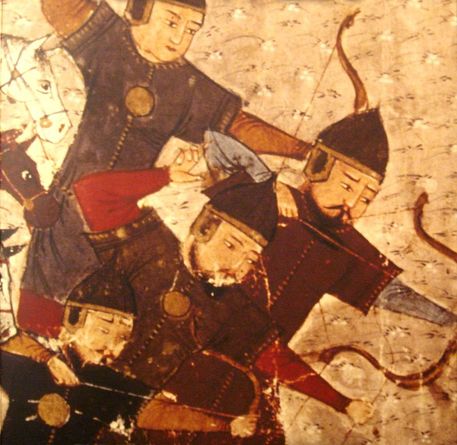
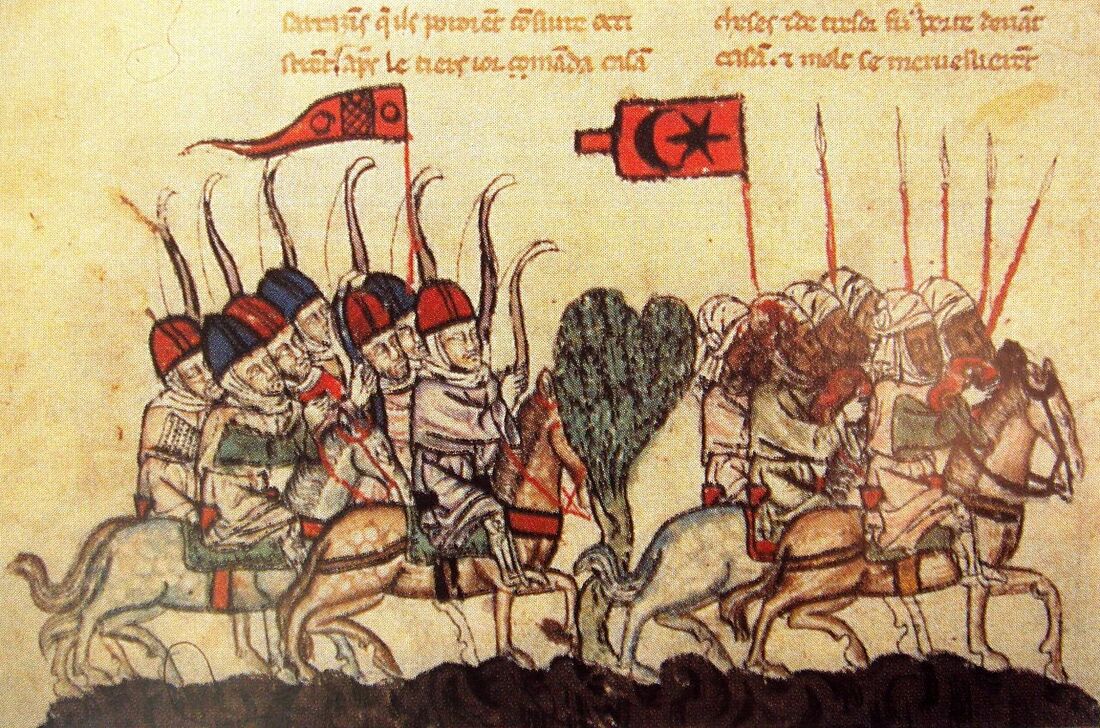
Mongol soldiers, in Jami al-tawarikh by Rashid-al-Din Hamadani, 1305-1306
|
audio pronunciation guide:
Article: Mongol Fashion Statement
|
Mongol Empire (comprehensive)Mongol Empire (abridged)
|